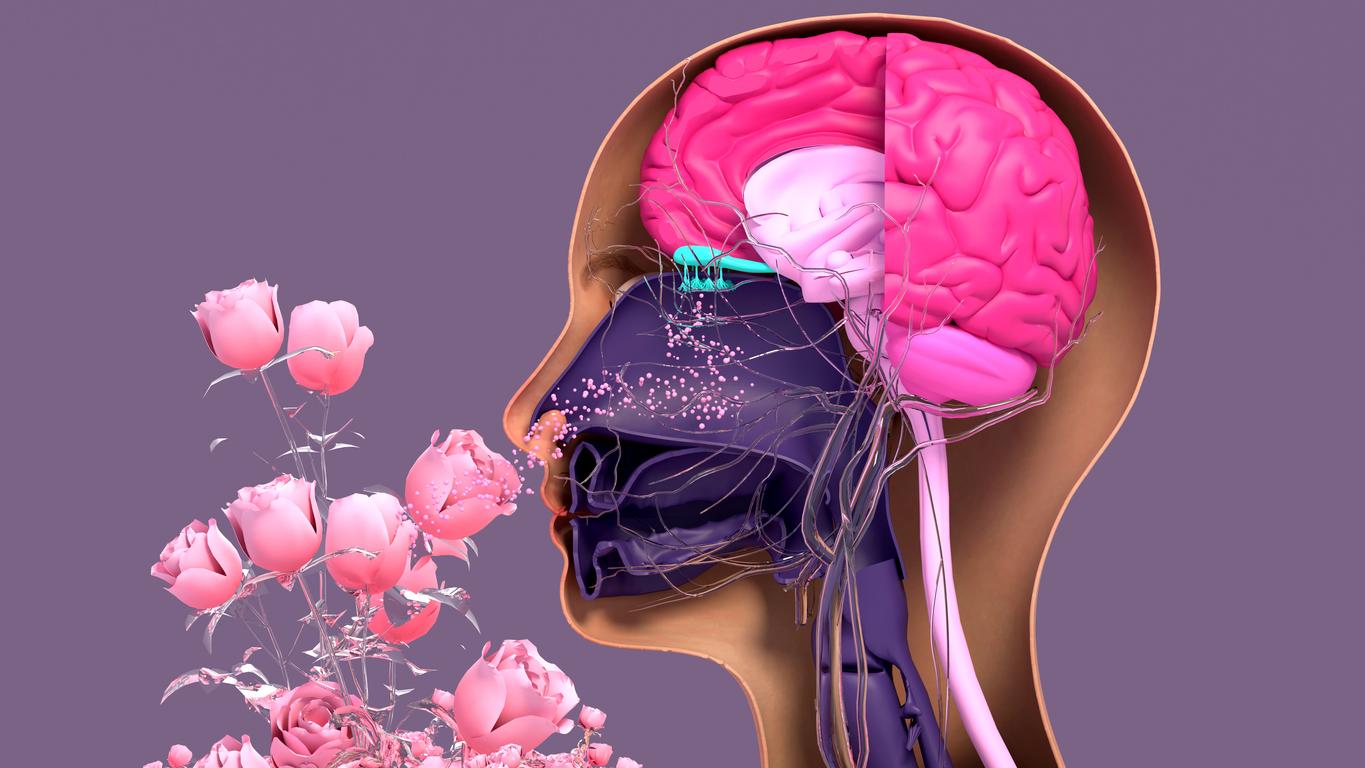
Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, have recently identified a new brain region involved in consolidating dream memories. This breakthrough could revolutionize our understanding of the role of dreams in learning and memory.

- Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, have identified the dorsomedial prefrontal cortex as a key brain region involved in consolidating dream-related memories during REM sleep.
- Dreams play a critical role in memory integration and emotional regulation. This new understanding reinforces the importance of dreams in information processing and long-term memory, particularly in patients with memory disorders.
- This discovery opens new perspectives for the treatment of memory disorders and neurodegenerative diseases. It also highlights the importance of improving sleep quality to optimize learning and mental health, offering healthcare professionals innovative approaches for their patients.
A study led by a team of neuroscientists at the University of California, Berkeley, has shed light on a previously little-studied region of the brain in the context of dreams: the dorsomedial prefrontal cortex. This area, known for its role in planning and decision-making, also appears to be crucial for the consolidation of dream-related memories. The researchers used advanced brain imaging techniques to observe brain activity during REM sleep, the phase when dreams are most intense.
The results show that the dorsomedial prefrontal cortex is activated during this phase, in correlation with areas involved in memory and emotions. This discovery sheds new light on the complex functioning of the brain during sleep and opens the way to new research on the function of dreams.
The role of dreams in learning and memory
Dreams have long been a subject of fascination and mystery. They play a crucial role in learning and memory, helping to consolidate information acquired during the day. The discovery of the role of the dorsomedial prefrontal cortex in this process reinforces the idea that dreams are not simply random experiences, but important mechanisms for the brain.
Researchers suggest that during REM sleep, the brain uses dreams to process emotions, solve problems, and integrate new information. This consolidation of memories is essential for long-term memory and effective learning. Understanding this process may offer new insights into memory disorders and neurodegenerative diseases.
Functions of dreams
- Integrating memories: Dreams help transform recent experiences into lasting memories.
- Emotional regulation: Dreams help process and regulate emotions experienced during the day.
- Problem Solving: Some dreams can help you find creative solutions to complex problems.
Implications for research and medicine
The discovery of the involvement of the dorsomedial prefrontal cortex in dreams opens new avenues for scientific research and medicine. For example, it could help to better understand and treat sleep and memory disorders. Patients with memory disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease, could benefit from new therapies targeting this region of the brain to improve the consolidation of memories.
Additionally, this discovery could have applications in the field of learning. By better understanding how the brain consolidates memories during sleep, it might be possible to develop techniques to optimize learning and retention of information. Students, for example, could benefit from improved sleep strategies to maximize their academic performance.
Practical applications
- Treatment of memory disorders: New therapies for patients with neurodegenerative diseases.
- Optimizing learning: Sleep strategies to improve information retention.
- Improving Mental Health: Techniques to Manage Stress and Emotions Through Sleep.
The discovery that the dorsomedial prefrontal cortex is involved in the consolidation of dream memories represents a significant advance in our understanding of the brain and its functions. By further exploring this region and its role in dreams, researchers are opening the way to new approaches to treating memory disorders and optimizing learning. Dreams, long considered mysterious, are gradually revealing their secrets and their crucial importance for our mental and cognitive well-being.
This discovery underscores the importance of sleep and dreams for overall health. By taking care of our sleep, we can not only improve our memory and learning, but also our emotional well-being. Future research will continue to unravel the mysteries of sleep and dreams, offering innovative solutions to improve quality of life.