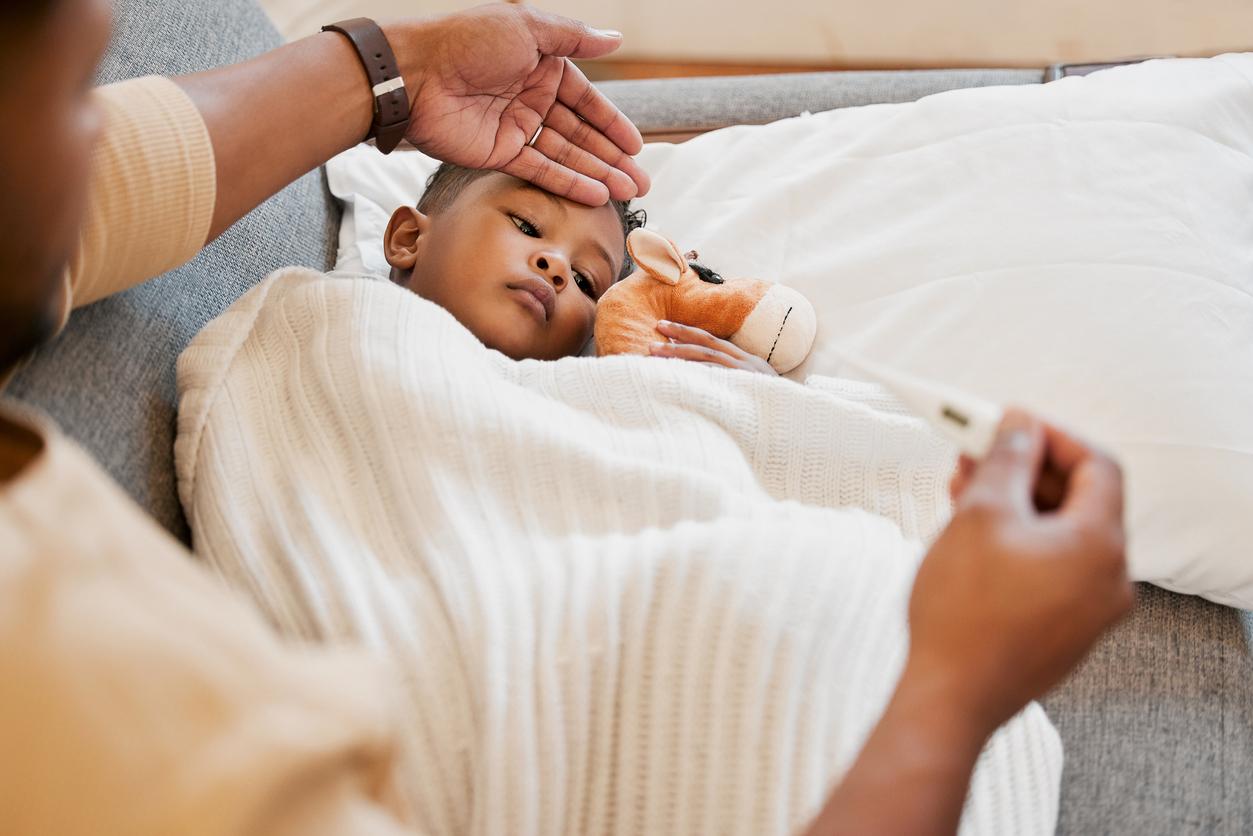
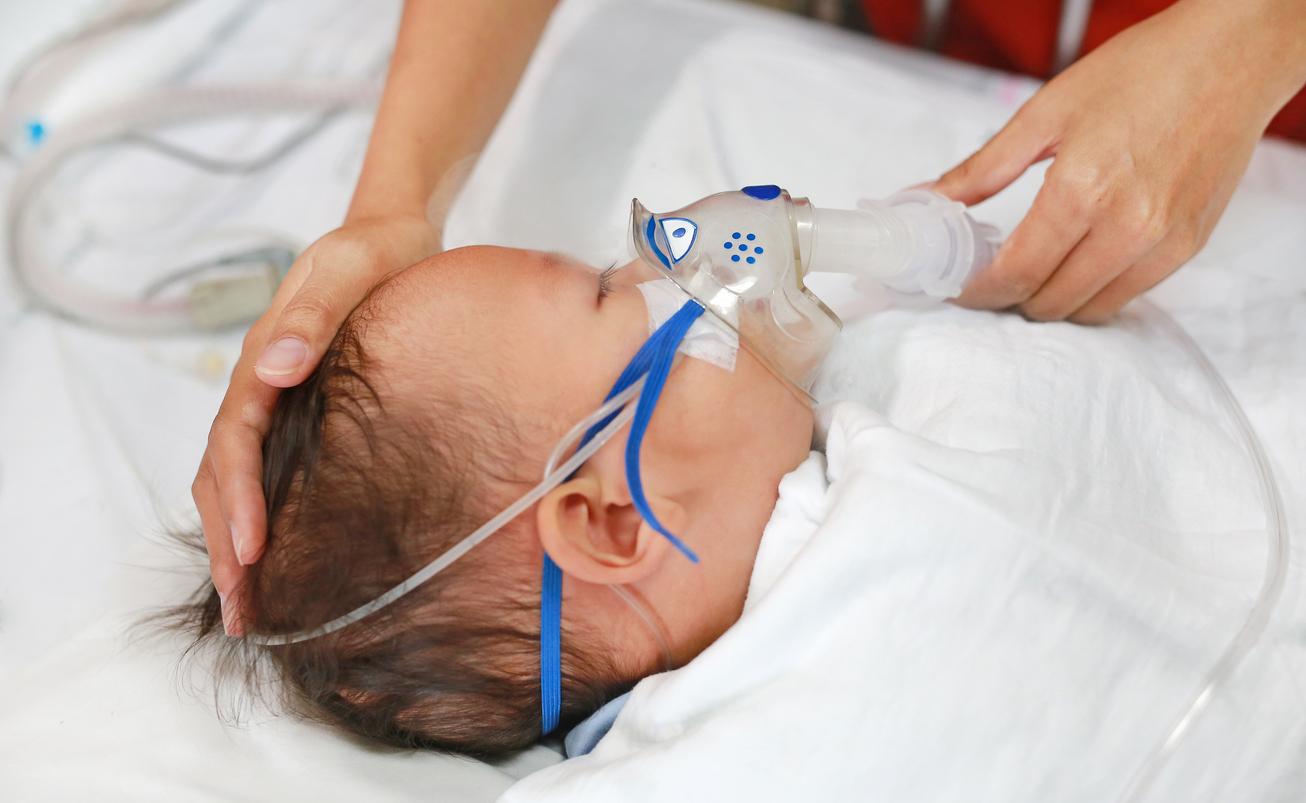
the bronchiolitis virus is making a comeback. This week, it was the source of 3,394 emergency room visits including 1,151 hospitalizations and 546 home visits by the SOS doctors network, according to figures from the National Institute for Public Health Surveillance (Invs). Active in all regions, with the exception of Provence-Alpes Côte d’Azur, bronchiolitis is particularly present in Ile-de-France, in the North, West and South-West.
“The epidemic is at least as large as that of the previous two years and it may well be even larger” Dr Daniel Lévy-Bruhl, head of the InVS respiratory infections and vaccinations unit, told Francetv info.
A virus spread through saliva and coughs
Bronchiolitis is a viral disease that primarily affects children under 2 years of age. In more than 7 out of 10 cases, bronchiolitis is caused by respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), a particularly contagious virus that is transmitted by saliva droplets, coughs or by contact.
The rules of prevention
In order to avoid the transmission of the virus, a few preventive actions and precautions should be taken:
• Always wash your hands with soap and water, several times a day for 30 seconds, and always before taking care of your baby (a precaution to be generalized to all those around you).
• Do not kiss your baby on his face when you have a cold. In this case, make sure to wear a cloth mask when changing your baby.
• Avoid frequenting public places as much as possible (public transport, department stores, etc.) where you may be in contact with people with colds.
• Limit the number of soft toys in your baby’s room: you don’t necessarily think about washing them when the virus remains there for several hours.
• Clean his toys (especially those he puts in his mouth) with soapy water and a small brush.
• Avoid smoking at home to respect your baby’s bronchial tubes and ventilate his room daily.
Read also :
Bronchiolitis: what are the symptoms?
Bronchiolitis: what baby care in hospital?
Bronchiolitis: twice the risk in baby swimmers