To succeed in doing business and not leave disappointed with an auction, it is necessary to know this type of sale. Origin of the vehicles, information available before the sale, costs or guarantees are elements to which you must pay particular attention.
Buying a vehicle at auction is often an exhilarating act, as the atmosphere and the auction competition make the adrenaline rush. However, it is important to know this type of sale before going there to avoid disappointment. Organized and carried out by auctioneers or approved commercial companies, these public sales make it possible to acquire vehicles at sometimes very attractive prices. The offer is very diversified and the result of the auctions is often very variable. Here is an overview of what you need to know to bid serenely.

Eclectic vehicles from a variety of sources
- voluntary auctions
Voluntary auctions concern vehicles voluntarily handed over by private individuals or professionals to auctioneers so that they can sell them to the highest bidder. There are mainly vehicles from company fleets, rental companies, leasing or credit companies.
- judicial auctions
These are vehicles seized in the context of bankruptcy or following a court decision.
In both cases, the vehicles on offer can be very different: sports cars, utilities, carts, city cars, motorhomes, more or less luxurious sedans, all these cars are often found side by side within the same sale.


Information available before the sale
A successful auction is above all a matter of preparation! The first step is first to gather as much information as possible about the vehicle whose purchase is being considered.

Auction listings, often grouped together in a catalog, contain useful vehicle information. In particular, we find the starting price, sometimes an estimate of the value, the date of first entry into circulation, the mileage, the finish, the mention of the possible presence of the maintenance book (updated or not), or even the date of the last interview. The origin of the vehicle is also sometimes mentioned.
Barring exceptions (non-driving or damaged vehicles), the cars have previously been subject to a technical inspection, the report of which is available on request. These advertisements also include photos of the vehicles, or even of their main aesthetic defects. Some auction sites also offer a virtual tour of vehicle interiors.

Then comes the essential inspection of the vehicle. It can be carried out the day before or in the hours preceding the holding of the auction within the auction house which opens its doors for this purpose. The vehicles can then be started, but no test drive is possible. Being accompanied by a professional or an experienced amateur is definitely a plus.
Additional costs to be expected
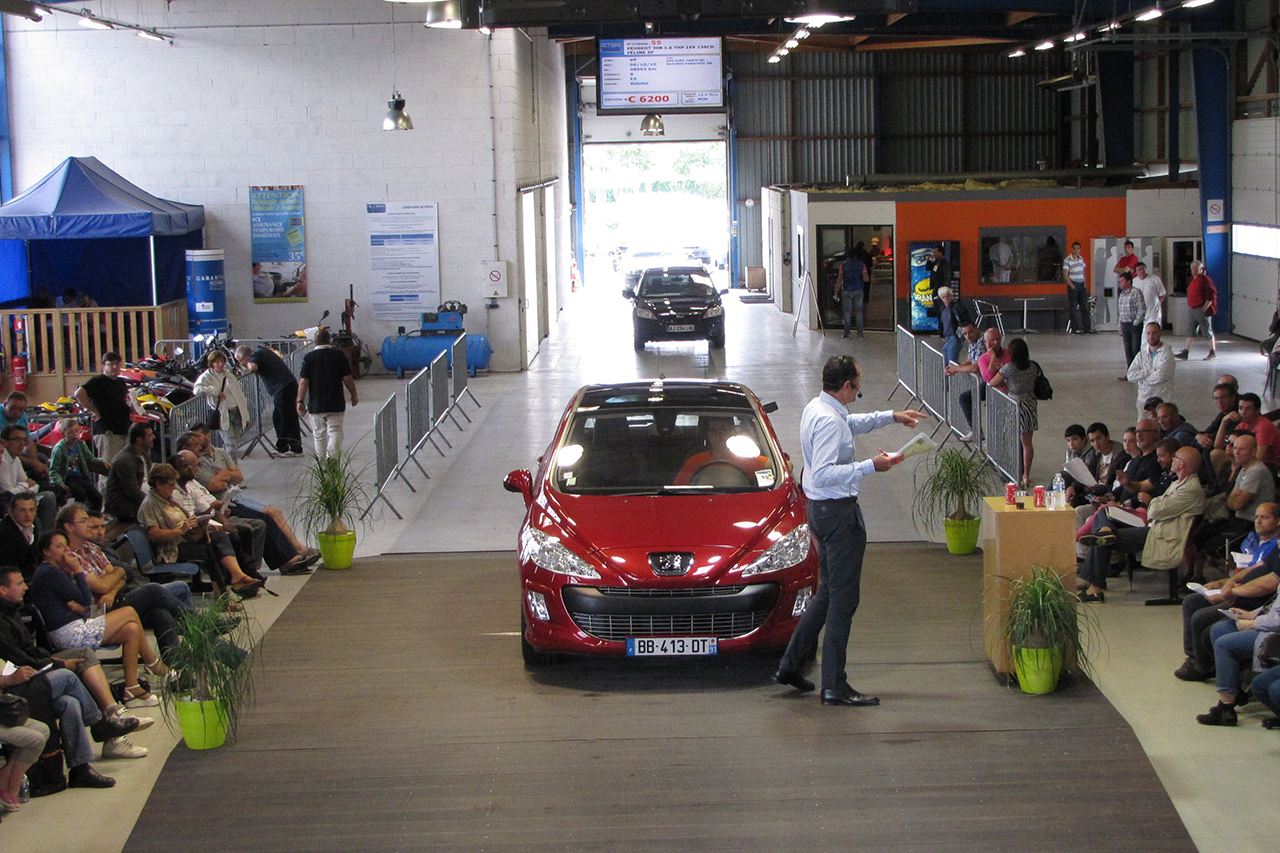

It is important to keep in mind that costs will be added to the hammer price of the vehicle. These costs are mentioned in the general conditions of sale presented on the Internet or in the catalog of the sale. They are also reminded by the auctioneer before the start of the auction.
- For judicial auctions, these costs are regulated and amount to 14.28% including tax of the auction price.
- For voluntary sales, the costs are free and vary according to the houses and the types of sale. Around 15% on average, they are often decreasing and can reach up to 30% including tax of the selling price.
Administrative fees of around one hundred euros are also often requested. Please note that additional fees are sometimes charged for online auctions. The price plus these costs can generally be paid by credit card, bank transfer or check. Once the payment has been made, you will finally have to think about taking out temporary insurance to be able to set off again at the wheel of your precious acquisition.
Remedies and responsibilities in the event of a problem
Remedies exist if problems arise after the sale. They vary according to the type of sale, voluntary or judicial.
- Within the framework of voluntary sales, the commercial company which organizes the sale is only the agent of the owner of the vehicle. It is therefore only a simple intermediary and the purchaser has the same recourse against the seller as in the context of an amicable sale. It is therefore possible to act in the event of hidden defects or lack of conformity to request the resolution (cancellation) of the sale or the reduction of the price, or even compensation for additional damages.

- However, the law prohibits any action for latent defects in the context of judicial sales. There is, however, a potential remedy. The auctioneer who organizes the sale is indeed civilly liable for any shortcomings committed in the context of the execution of his mission if they cause damage to the successful bidder. This will be the case if the auctioned vehicle has not been correctly described or if it has been presented in a misleading way and does not conform to what appears in the catalog of the sale. However, this type of liability action against the auctioneer does not offer the possibility of requesting the cancellation of the sale. Only damages in compensation for the damages suffered may be requested. For example, it will be possible to request compensation for the difference in value between that of the vehicle acquired and that which results from the erroneous description on the basis of which the buyer has decided to bid victoriously. The action against the auctioneer must be launched within 5 years of the sale. A delay that leaves time to have the vehicle appraised before acting. This is indeed an essential prerequisite for any action to demonstrate non-compliance and therefore the lower value of the car.