A new compound called C28, given in addition to some common medications, may reduce the risk of developing cardiac arrhythmia.

- Certain medications can cause a form of heart arrhythmia called long QT syndrome.
- The risk of developing this side effect could be reduced with a compound called C28.
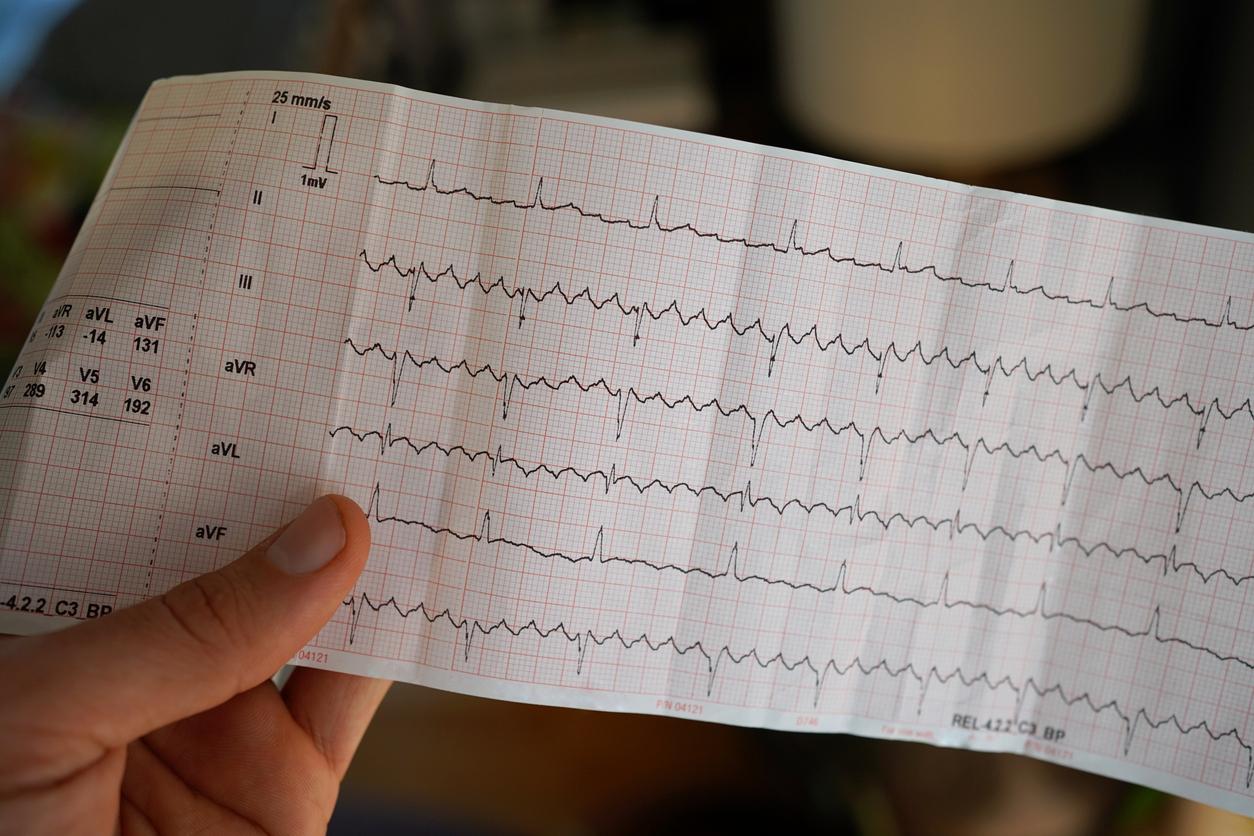
Antibiotics, anti-nausea or even anti-cancer drugs… These common drugs provide short-term relief but also have harmful side effects. They are notably accused of disturbing the heart rhythm of certain patients, causing a form of cardiac arrhythmia called long QT syndrome. It is an abnormality of the electrical system of the heart, which controls heart rate and rhythm. To measure the electrical activity of this organ when it beats, patients must perform an electrocardiogram. At the end of the exam, a graph represents each part of the heartbeat with the letters P, Q, R, S, and T. The diagnosis of long QT syndrome is made when a person has too long an interval between Q and T points on his EKG graph. Symptoms that patients may suffer from are rapid and uneven heartbeats which can cause seizures, fainting and, in the most severe cases, sudden death if the heart stops beating.
C28 would reduce the risk of long QT syndrome
The consequence of this risk of developing a long QT syndrome is that doctors limit the prescribed doses of the drugs involved, thus reducing their therapeutic effectiveness. Some of them have even been withdrawn from sale. But a team of researchers could change things. They have just discovered a compound, named C28, which prevents the lengthening of the interval between the Q and T points, and reduces ultimately the risk of developing long QT syndrome. This compound C28, administered in addition to the drugs in question, could make it possible to increase the prescribed doses and therefore the effectiveness of these treatments. Especially since C28 has no impact on the benefits of these drugs, it only annihilates their side effects. The scientists have just published their study in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
C28 influences certain potassium channels of the heart
In the heart, cardiac performance depends on potassium channels. It is a type of ion channel that allows high speed passage of ions, i.e. atoms or molecules carrying an electrical charge. To carry out their work, the researchers therefore targeted these potassium channels: the faster IKr and the slower IK. “The fast ones have a major role, explains Ira Cohen, one of the authors of the study. If you block them, the result is a long QT syndrome. IKs are very slow and contribute much less.” From this difference, the scientists estimated that the increase in IKs could contribute to maintaining a normal electrical activity of the heart and would reduce the risk of developing a long QT syndrome. Thus, they looked for a component that could play a beneficial role on IKs. Once the compound C28 was found, they measured its impact, at different concentration levels, on the IKs. They deduced that C28 improved the function of the potassium channel IKs and prevented the lengthening of the interval between the Q and T points caused by the drugs. Finally, they found that C28 did not interfere with the therapeutic action of the treatments.
Eventually, some drugs could be remarketed
“We are very excited about itconcludes Ira Cohen. For many of these treatments, there is a concentration of the drug that is acceptable, but it becomes dangerous at higher doses. If C28 can eliminate the risk of prolongation of the interval between the Q and T points, then these drugs can be used at higher concentrations, and in many cases they can be more effective..” Ultimately, this discovery could make it possible to remarket drugs and improve patient care.

.