A natural chemical found in this vegetable reduces blood clotting and improves the effectiveness of medications intended to remove blood clots.
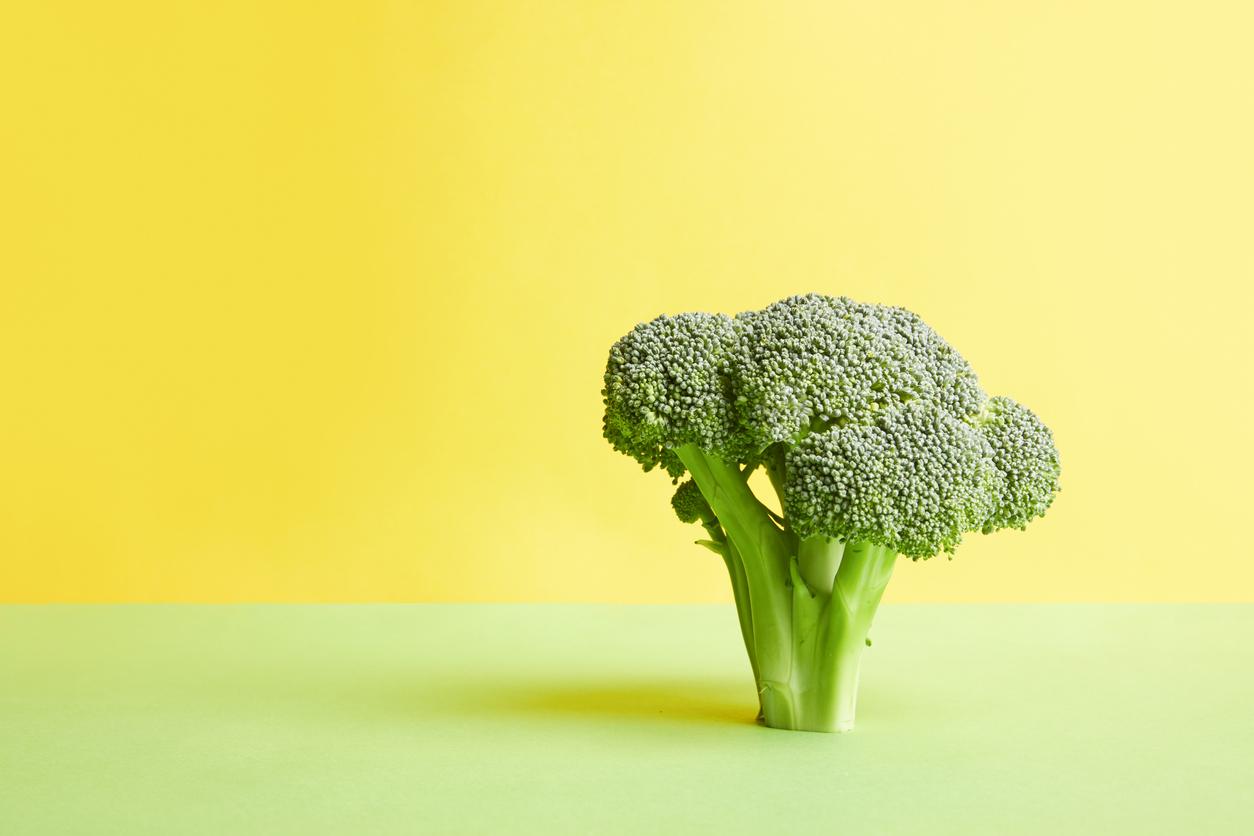

- Sulforaphane is a natural chemical found in cruciferous vegetables, including broccoli.
- It reduces the formation of blood clots, a condition that often leads to stroke.
- In addition, the effectiveness rate of anticoagulant treatment (tPA) increased to 60% when the drug is administered with the compound derived from broccoli.
Cruciferous vegetables, especially broccoli, contain a compound called “sulforaphane.” According to a recent study, they have selective and irreversible antiplatelet effects and act synergistically with vascular recanalization therapies without increasing the risk of bleeding. To reach this conclusion, researchers from the University of Sydney (Australia) carried out a study, the results of which were published in the journal ACS Central Science. As part of the work, the team analyzed 23 electrophilic phytochemicals with platelets and found that sulforaphane could reduce the formation of harmful blood clots that, in some cases, lead to stroke.
Stroke: sulforaphane makes anticoagulant treatments more effective
After an ischemic stroke, a patient is treated with tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), a type of medication that destroys clots and slows the progression of brain damage. “Unfortunately, this treatment is only effective in 20% of cases,” has explained Xuyu Liu, co-author of the research. However, when the drug was administered with the compound derived from broccoli, its effectiveness rate increased to 60%. According to the scientists, this substance did not cause any signs of bleeding, which is a common side effect associated with blood thinners tested in the treatment of stroke. “This means that paramedics could treat ischemic stroke patients with broccoli medication as well as tPA on the way to the hospital.”
A potential preventive treatment against stroke within 5 years
From now on, the authors will carry out clinical trials, with the possibility of having a new preventive and anticoagulant treatment for stroke within five years. Their future research will continue to explore how compounds in vegetables may have beneficial effects on disease processes. “We have already identified another compound from another vegetable that shows promise in thrombotic diseases”Xuyu Liu said.