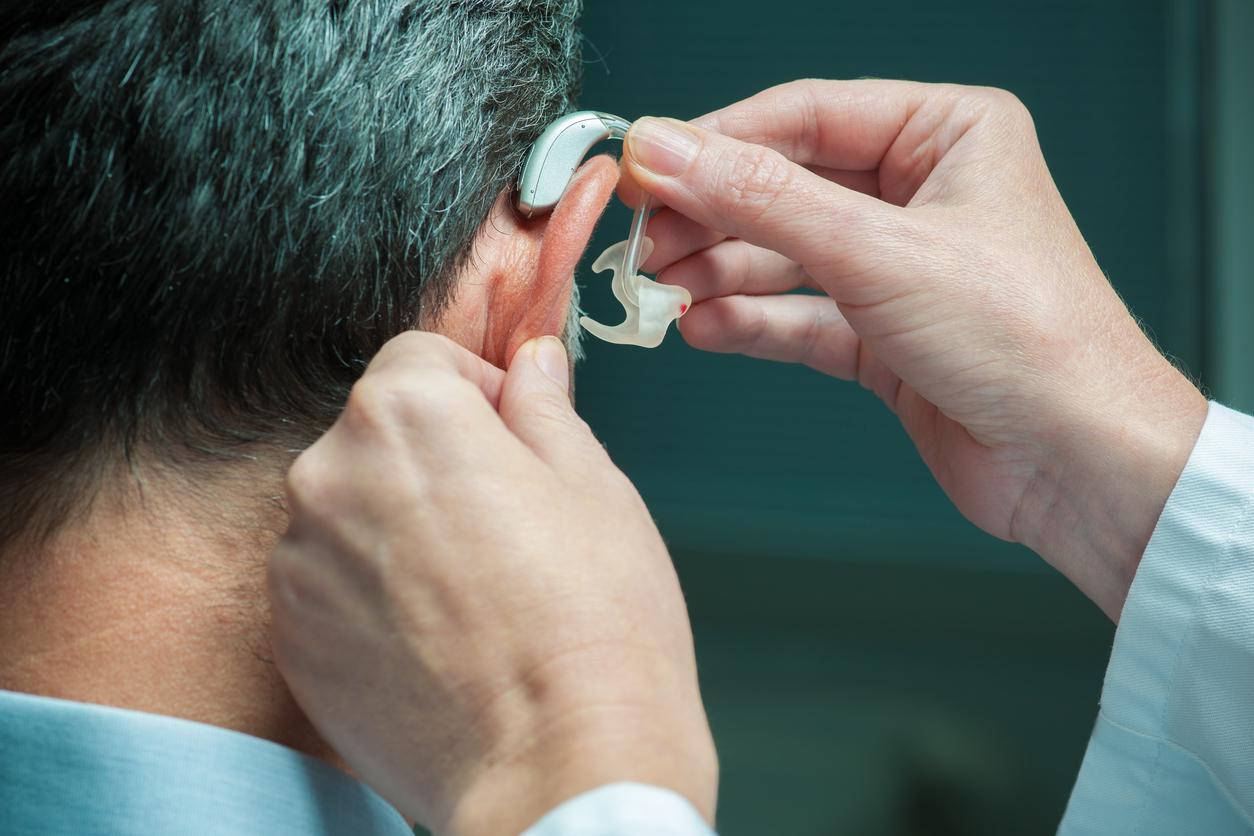
The different parts of the ear can be damaged by, for example, old age, illness, repeated exposure to noise.
In normal hearing, sound waves travel through the ear canal to the eardrum, which will vibrate by the waves. The eardrum is connected to three small bones in the middle ear. The last bone, the stapes, exerts pressure on a fluid-filled chamber in the inner ear called the cochlea or cochlea. This fluid movement bends sensitive hair cells in the cochlea.
By bending the hair cells, an electrical signal is generated, which is sent to the brain. The parts of the ear can be damaged (resulting in hearing loss) from old age, illness, injury or repeated exposure to noise.
There are two types of hearing loss: conductive hearing loss, caused by a mechanical disorder in the ear canal or middle ear, which blocks sound conduction, and inner ear hearing loss, a result of damage of the inner ear, auditory nerve, or auditory nerve pathways in the brain. Conductive hearing loss can be cured in many cases, inner ear hearing loss is usually irreversible.