It is indeed possible to transmit your fears, according to American scientists. When some are frightened, they would be more likely to have a strong physical reaction that would surprise those present at the time of the event. Explanations.

- Fear is a feeling of anguish experienced in the presence or thought of a danger, real or supposed, of a threat.
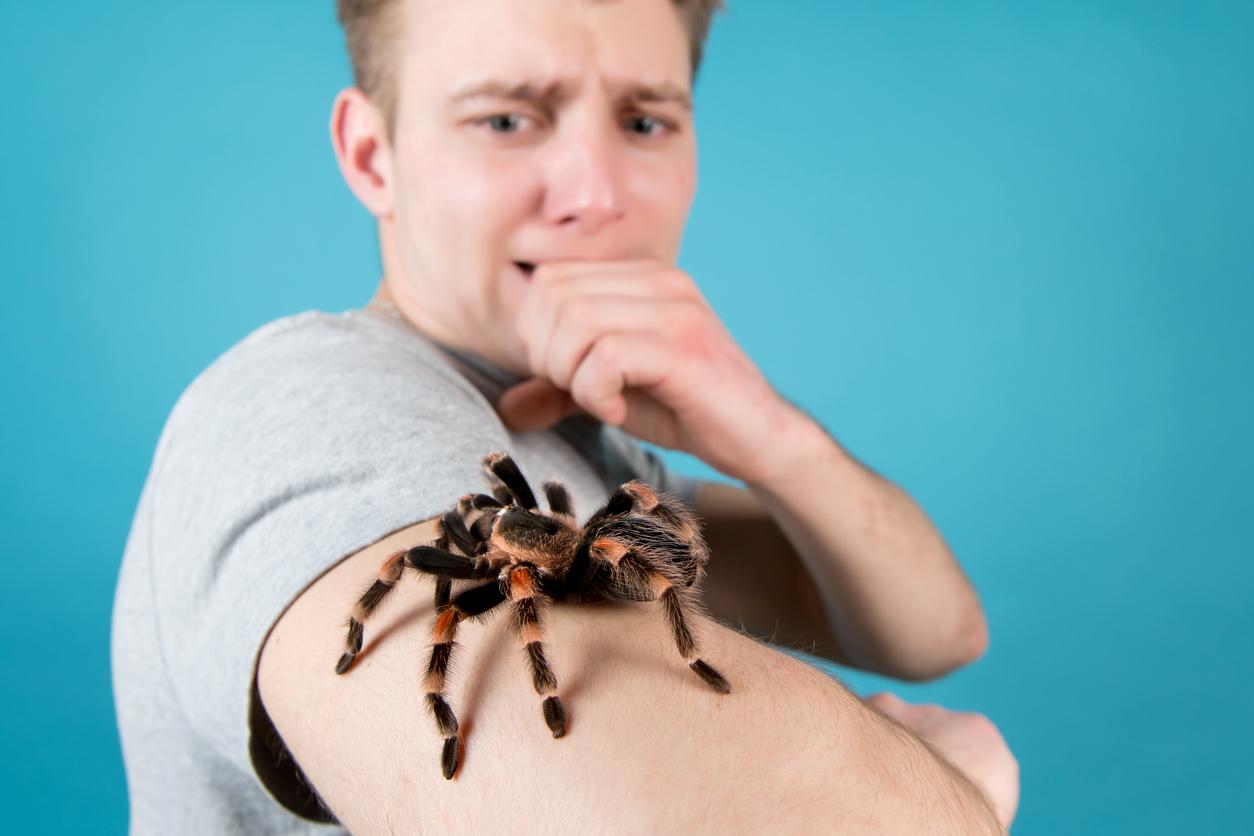
- As part of a haunted house experience, visitors accompanied by other people were more frightened.
Jumping when you see a pigeon, having trouble breathing in an elevator, shaking and blushing when speaking… Fear can overwhelm us in different situations. During these times, others can be seen as sources of comfort. But according to a study published in the journal Psychological Science January 10, being around many people when we are scared could not help us overcome our fears. The reason is simple: this feeling of anguish would spread quickly.
To reach this conclusion, researchers from the California Institute of Technology conducted an experiment. They invited 156 adults to visit a haunted house in small groups. For 30 minutes, they faced situations mimicking a choking threat, a speeding car, or gunfire. During the experiment, participants wore connected bracelets to assess their electrodermal activity or sweat-induced changes.
The more participants, the greater the fear
The results of the work revealed a positive association between the number of people in a group and “tonic excitement”, which reflects the body’s overall physical response to stress. According to the authors, the volunteers were more afraid when the group visiting the haunted house was larger. They also found that fear increased as people moved from room to room.
According to the team, when participants were confronted with a frightening situation, they were more likely to have an increased physical reaction in the presence of other people. This ‘phasic effect’ involves rapid changes the body goes through as it reacts to an event and is more likely to happen when other people are experiencing the same thing. Thus, if someone is shaking with fear in the face of an event, the calmest person may be surprised by their reaction and may in turn be frightened. “If your body reacts more to the threatening event, you also psychologically feel more fear,” said Sarah M. Tashjian, lead author of the study in a statement.
“The body picks up the signals” of frightened people
“We interpreted this phenomenon as a reflection of the contagion of fear: if your friends or people are around, your body picks up their signals and exhibits a higher level of arousal, even in the absence of fears or fears. specific bursts”, added the researcher.
“This study is different from others because we measure several aspects of skin conductance, including slow response, fast response, frequency of responses, and level of responses. Most studies use only one of these measurements. , which limits our understanding of the dynamics of the nervous system and how different factors exert different influences on the body.” said Sarah M. Tashjian.
.