Pain management is a major concern for many people, whether it is acute pain after an injury or chronic pain related to a medical condition.
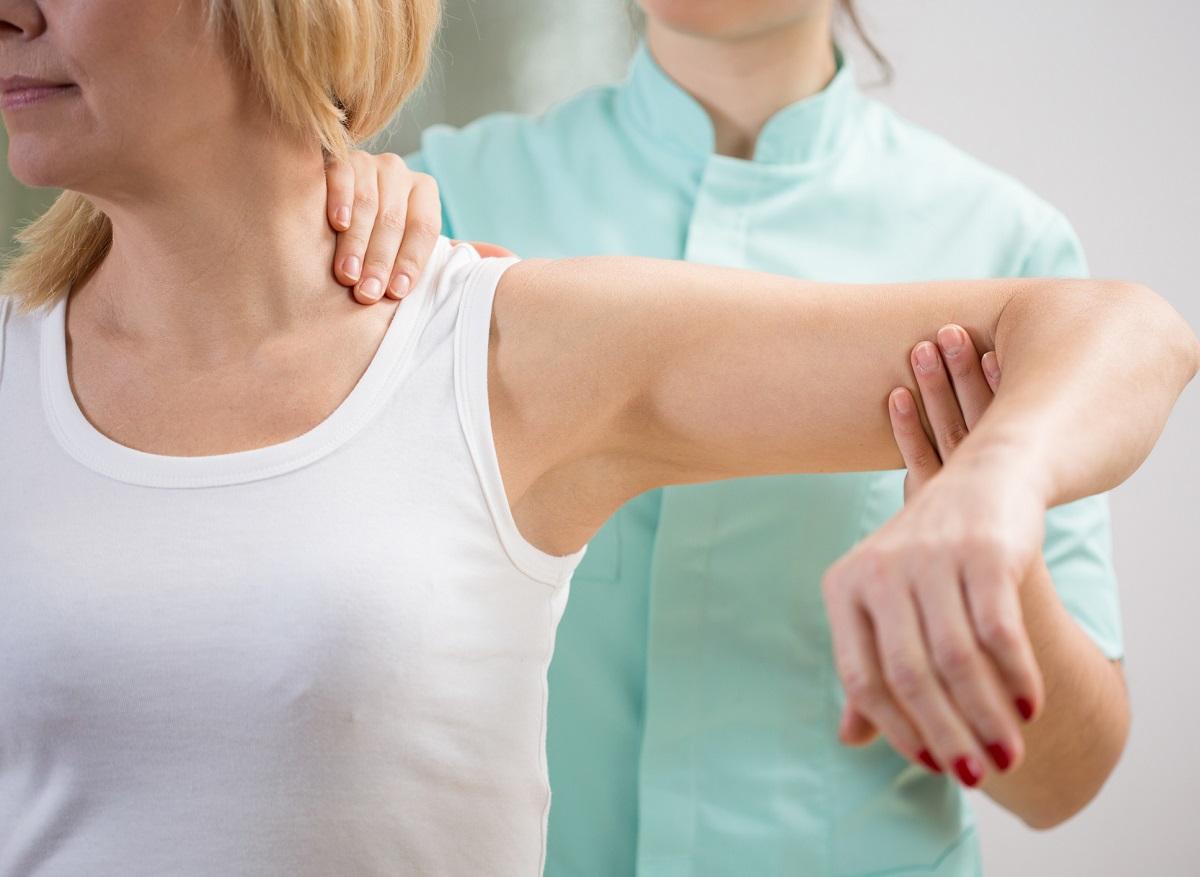

- The first step in pain management is to consult a healthcare professional.
- Pain management centers are facilities that specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of chronic pain.
- Psychological support is also an essential component of pain management.
There are many resources and options available for getting help. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you navigate the different sources of support available.
1. Medical consultation
The first step in pain management is to see a healthcare professional. Primary care physicians can assess your pain, determine its cause, and suggest a treatment plan. They can also refer you to specialists if necessary.
- General practitioners: They are often the first point of contact for assessing and treating pain. They can prescribe medications, recommend specific exercises, or refer you to other specialists.
- Pain specialists: These doctors, often anesthesiologists or neurologists, specialize in managing chronic and complex pain. They may offer advanced treatments such as nerve blocks, epidural injections, or electrical stimulation.
2. Pain management centers
Pain management centers are facilities that specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of chronic pain. They offer a multidisciplinary approach, combining different types of treatments for comprehensive care.
- Hospital Pain Centers: Often associated with university hospitals, these centers offer advanced treatment and rehabilitation programs.
- Private clinics: These facilities can offer specialized care and quick access to treatment.
3. Drug therapies
Medications play a crucial role in pain management. There are several categories of medications that can be used alone or in combination.
- Painkillers: Such as paracetamol and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) which are often used for mild to moderate pain.
- Opioids: Used for moderate to severe pain, but require strict management due to risk of addiction.
- Antidepressants and anticonvulsants: Sometimes used to treat neuropathic pain.
4. Non-drug therapies
Non-drug options are increasingly recognized for their effectiveness in pain management, often in addition to medications.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapists use exercises, massage, and other techniques to improve mobility and reduce pain.
- Occupational therapy: Helps patients adapt their daily activities to minimize pain and improve quality of life.
- Acupuncture: A traditional Chinese medicine technique that can help relieve certain chronic pains.
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT): Helps patients manage pain by changing their perceptions and emotional reactions to pain.

5. Psychological support
Chronic pain can have a significant impact on mental health, so psychological support is an essential component of pain management.
- Psychologists and psychotherapists: Can provide therapies to help manage stress, anxiety, and depression associated with chronic pain.
- Support Groups: Participating in support groups allows you to share experiences and pain management strategies with others going through similar situations.
6. Relaxation and mindfulness techniques
Relaxation and mindfulness techniques can be very effective in managing pain by reducing stress and increasing the ability to cope with pain.
- Meditation: Mindfulness meditation helps focus the mind and reduce the perception of pain.
- Yoga and Tai Chi: These practices combine gentle movement and meditation to improve flexibility, strength and pain management.
7. Online resources and applications
There are many online resources and mobile apps available to help manage pain.
- Pain management apps: Apps like “Pain Coach” or “MyPainDiary” help users track their pain, identify triggers, and find effective management strategies.
- Online Forums and Communities: Websites like “PatientsLikeMe” or “PainConnection” provide a space to discuss and share advice with others living with chronic pain.
8. Education and training
Education about pain and pain management is essential for patients and caregivers.
- Pain management programs: Educational programs offered by hospitals or clinics can help patients understand their pain and learn effective management techniques.
- Workshops and Seminars: Attending pain management workshops can provide valuable information and practical skills.
Conclusion
Pain management is a complex task that requires a multidisciplinary approach. By combining medical consultations, drug and non-drug treatments, psychological support, relaxation techniques, and the use of online resources, it is possible to better manage pain and improve quality of life. If you suffer from chronic pain, do not hesitate to explore these different options and discuss with your doctor to determine the best approach for you.