Spina bifida is a serious malformation of the fetus that develops during the first months of pregnancy. Children are born with the contents of their spine exposed.
The cases of spina bifida, a malformation of the fetus that develops during the first months of pregnancy, are increasing in France. According to the EUROCAT online register, their incidence fell from 3.87 / 10,000 cases over the decade 1991 to 2000 to 5.77 / 10,000 cases over the following decade, or more than 450 cases per year. Figures which are moved by the French association of urology, which recalls that the management of this disease must be done from birth.
Failure to close the rear part of one or more vertebrae
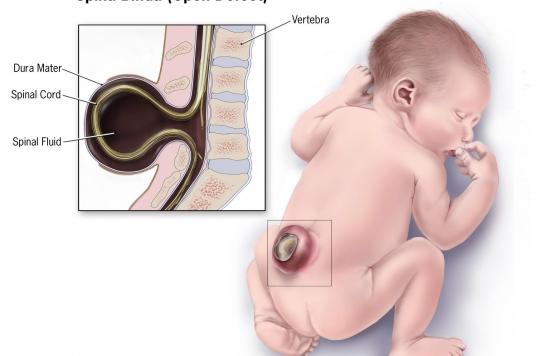
Spina bifida is a defect in the closure of the rear part of one or more vertebrae, leaving bare and unprotected the contents of the spine (meninges, spinal cord, nerve roots, etc.). A lump will then form on the lower back, as shown in the illustration below.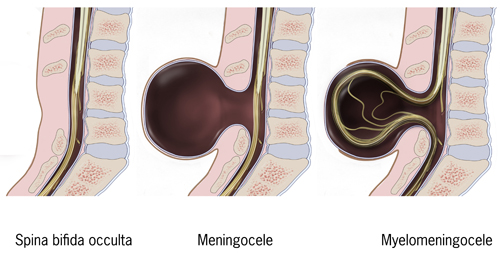
Credit: Common Wikipedia.
The deficiency in certain nutrients – in particular folic acid (vitamin B9) and methionine – is one of the reasons for the occurrence of this anomaly, the origin of which remains largely mysterious.
The consequences of this exposure of the spinal cord or its appendages are numerous. Spina bifida can cause:
– Hydrocephalus (and associated cognitive disorders or mental retardation).
– Muscular paralysis.
– Urinary and fecal incontinence.
– Sexual problems.
– A malformation and deformation of the limbs.
In 80%, doctors offer an abortion
“The disorders are very variable. They depend on the degree of nerve damage and the level of the spina”, specifies Professor Xavier Gamé, urologist at Rangueil hospital in Toulouse, member of the AFU neuro-urology committee and Secretary General of AFU. Some patients are affected by “spina bifida occulta” or “closed”: the vertebral arches are poorly welded but the marrow remains protected by the spine and by the skin, unlike “open” spina bifida (“spina bifida aperta”) which leaves bare nervous material.
Spina bifida can be detected in the sixth month of pregnancy. In 80% of cases, doctors offer an abortion. If the parents refuse it, “these disorders must be managed from birth, otherwise they lead to a rapid deterioration of the urinary system (bladder and kidney)”, insists Xavier Gamé. Repeated infections can lead to pyelonephritis, which in turn causes impaired kidney function. In the long term, for lack of a well-conducted preventive treatment, the patient becomes precociously renal insufficiency and may find himself awaiting transplantation from the age of 20 years. Stones (urolithiasis) can also disrupt daily life. On the side of the bladder, the mucosa, subject to a permanent inflammatory state, is also at risk of becoming cancerous (urothelial carcinomas, squamous cell carcinomas, etc.).
Psychological support
Urological follow-up is therefore essential. If the bladder is retentionist, the solution is to catheterize the child regularly to prevent the urine from accumulating and the organ from distending. “It is done initially by the parents but from the age of 5 or 6, the child can learn to do his self-polling”, explains Professor Gamé. In parallel, it is necessary to treat the incontinence. An annual kidney and bladder ultrasound should also screen for structural abnormalities, as well as an annual assessment of kidney function.
Finally, an evaluation of the functioning of the bladder and the sphincter is required every 2 years (urodynamic assessment). These disorders sometimes require psychological follow-up because they can be the cause of suicide in adolescents. “The management of a spina bifida patient is necessarily multidisciplinary: pediatric, neuropediatric, urological, psychological, physical medicine and rehabilitation … All care must be carried out in consultation”, adds Xavier Gamé. At this cost, children with spina bifida can lead near-normal lives with an acceptable quality of life.
.