What is oral thrush?
Oral thrush is an infection of the mouth caused by a fungus (thrush) called Candida albicans. The latter is present naturally on the skin, in the digestive tract and in the mouth. But sometimes, external factors lead to its proliferation, causing a fungal infection, called candidiasis.
What are the symptoms of oral thrush?
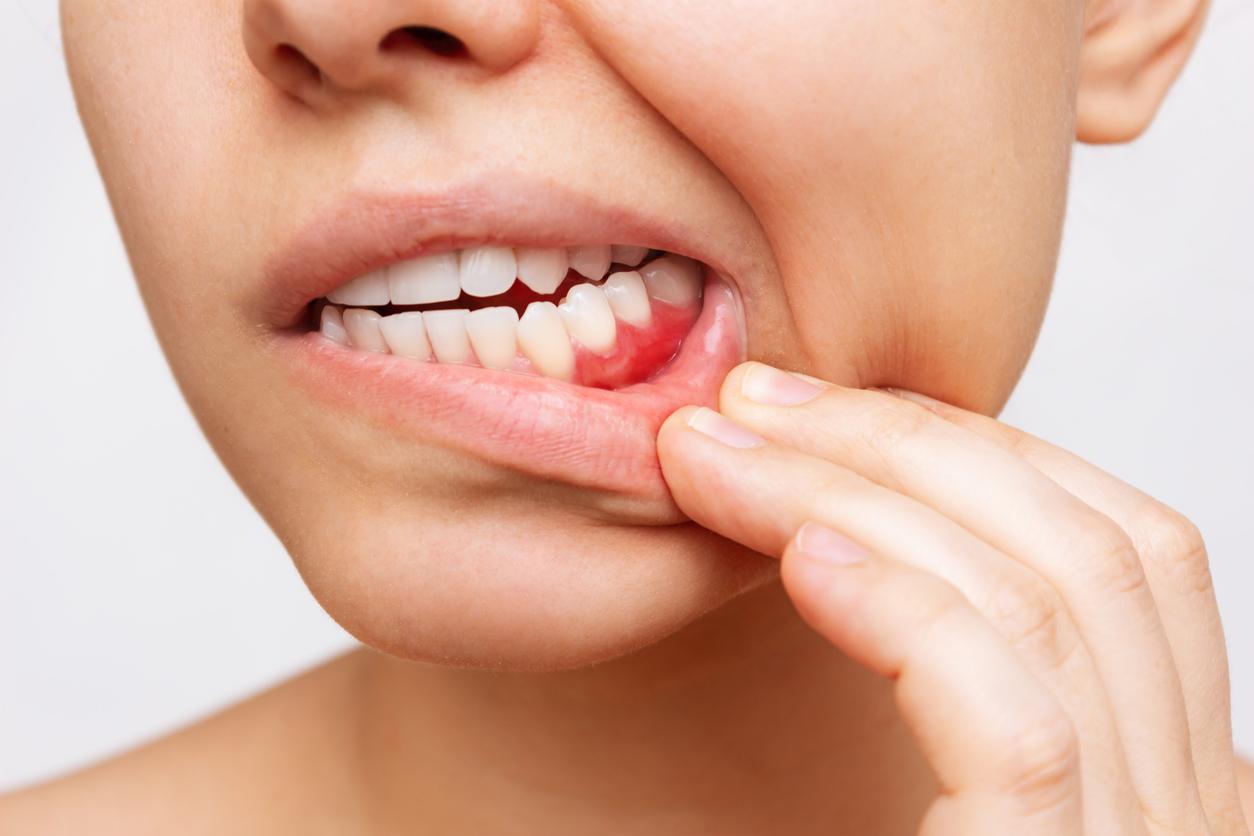
Oral thrush is manifested by whitish plaques on the tongue and reddish lesions at the corners of the lips, on the palate and the mucous membrane of the cheeks. The patient may sometimes feel a burning sensation in the mouth or throat.
What causes oral thrush?
Oral thrush is not caught because the organism causing the disease is already present naturally in the mouth. It is therefore external factors or a fragility of the immune system that are involved.
Taking antibiotics over a long period or inhaled corticosteroids can upset the balance of the oral flora. Yeasts are no longer controlled by bacteria: they grow and multiply.
pregnancy, diabetes and urinary infections chronic can be the cause of oral thrush. More serious pathologies such as HIV can also be a risk factor because the patient has a weakened immune system.
Why are infants more affected?
Oral thrush is a benign condition in infants. It is common in babies under 2 months old because their immune system is immature and therefore more susceptible to infections. Thrush is transmitted by the mother during childbirth or breastfeeding and usually heals spontaneously within a few weeks.
How is oral thrush treated?
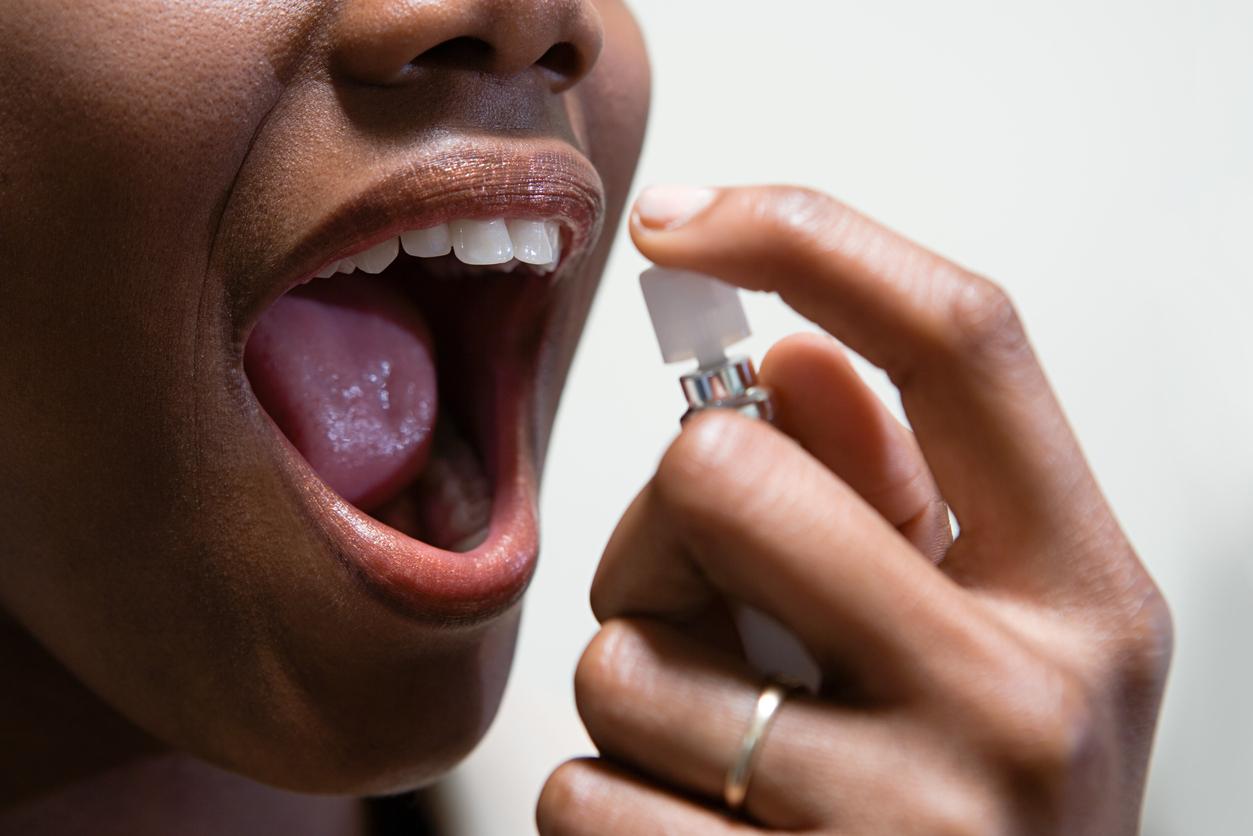
Taking an antifungal in suspension or tablet as well as the use of antiseptic mouthwashes can treat the problem in a few weeks.
If oral thrush is due to the use of inhaled corticosteroids, rinsing the mouth after using the inhaler can prevent infection.
Concerning oral thrush in infants, the treatment can be in the form of an oral gel to be applied with a finger to the infected areas of the mouth for a fortnight.