Researchers from the Institut du thorax and the CHU de Nantes have just discovered the mutation of the gene which is responsible for arterial aneurysms, these dilations of the vessels which can explode at any time from a certain stage. A blood test should be developed to detect them and finally prevent aneurysm ruptures.
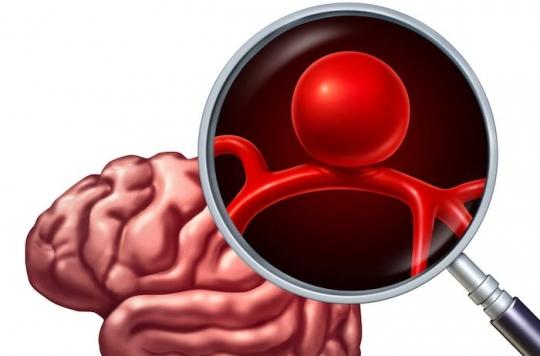
It was by analyzing the DNA of several members of the same family that scientists from the Institut du thorax, in Nantes, discovered the mutation of the ANGPTL6 gene in people who have a family form of cerebral aneurysm. Analyzes were then carried out on other patients, and found anomalies in this same gene. The work of Nantes researchers is published in The American Journal of Human Genetics and are the subject of a patent.
A genetic origin and risk factors
An aneurysm is the malformation of an artery, which can be compared to a hernia on an inner tube. All the arteries can theoretically present one day this malformation which, in fact, affects essentially only two types of vessels: certain arteries of the brain and the abdominal aorta, the largest artery of our body nestled deep in our belly.
In both cases, the rupture is like a real clap of thunder in a serene sky. If it occurs in the middle of the belly, the bleeding is most of the time unstoppable. In France, more than 10,000 people die each year from a ruptured aneurysm. We know how to detect that of the abdomen with a simple examination: an abdominal ultrasound in people at risk. From now on, we will soon be able to do it also for the brain, where only an arteriography or a scanner made it possible to detect them.
Few warning signals before the break.
The arteries are strong, but there is a tendency to dilate, especially in the event of risk factors: when the blood is rich in cholesterol which weakens the different layers that compose them or if the pressure is high in the arteries. Those who suffer from it feel nothing, especially since nestled deep in the stomach, or the brain, this hernia has room to develop quietly, over several years. There are no symptoms that can alert.
Suddenly, because the tension has increased, because the hernia is too large, or the wall is in too bad a state, the bubble bursts, with the same effects as that of a tire at high speed. It’s an extreme emergency, because it’s massive internal bleeding. There is very little time left for the surgeon for a long and heavy intervention, whereas cold this surgery is much simpler
A blood test
This is why the results of research by Nantes researchers are remarkable. They have also led to the filing of a patent which for the moment only concerns familial forms of cerebral aneurysm. This discovery opens the door to screening for cerebral aneurysms. This genetic anomaly results in the presence of a protein in the blood which can be measured with, in the long term, a test probably easy to develop.
In people who will be carriers of this anomaly, it will then be easy to do a cerebral MRI regularly to monitor its development and possibly intervene before it ruptures. On the other hand, this examination is much too expensive to do it systematically for everyone.

.