Disease and treatment
Continuous red bumps on the tip of your nose, your cheeks, the center of your forehead and your chin. That’s what happens when you have the chronic skin disease rosacea. Here you can read everything about this disease, its causes and what you can do about it.
Rosacea is a common skin disease that affects nearly ten percent of the population. Rosacea is most common in adults and the first symptoms often appear in people between the ages of 30 and 60. The condition is most common in fair-skinned people.
It affects many people, especially in Northwestern Europe. Rosacea is more common in women, but the symptoms are more severe in men.
fases of rosacea
The disease occurs in several stages:
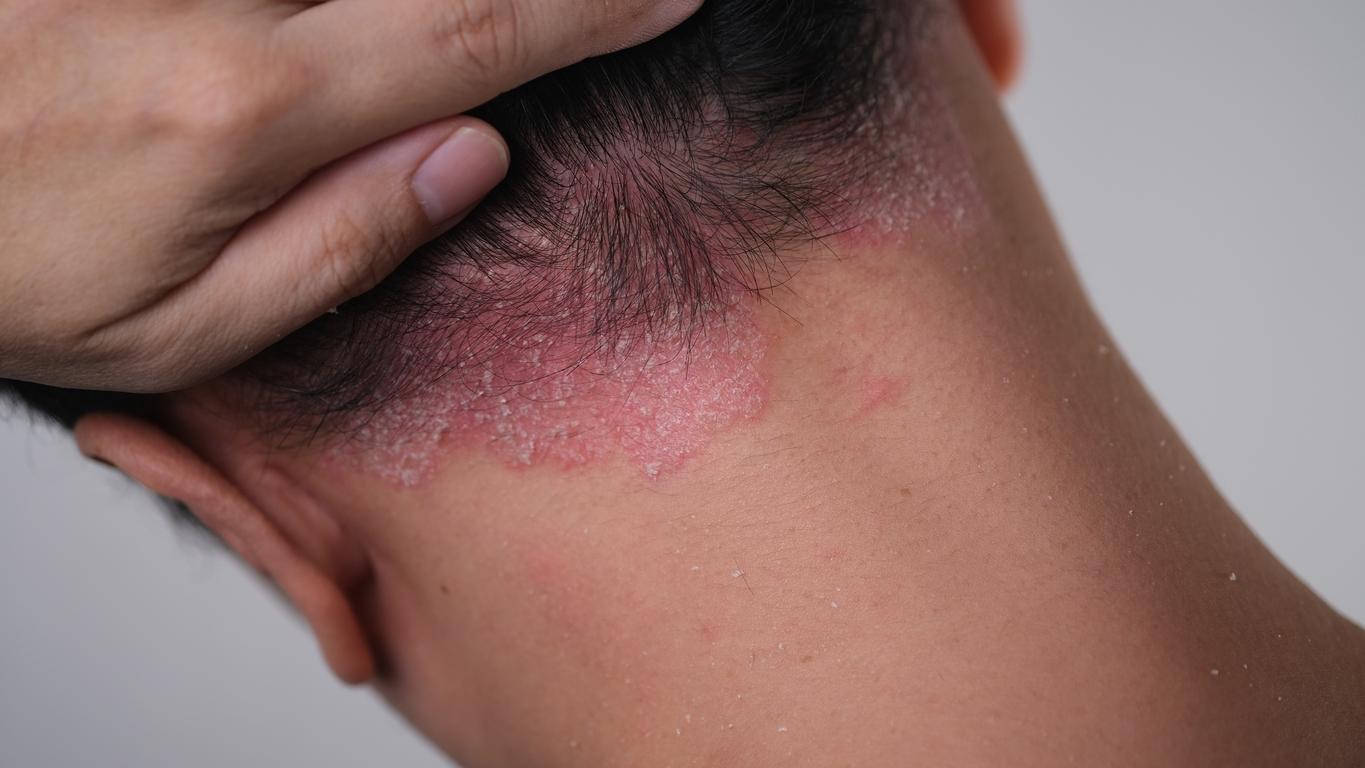
- Phase 1: Everyone blushes from time to time, but in people with rosacea, the blushing can last for hours. On the face – and especially on the cheeks – small blood vessels become visible that no longer disappear. The face can hurt especially due to cold and water.
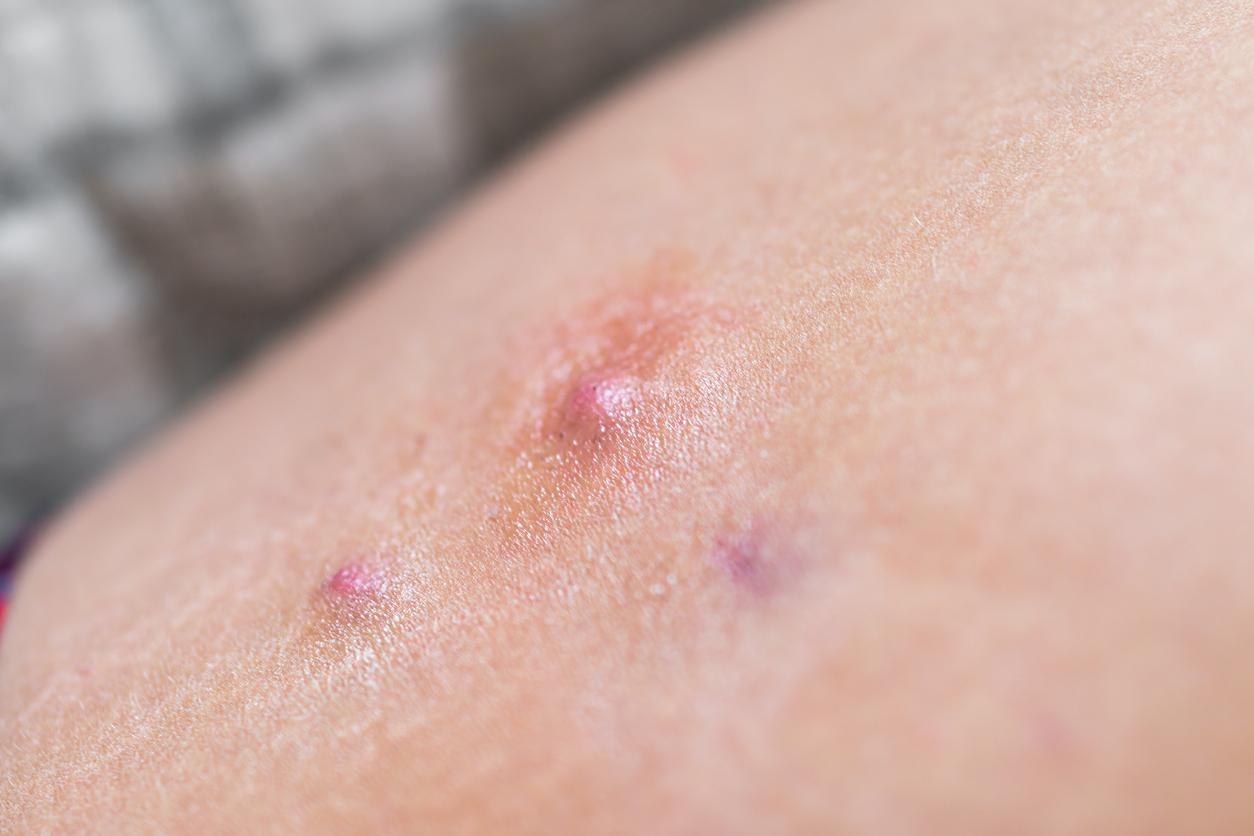
- Phase 2: In addition to redness, red bumps and pimples appear on the face.
- Phase 3: Larger pimples develop, the skin feels rough and becomes thick. This can change the shape of the face. In the worst case, the eyes can also be affected.
The diagnose
A doctor will probably immediately realize that it is rosacea. The symptoms of the skin condition are clearly visible and very typical. In some cases, redness or widening of the blood vessels may indicate something else. Then a piece of skin is removed and examined under a microscope.
The causes
The cause of rosacea is unknown. It may be genetically determined. Rosacea is in any case not caused by alcoholism or poor hygiene, as people often think. However, these prejudices are so persistent that 40 percent of men and 80 percent of women with rosacea are considered alcoholics.
A number of factors are known to aggravate the disease:
- Alcohol, hot drinks and highly spicy food.
- Skin hypersensitivity to certain creams, lotions and make-up.
- Heavy physical exertion and emotional strain.
- Transition from low to high temperatures.
- Rosacea is worst in the winter for most people. Most patients get better in the summer, but in some cases it works the other way around.
- vasodilator drugs – often prescribed for the elderly – and corticosteroids; ointments and creams to relieve redness. The corticosteroids work well at first, but when you stop using them, the symptoms return to a greater extent.
Influence on daily life
Without treatment, rosacea can become more serious. It is not just a color that can be camouflaged. It is a disease that must be treated early to prevent the disease from getting worse.
It is also advisable that the negative effects on daily life are contained as much as possible. Rosacea exerts an important influence on daily life: 92 percent of patients are hindered psychologically and relationally. The disease is a source of stress and reduces self-confidence in 40 percent of men and 44 percent of women.
Treatment methods
Although rosacea is a persistent condition, it is not a health threat. The skin disease is -usually- treatable. However, when treatment is stopped, there is a high chance that the symptoms will return.
Your doctor or dermatologist can prescribe a cream – metronidazole – to prevent redness and pimples. In most cases, improvement will occur after four to eight weeks. In more severe cases – for example if the eyes are affected – antibiotics in the form of tablets can help. Examples are tetracycline, doxycycline or minocycline. Always consult a doctor before use.
You can do this yourself
- Try to avoid the factors that make rosacea worse.
- Use good sunscreen when exposed to sunlight.
- Avoid saunas, hot baths and showers that are too hot; the dry air is not good for the skin
- Use mild soaps and cleansers without alcohol.
- Wash your face with lukewarm water and pat dry with a towel (do not rub).
Related skin diseases
A number of skin diseases show similarities with rosacea. Sometimes the diseases also occur together.
- Coupereuse: increase in small blood vessels in the face that can only be removed with a laser. Most rosacea patients suffer from this.
- Rhinophyma: a heavily thickened and red colored nose. This occurs in the end stage of rosacea and can usually be treated with antibiotics.
- Blepharis: Chronic inflammation of the eyelids that causes itching, irritation and redness. This is the most common form of rosacea. Sometimes people only suffer from this, without redness in the face.
- Acne: pimples or blackheads that are usually caused by a bacterial infection.