Diabetes is a chronic disease characterized by the presence of excess sugar in the blood called hyperglycemia and measured by a fasting blood sugar level equal to or greater than 1.26 g / l (7 mmol / l) of blood. There are two types of diabetes:
the so-called “type 1” diabetes is due to a lack of insulin secretion by the pancreas. It affects about 10% of diabetics and mainly affects young people.
the so-called “type 2” diabetes is caused by improper use of insulin by the body’s cells. It is much more common and represents 90% of diabetes. In France, it affects around 3 million people, or 4.7% of the population. Figures that increase every year due to bad eating habits and an increasingly sedentary daily life.
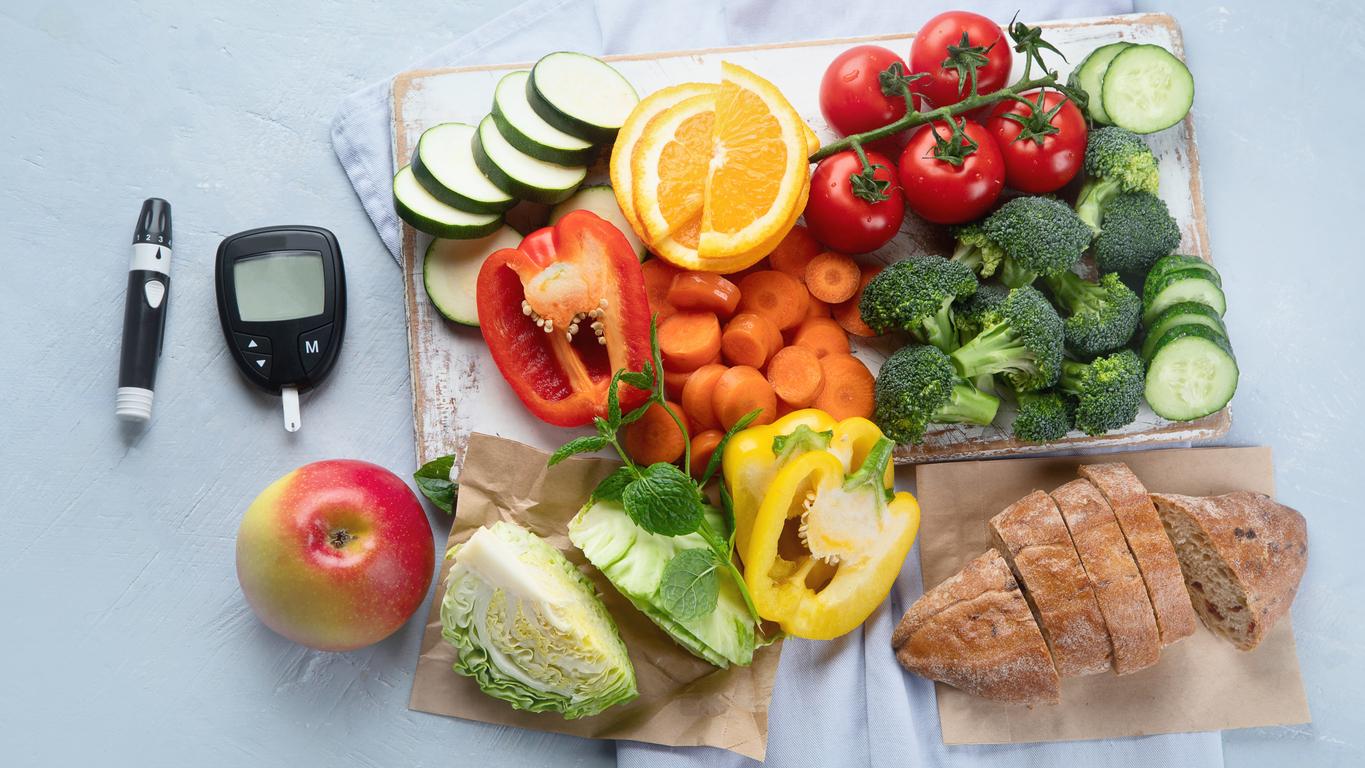
Practicing regular physical activity, even moderate, adopting a balanced diet and following the treatment prescribed by your doctor (and the associated follow-up examinations) are the three pillars for preventing irreversible complications of this disease, often described as devious.
Discover the differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes here: