If detected early, the chances of recovery from lung cancer increase considerably. That is why it is crucial to know the most common symptoms of this disease in order to consult a doctor without delay if you have one or more of them.
- Persistent cough, shortness of breath, chest pain: symptoms not to be ignored.
- Smoking and exposure to certain carcinogens: main risk factors.
- Medical consultation essential at the first symptoms.
Lung cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer death worldwide, affecting millions of people each year, including nearly 30,000 in France. Despite medical advances, early diagnosis remains a major challenge, often due to symptoms which may seem harmless or be confused with other conditions. This article explores the most common symptoms of lung cancer to help with early detection and improve the chances of effective treatment.
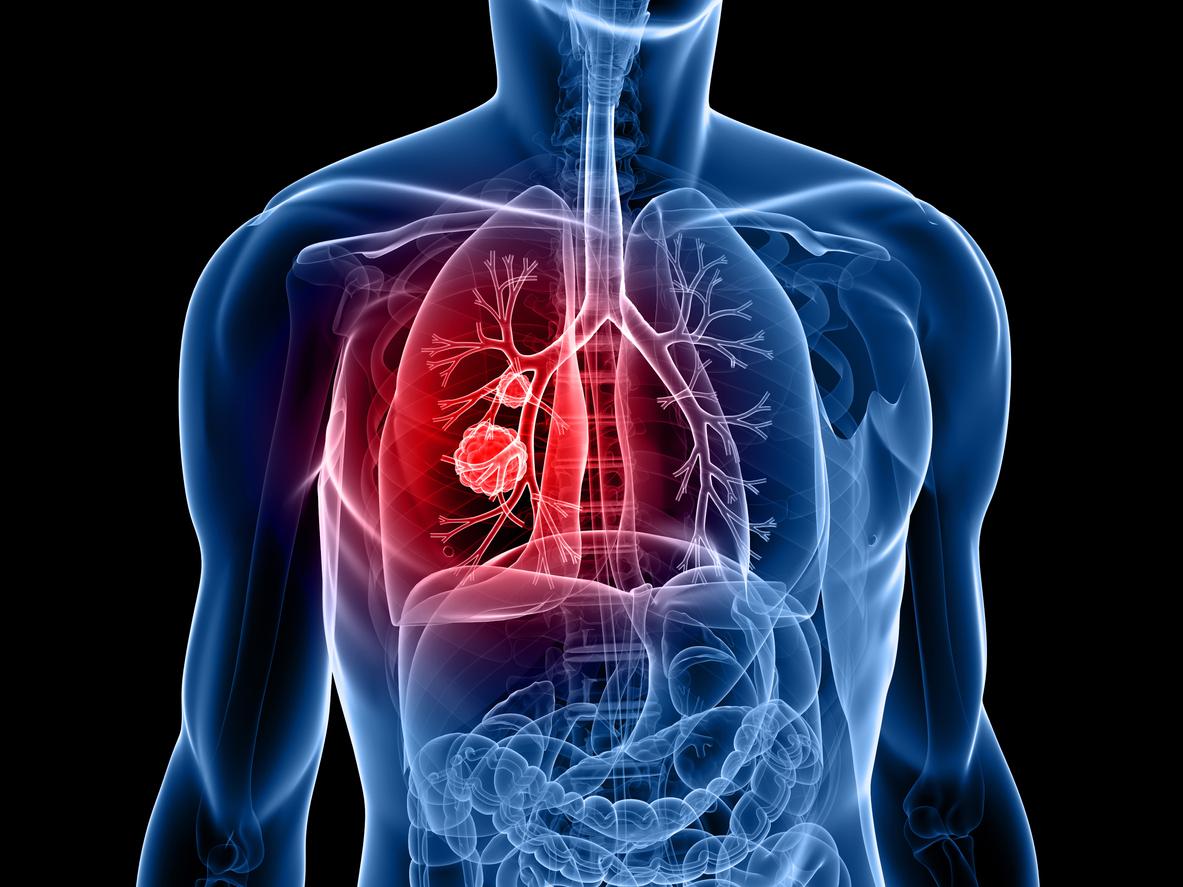
Lung cancer develops when abnormal cells multiply in the lungs out of control, forming tumors. There are two main types of lung cancer: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), which is the most common, and small cell lung cancer (SCLC), which is more aggressive and fast-growing. Major risk factors include smoking, exposure to secondhand smoke, air pollution, and exposure to toxic substances such as asbestos and radon.
Persistent cough: a signal that cannot be mistaken
The main symptom of lung cancer is a persistent cough, which cannot be explained by a cold or bronchitis and which lasts more than three weeks. This cough can be dry or productive, and sometimes be accompanied by coughing up blood, a sign of hemoptysis.
Shortness of breath and chest pain: signs not to be ignored
Unusual shortness of breath, especially with light exertion, may also be a sign of lung cancer. It may be accompanied by chest pain, which may be localized or diffuse, and is often worsened by deep breathing or coughing.
Symptoms of lung cancer can vary depending on the type, location, and size of the tumor. Here are the most common symptoms to watch for:
Blood in sputum
Hemoptysis, or blood in the sputum, is an alarming sign that should be evaluated by a doctor immediately. Even a small amount of blood can indicate a serious problem.
Chest pain
Chest pain, often made worse by deep breathing, coughing, or laughing, may indicate lung cancer. This pain may also spread to the shoulders or back.
Hoarseness
A change in voice, especially persistent hoarseness, may be a sign that the tumor is affecting the nerve controlling the larynx.
Unexplained weight loss
Rapid, unexplained weight loss, associated with decreased appetite, is a common symptom in many types of cancer, including lung cancer.
Fatigue
Persistent, unexplained fatigue that does not improve with rest may be a sign of cancer. This fatigue may be due to the body’s energy being used to fight the disease.
Recurrent respiratory infections
Frequent or recurring infections such as bronchitis or pneumonia may be a sign of lung cancer, especially if they persist despite treatment.
Less common symptoms of lung cancer
In addition to common symptoms, there are less common but equally important signs:
1. Bone pain:
- Pain that spreads to the bones, especially the spine, hips, and ribs, may indicate that the cancer has spread.
2. Headaches:
- Headaches can occur if the cancer has spread to the brain or if a chest tumor is pressing on the superior vena cava, disrupting blood flow.
3. Pancoast syndrome:
- A specific type of lung tumor that grows at the top of the lungs and can cause severe shoulder and arm pain, and muscle weakness.
Importance of screening and early diagnosis
Early detection is crucial to improving lung cancer survival. Screening tools such as low-dose computed tomography (CT) scans can help detect cancer early in people at high risk, including current or former smokers.
If you have one or more of the symptoms described, it is essential to seek medical attention without delay. Early diagnosis allows treatment to begin more quickly, increasing the chances of success. Treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapies, depending on the type and stage of the cancer.
Preventive measures to reduce risks
Although not all cases of lung cancer can be prevented, there are some steps you can take to reduce your risk:
1. Quit smoking:
- Smoking is the leading risk factor for lung cancer. Quitting smoking at any age can significantly reduce this risk.
2. Avoid second-hand smoke:
- Exposure to secondhand smoke is also dangerous. Avoid environments where cigarette smoke is present.
3. Reduce exposure to toxic substances:
- Take steps to minimize exposure to substances like asbestos and radon at home and at work.
4. Adopt a healthy lifestyle:
- A balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables and regular physical activity can strengthen your immune system and reduce the risk of many types of cancer.
Lung cancer, while fearsome, can be fought more effectively with early detection and proper treatment. Knowing the most common symptoms is a crucial first step in this fight. If you or a loved one are showing signs of this disease, do not hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for screening. With increased vigilance and preventative measures, it is possible to reduce the impact of this disease on the lives of millions of people.