A recent study shows that the response of neurons to sucrose and stevia, which is just as good but healthier, is similar.
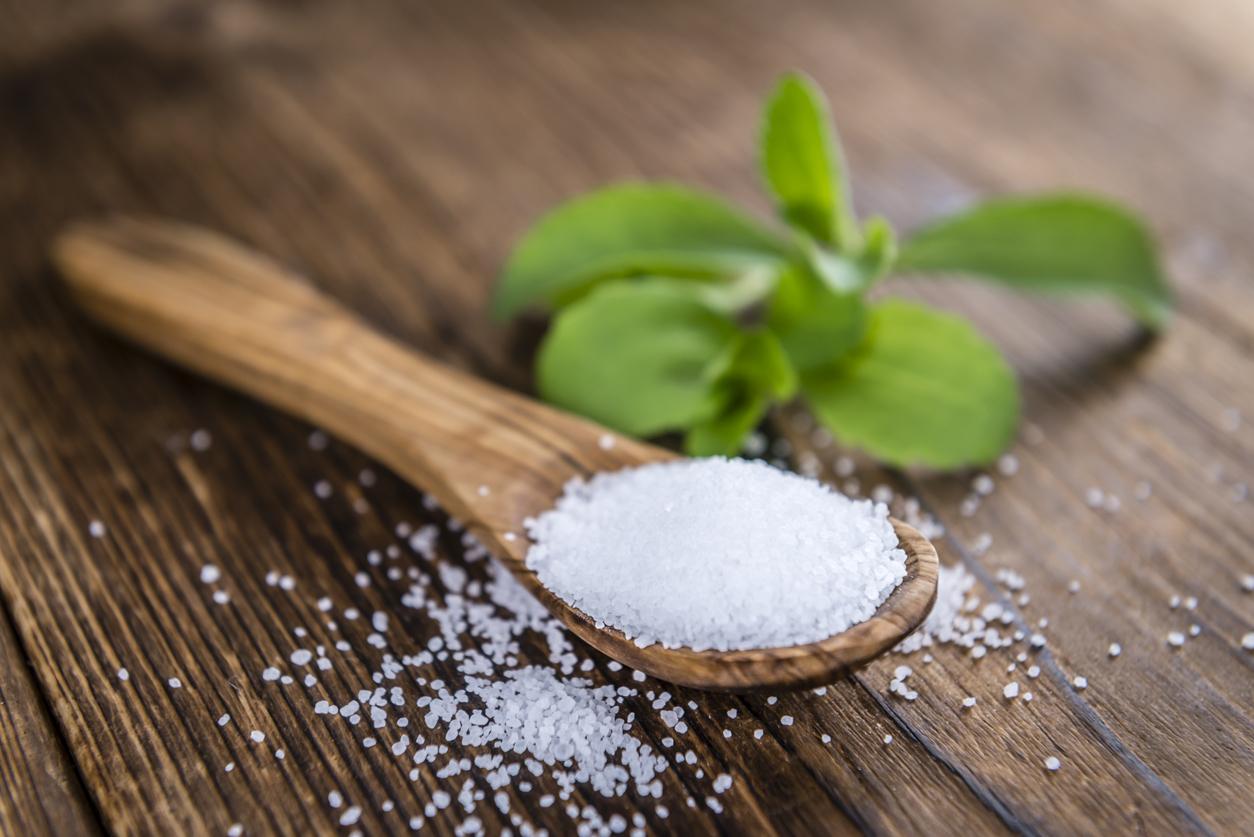

- Stevia is a sweetener that contains fewer calories and has minimal effects on blood sugar compared to sucrose.
- In one experiment, mice preferred stevia, as much as sucrose, to other sweeteners.
- Consumption of sucrose and stevia activated neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the rodent thalamus.
“Although the brain can discriminate between multiple sweeteners, the neural mechanisms underlying this complex behavior remain elusive.” This was stated by researchers from Shanghai University of Science and Technology, the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and other institutes in China. As part of a study, published in the journal Neuroscience Researchthey analyzed the role of the anterior paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus in managing the preference for sweeteners in mice.
Stevia caused neuronal activity similar to that of sucrose
To carry out their research, the scientists subjected the rodents to six different diets for six weeks. One group of mice was put on a so-called control diet, with a mixture of sweeteners, while the other groups were fed high amounts of sucrose (i.e. “table sugar”), stevia, xylitol, glycyrrhizin or mogroside. During the experiment, the team recorded the activity of neurons in the animals’ brains in real time, using in vivo fluorescence calcium imaging. “This is an experimental technique that can monitor changes in calcium levels inside cells, which reveals the activity patterns of those cells.”
According to the results, the mice showed a marked preference for diets rich in sucrose and stevia. In detail, stevia induced an activity in the anterior paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus which more closely resembles that caused by the ingestion of sucrose. According to the authors, this suggests that stevia may be the most “brain-friendly” sugar substitute among the most widely used sugar substitutes, most closely reflecting the perceived taste of sugar. As a reminder, stevia, derived from the leaves of a plant native to South America, is a sweetener, which contains fewer calories and has minimal effects on blood sugar compared to sucrose.
Incorporate stevia into foods and drinks?
“Therefore, stevia should receive more attention from relevant food and beverage industries in order to reduce the number of calories.” The researchers added that this study could inspire other neuroscientists to further examine the neural underpinnings of stevia consumption and this time in humans.