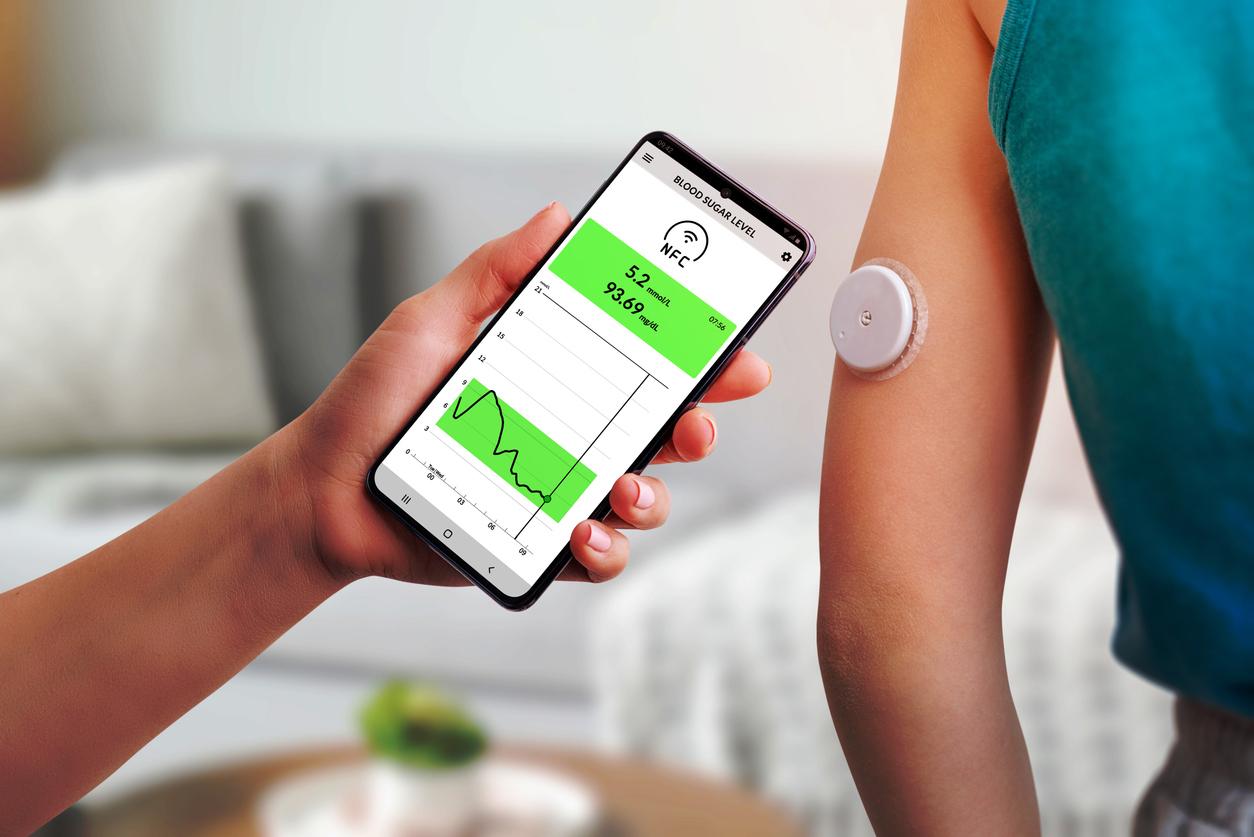
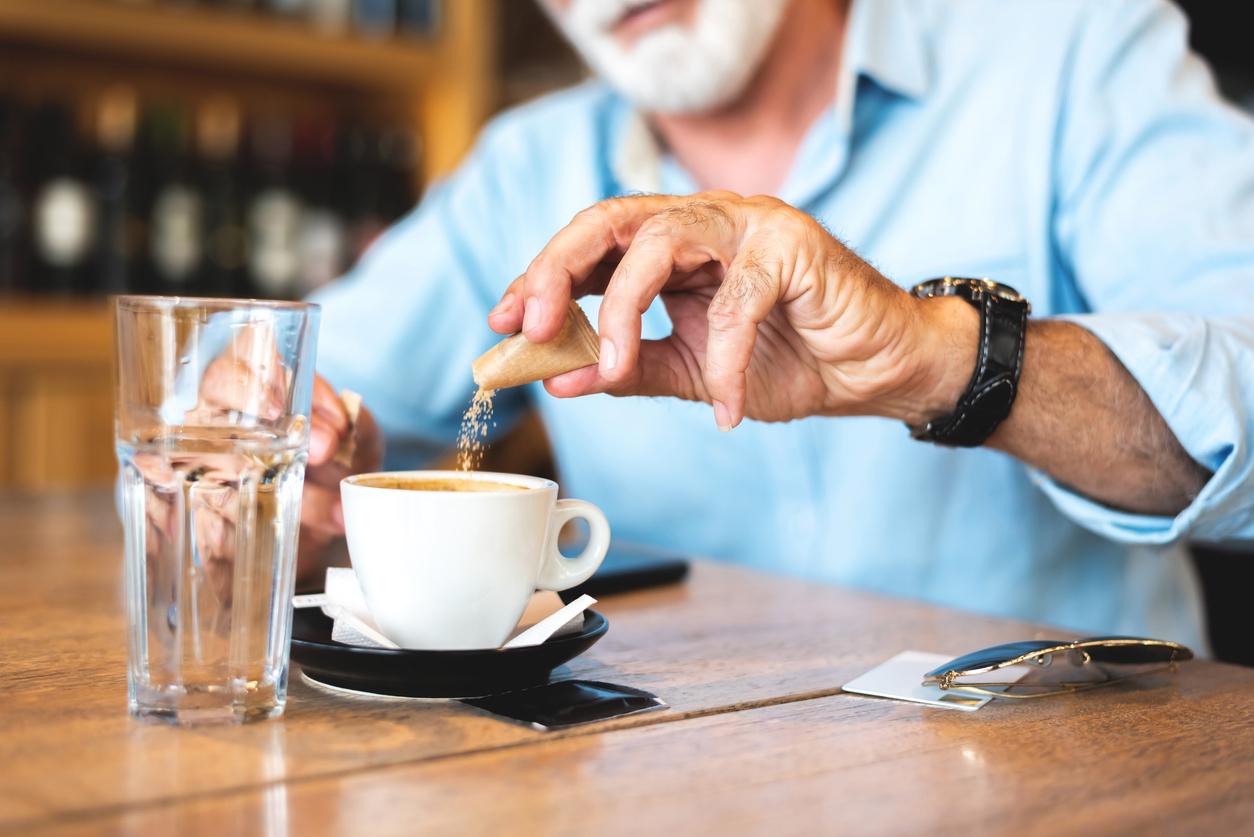
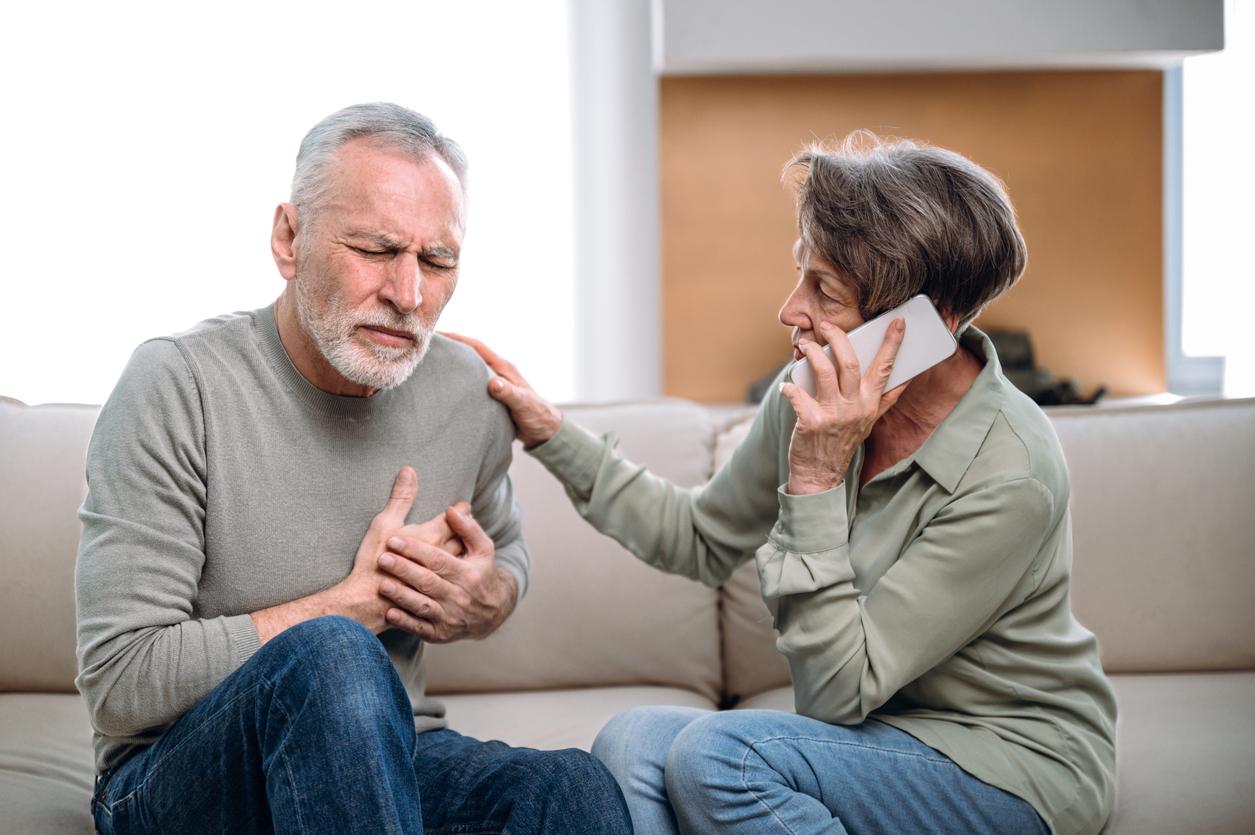
High levels of glucose in the blood can cause blood vessels to contract and increase the risk of a heart attack.

For the first time, researchers at the University of Leicester in Great Britain have shown how high blood glucose levels can cause blood vessels to contract, with potentially dangerous effects on the heart and on blood pressure. arterial. Their results are published in the Journal of Pharmacology.
“We have shown that the level of sugar, or glucose, in the blood changes the functioning of the blood vessels by causing them to contract, more than usual. This leads to higher blood pressure or reduces the amount of blood that passes through vital organs, ”says Dr. Richard Rainbow, lead author of the study.
In France, 50,000 people are victims of heart attacks each year. These take place when a coronary artery becomes blocked. A high level of glucose in the blood could therefore increase the severity of the attacks, in addition to constricting the blood vessels and reducing the irrigation of the vessels.
And according to the researchers, it is not enough to eat a lot of treats to end up in a dangerous situation. A heavy breakfast may be enough to cause problems and increase the risk of a heart attack.
Role of a protein
To arrive at these conclusions, the researchers relied on techniques of electrophysiology, a recording of the electric currents which traverse the muscles. They showed that the cells that make up the blood vessels constrict in the presence of glucose. The higher the glucose level, the greater the contraction.
A protein is at the origin of this phenomenon, kinase C. This plays a role in the contraction of the vessels. When the glucose level increases, the protein becomes more active. Researchers have shown that by inhibiting the functioning of this protein, the vessels appear less contracted in the presence of sugar.
These discoveries could eventually lead to the development of a new therapeutic arsenal. They could give rise to the development of drugs which block the action of the identified Kinase C proteins.
.