About reimbursement and the HEARING questionnaire
One in ten Dutch people suffer from impaired hearing to a greater or lesser extent. To be eligible for reimbursement for a hearing aid, the loss must be 35 dB or more. Is such a hearing aid fully reimbursed? And what should you pay attention to when purchasing? Tips for buying a hearing aid.
When you are about to purchase a hearing aid, you will notice that most hearing care professionals work according to the Hearing Protocol 2.0. This is also necessary, because it must be met if you want to be (partly) reimbursed for your hearing aid. How does that work?
You will first undergo an extensive hearing examination. Choose a certified and StAr-registered hearing care professional (the quality mark for hearing care). They have followed a thorough training and are also triage hearing care professionals; this means that they have followed additional training and are allowed to determine whether you are eligible for a hearing aid without a referral from an ENT specialist. And just like doctors, they continuously train to keep their knowledge up to date.
HEARING questionnaire
Part of the hearing protocol is the HEARING questionnaire that you must complete before you come to your appointment. These are about thirty questions ranging from ‘do you understand the newscaster on the radio at normal volume?’ to ‘can you hear the birds singing outside?’ If you qualify for a hearing aid, this questionnaire will also help the hearing care professional to determine which functional category of hearing aids you fall into.
Five hearing categories
Based on the HEARING questionnaire and the hearing test, the hearing care professional knows the most optimal category of hearing aids for you. You will be divided into one of the five main categories, where 1 is simple and 5 is complex. You can choose between different brands and types.
The classification of these categories is based on your hearing loss and lifestyle. The principle is that you are reimbursed for a medical aid that allows you to function properly. This means that if you have mild hearing loss, you will get a simpler hearing aid than if you have severe hearing loss that requires a more advanced hearing aid. Of course you can always choose a hearing aid outside your category, but then the purchase costs are usually for your own account. It is therefore important to know what exactly your health insurer reimburses and with which hearing care professionals a contract has been concluded. Please ask in advance. Also note whether the reimbursement applies per person or per hearing aid.
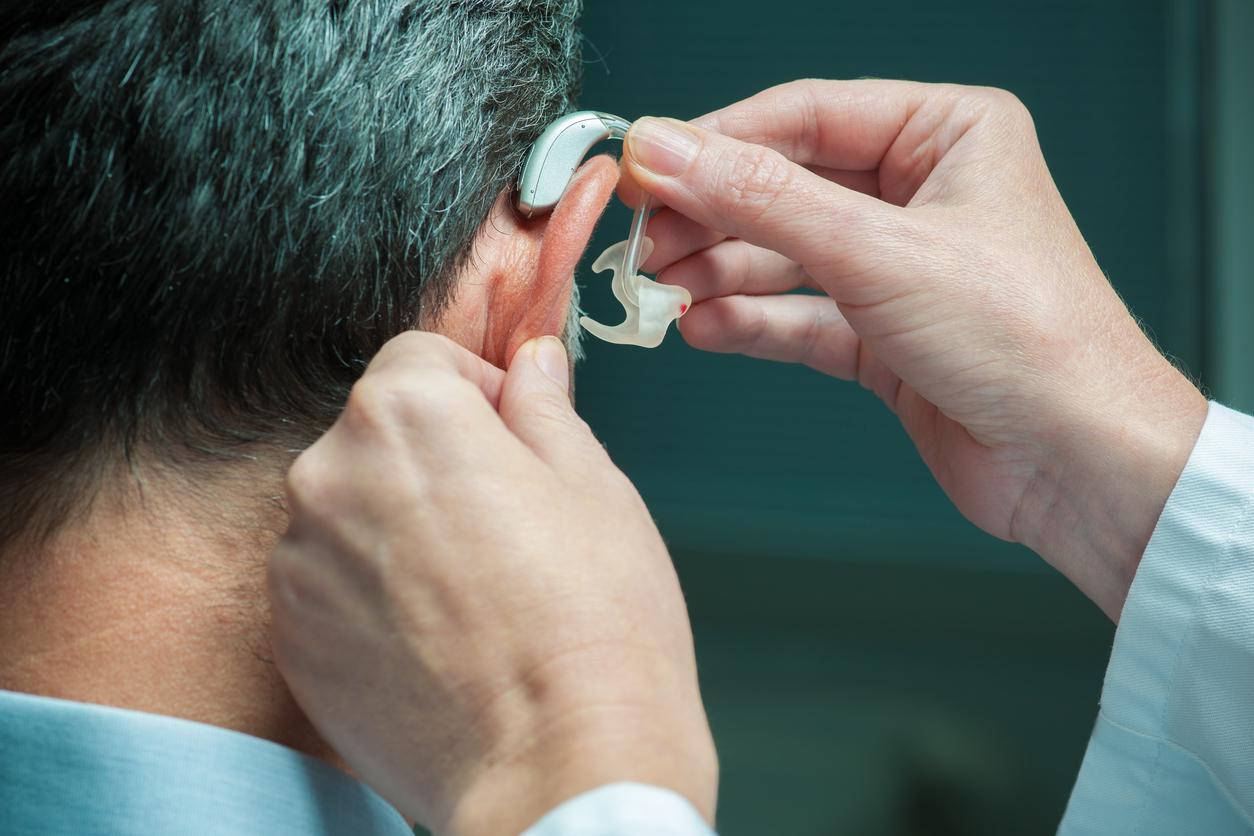
What types of hearing aids are there?
When choosing a hearing aid, there are several options in terms of wearing style:
- Open ear: Suitable for smaller hearing losses and ideal if you are wearing a hearing aid for the first time. With this model, the tube is connected to a soft plastic earplug in the ear canal.
- Receiver in the ear canal: similar to the ‘open ear’, but suitable for a wider range of hearing loss and more experienced wearers. With this model, a thin wire runs in front of the ear, which is connected to the loudspeaker of the hearing aid. The latter is in your ear.
- Behind the ear: This is a hearing aid for people with greater hearing loss. A thin tube runs from behind the ear into the ear, which is connected to an earmold in the auricle.
Trial period
Because wearing a hearing aid takes getting used to and patience, most hearing care professionals offer a trial period. This will give you time to familiarize yourself with wearing a hearing aid. This applies not only to getting used to the device itself, but also to the sound that comes in. Your brain will have to adapt to this and that takes a while. Some people get used to it within a few days and for others it takes a little longer. If you are not satisfied after a short wearing period, the hearing care professional may be able to adjust the device differently or give you another device to try. A trial period generally only ends when you are completely satisfied, usually this takes a month.
The cost of a hearing aid
When you have made the choice for a hearing aid, the next question is: who pays the bill? The costs of purchasing a hearing aid vary widely. The costs depend on your health insurance and the type of hearing aid you purchase. The good news is that your health insurer reimburses 75 percent of the costs from the basic insurance. Because this is reimbursed from the basic insurance, this is at the expense of your deductible. The remaining 25 percent can be reimbursed from supplementary insurance. If there is a residual personal contribution, it will usually come from your own pocket.
In addition to the costs for the device itself, there are of course additional costs. Depending on the type of hearing aid, you sometimes need batteries. You also need cleaning products such as cleaning tablets, cleaning tissues or a spray. You can also choose to buy accessories. Finally, a drying box is recommended, so that you can thoroughly dry your hearing aid in humid weather or if you perspire a lot.
How long does a hearing aid last?
With intensive use, a hearing aid lasts about 5 years. After 5 years you will also be eligible for compensation again. If you need a new hearing aid sooner, you will not be reimbursed. You can then deduct part of the costs from your income tax. You can extend the life of your hearing aid by regularly cleaning and maintaining it. The hearing care professional can explain how to do this.