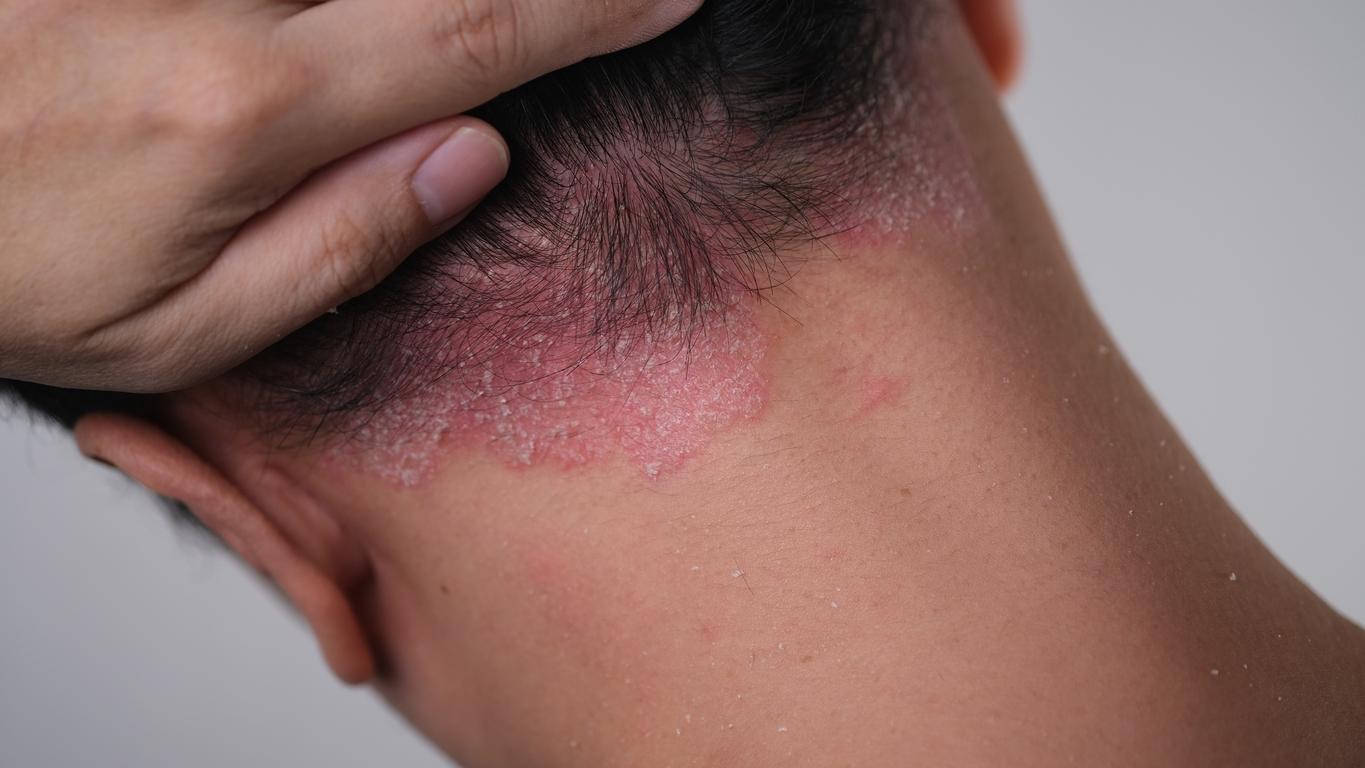
Ringworm is a common, highly contagious skin infection caused by dermatophyte molds belonging to the genus Trichophyton. Usually benign, this dermatosis worries the American health authoritieswho have just reported two cases of ringworm resistant to the usual treatments, which appeared in adults.
What raises the concern of scientists is that these two cases were caused by a new species of dermatophyte, the Trichophyton indotineae, which had been responsible for a severe and resistant ringworm epidemic in South Asia over the past decade.
How do you catch ringworm?
First thing to know: despite sometimes impressive symptoms, ringworm is generally not a serious illness. This skin disease (“dermatosis” in medical language) mainly affects children of school age, between kindergarten and the beginning of college.
Ringworm is a skin and hair infection caused by a microscopic fungus from the dermatophyte family.
This fungus (it can be T. Mentagrophytes, T. Verrucosum, M. Audouinii or even M. Canis) feeds on keratin: it attacks all the areas where there is hair and causes the appearance of “plaques”, often red and crusty.
The transmission of the fungus can be done from humans (by direct or indirect contact, through a hairbrush or a hat, for example), from animals (cats, dogs, rabbits, hamsters, farm animals. ..), or even from the environment (this is much rarer).
Ringworm is a highly contagious disease which can cause small local epidemics, especially in schools: the incubation period of the fungus is, on average, 2 to 14 days. It is a dermatosis that concerns more urban areas.
Good to know: thanks to a specific immune reaction, it is not possible to catch ringworm several times during your life.
What are the symptoms of ringworm?
-
Inflammatory ringworm is related to zoophilic dermatophytes, which means that the fungus (T. Mentagrophytes Or T. Verrucosum) is transmitted by contact with an animal. We observe a red and rounded “macaron” several centimeters in diameter: in children, it generally appears in the scalp, in humans, it can appear in the beard.
When pressed on it, there is an oozing of pus; the “macaroon” is dotted with small pimples and/or small lesions. Inflammatory ringworm is often accompanied by headachesof aches and/or a fever moderate.
-
Ringworms (caused by Mr. Audouinii or Mr. Canis in case of microsporic ringworm; by T. Violaceum, T. Tonsurans, T. Rosaceum or T. Soudanensae in case of trichophytic ringworm) are the most common, especially in children over 3 years of age.
They are characterized by red/pink “spots” that quickly become covered with fine, powdery scales that look like dandruff; in the area, the hair breaks a few millimeters from its root. The spots may be few in number (in the case of microsporic ringworm: 1 or 2 patches maximum) and be covered with healthy hair (in the case of trichophytic ringworm).
-
The favic moth is transmitted exclusively between humans: it is caused by Trichophyton schönleinii Or Achorion schönleinii. It can affect children, adults and seniors, mainly in precarious environments.
The favic ringworm is characterized by crusty patches in relief, gray or yellowish, more or less extensive. The contours are irregular, the smell is unpleasant, the plaque crumbles to reveal reddened, even suppurating skin. Hair that persists is dull and brittle, often atrophied.
Treatment: how is ringworm treated?
Very contagious, ringworm requires long treatment (several weeks) and… impeccable hygiene!
If ringworm is not a notifiable disease, it is however recommended to warn the teaching staff / the staff of the drop-in daycare center… to avoid a local epidemic.
To diagnose ringworm, the doctor can first examine the lesions using a special light (Wood’s light) which, in some cases, can give a fluorescent appearance to the contaminated hair.
However, to confirm the diagnosis (and specify which ringworm it is), it will be necessary to cultivate the fungus in the laboratory (after a mycological sample): the result requires, on average, between 3 and 4 weeks of waiting.
- In case of inflammatory ringworm, local treatment with imidazoles (bactericidal antibiotics in the form of an ointment) may be sufficient: in the most extensive cases, the doctor may also prescribe general antibiotics and antifungals. A scar may persist, possibly with hair loss (alopecia).
- In case of ringworm capitis, the treatment is based on local care of the scalp (antimycotic shampoo associated with a fungicidal ointment) and on antimycotic drugs administered locally. Drug treatment depends on the age of the patient; it lasts between 4 and 8 weeks. In most cases, there is no scar or hair loss.
- In case of ringworm, it is necessary to shave the area since the parasite proliferates at the root of the hair. Then, treatment with griseofulvin (a fungistatic antibiotic administered orally) is necessary for 6 to 8 weeks. Griseofulvin is contraindicated in pregnancy, porphyria, lupus, taking anticoagulants, estrogens and barbiturates. Adverse effects may be observed, including abdominal pain.
How to prevent ringworm?
If a case of ringworm has been declared in your surroundings (family, school, daycare center, nanny…), start by examining your child in search of “red patches”, especially in the hair.
Carefully clean hats, scarves, pillowcases, hairbrushes, combs… with a wash at 60°C or with an antifungal disinfectant (caution: “classic” disinfectants do not kill the fungus ).
It is also necessary to examine his pets in search of “red patches”. Hands should be washed frequently.
Sources:
First Reported US Cases of Tinea Caused by Trichophyton indotineae — New York City, December 2021–March 2023Centers for disease control and prevention, May 2023