The treatment for kidney problems
Suppose your kidneys stop working properly and your body is slowly poisoning itself. Dialysis is the only option. A disaster, or good to live with?
You have probably seen it on television: someone who is connected to a device to have his blood purified. That was probably a kidney patient who was on dialysis. When kidneys no longer function properly, they no longer filter waste products from the blood. The good substances, for example from food, so no longer.
Only option
If drugs and diet no longer help with kidney problems, the doctor will appoint kidney dialysis as the only option left besides a kidney transplant. Kidney transplantation is the best possible treatment, but not everyone can be transplanted. In addition, there is a severe shortage of donor kidneys. In the Netherlands, 6500 people are dependent on dialysis. The treatment is tough. Every year 1 in 6 dialysis patients dies. Usually, dialysis occurs when the kidneys are only working 10 percent or less. They can then no longer sufficiently purify the blood and that will have to be done in a different way. Dialysis can be done in two ways: artificially or via the peritoneum. It depends on the medical condition and personal preference which dialysis is most appropriate.
artificial kidney
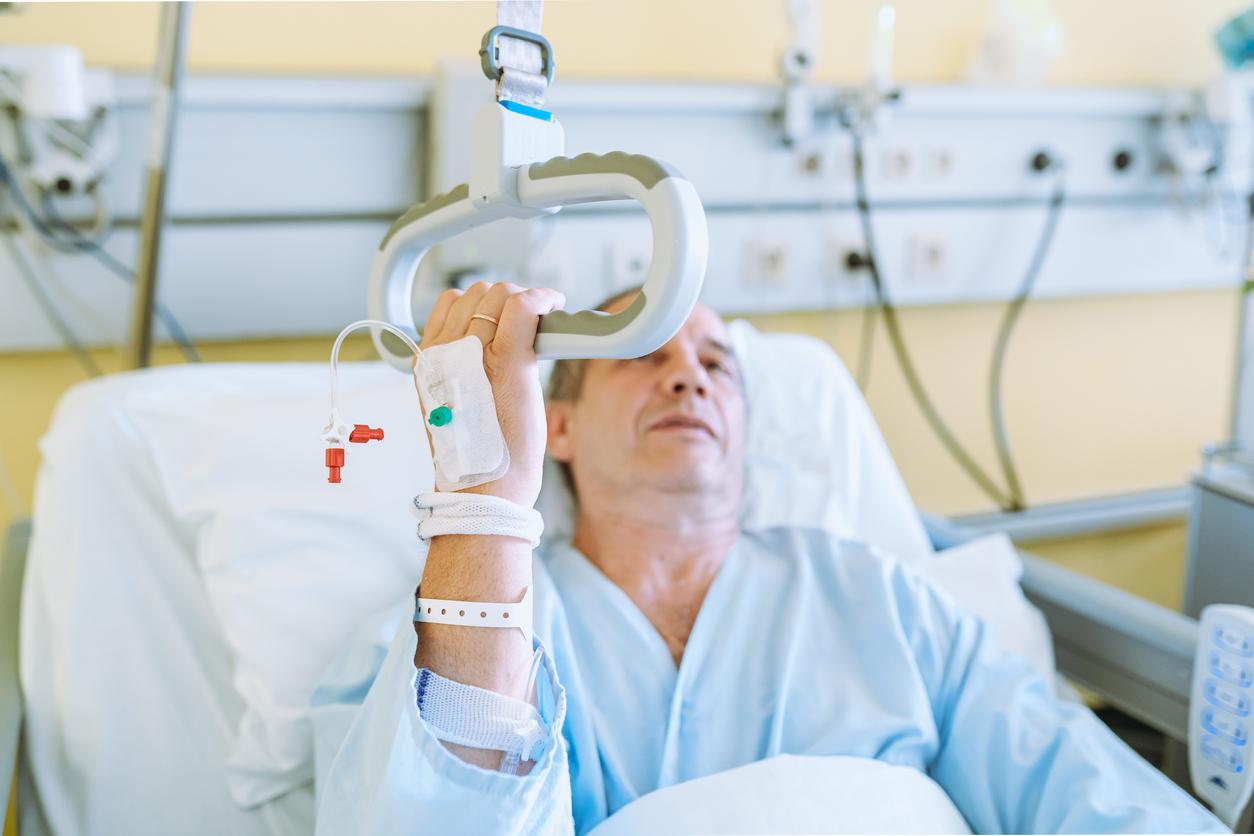
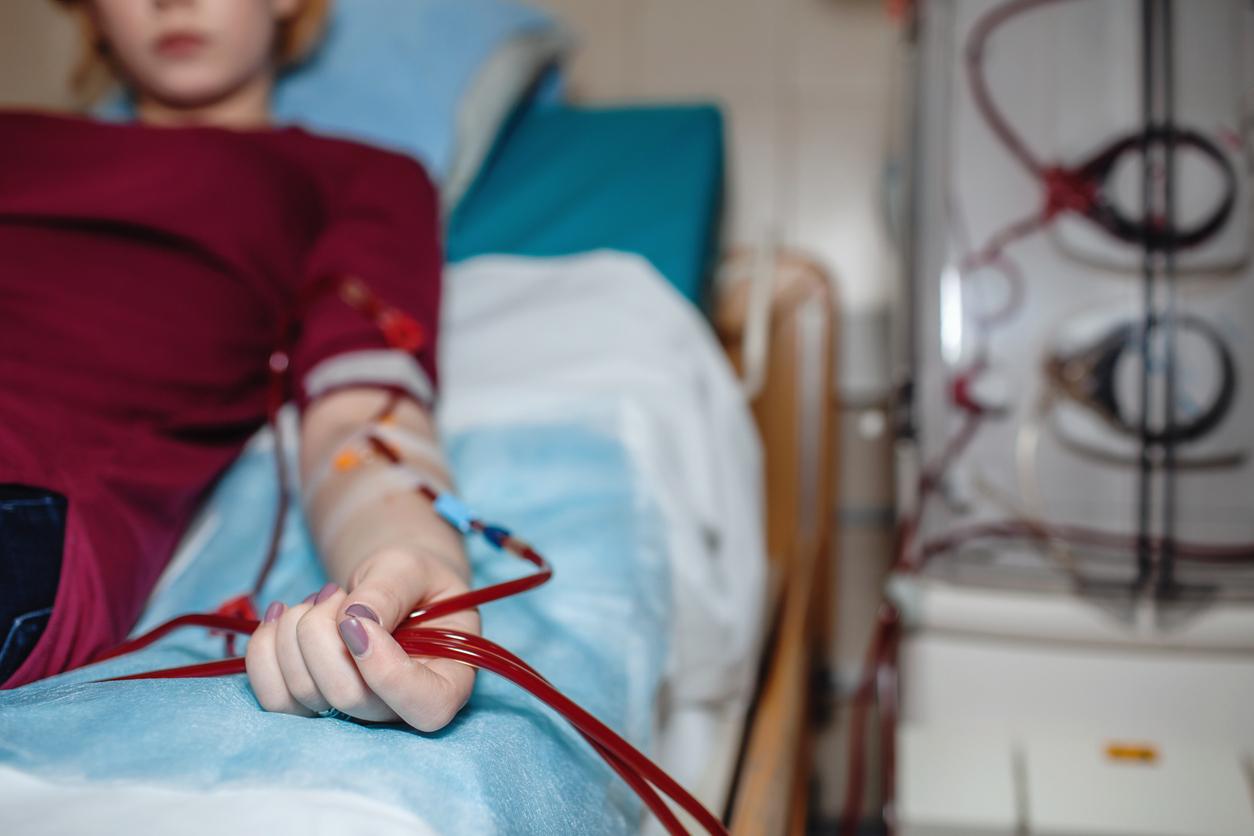
The artificial variant is called hemodialysis and the patient is connected to a large dialysis machine. This is an artificial kidney that cleans the blood. A tube is inserted into the body with a needle, which carries the blood to the machine.
The device purifies the blood of waste products and pumps the clean blood back into the body. This takes about four to five hours and should be done about three times a week, usually in the hospital or dialysis center. A permanent access for the tube, a shunt, is created before an operation. The shunt ensures sufficient blood supply during dialysis. This is necessary because a normal blood vessel can quickly become damaged and clogged. A shunt is only susceptible to infections. The Kidney Foundation therefore finances research into better vascular access and shunt care.
Hemodialysis is hard on the body because of the large fluctuations in blood values and fluid levels. Dialysis can cause fatigue, a sick feeling and eventually damage to the heart and blood vessels.
Peritoneal lavage
In the other form of dialysis, peritoneal dialysis, the blood remains in the body. The doctor inserts a tube into the abdominal cavity, through which a kind of flushing fluid runs. The fluid absorbs dirty substances through the peritoneum and thus purifies the blood. The liquid can be removed after about three hours and is replaced with a new bag of liquid. This happens on average about four times a day. The trained patient performs this dialysis himself, during the day and wherever he or she wants. Between changing the bags there is time and room to move to do other things
The peritoneal dialysis can also take place at night. In that case, the patient connects his hose to a device for an average of eight hours. The advantage of peritoneal dialysis compared to hemodialysis is that you have more energy and more freedom. It has to be done every day, but it can be done at home and even at work. But peritoneal dialysis is usually not possible for more than a few years. Because of long-term changes in the peritoneum and complications such as peritonitis.
Influence on daily life
As you can imagine, dialysis takes a lot of time and energy. People with kidney problems therefore have to organize their lives differently. After dialysis, many people also suffer from the so-called ‘dialysis hangover’. Such a dialysis hangover occurs because the composition of the blood changes completely in a short period of time. This can cause large fluctuations in blood pressure. When (too) much fluid is withdrawn from the blood, this can cause cramps, nausea or dizziness. But that’s not all. Almost everyone suffers from lingering fatigue. This is because dialysis only takes over the purifying effect of the kidney function for only 10-15 percent.
Moreover, few people realize that strict rules of life apply to kidney patients. They should not have too much moisture and should avoid certain foods. It takes a lot of discipline to follow those rules. This is even more true in company, because eating and drinking is often part of the fun. You can work or study as usual, but you have to take into account that you lose a lot of time and energy with dialysis. You can also get pregnant in most cases; dialysis moments will then have to take place more often.
Many people on dialysis wait for a donor kidney. After a successful kidney transplant, dialysis is no longer necessary. The new kidney can return about 50 percent of the original kidney function: that is enough to avoid the need for dialysis. A new kidney can last for decades. Unfortunately, as mentioned, there is a considerable shortage of kidney donors. The average waiting time is almost 2.5 years. Every year people on the waiting list die because a donor kidney comes too late. A transplant kidney can come from someone who has just died or from a living donor. Because there is a great shortage of post-mortem organ donors, nowadays even more kidney transplants are performed each year with kidneys from a living donor than with a kidney from a deceased donor.