According to the Sentinelles-Inserm network, gastroenteritis reached the epidemic threshold in ten French regions last week. Across the country, this threshold should be reached in a few days.

Faced with the gastroenteritis virus that hits France every winter, ten metropolitan regions are already on red alert! Thus, for a week, Lorraine, Brittany, Ile-de-France, Poitou-Charentes, Limousin, Champagne-Ardennes, Picardy, Nord Pas-de-Calais, Corsica and finally PACA , have exceeded the established epidemic threshold. And according to data from the Sentinelles-Inserm network, the whole of France should soon follow.
France just below the epidemic threshold
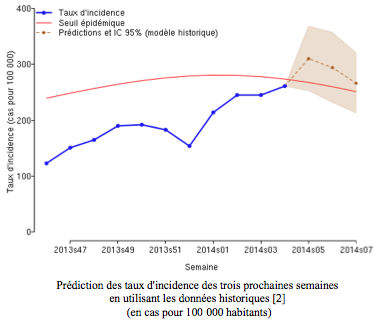
In its last bulletin from 01/20/2014 to 01/26/2014, the Sentinels Network-Inserm estimated that in metropolitan France, last week, the incidence rate of cases of acute diarrhea seen in general practice was 261 cases per 100,000 inhabitants (i.e. 167,500 new cases), an increase compared to previous weeks, and just below the epidemic threshold (274 cases per 100,000 inhabitants).
As proof, last week, two of the four drug classes monitored had reached their alert threshold, confirming the intensification of cases of gastroenteritis in mainland France.
Lorraine remains the most affected region
In detail, at the regional level, the highest incidence rates were observed in: Lorraine (464 cases per 100,000 inhabitants), Ile-de-France (390) and Brittany (390).
Regarding the reported cases, the median age of sick patients was 25 years (from 5 months to 94 years). Men accounted for 51% of the cases. In addition, the clinical pictures reported by the Sentinels network did not present any particular sign of seriousness (0.3% of the cases reported were hospitalized).
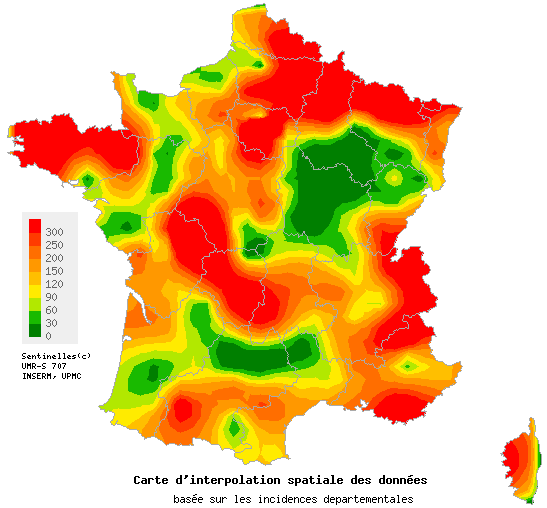
Acute diarrhea Week 2014s04 in number of cases per 100,000 inhabitants
The epidemic threshold expected in a few days
In addition, according to the forecast model based on historical data, the level of acute diarrhea activity should continue to increase and exceed the epidemic threshold, across the country, next week (see graph opposite). .
But, to try to escape the contamination, simple preventive measures exist: wash your hands with soap and water after going to the toilet. This gesture must also be performed several times during the preparation of meals. The same precautions must be taken before and after changing babies and always before and after their meals.
Finally, if it is too late and you are already experiencing the first symptoms (watery stools more than three times a day, sometimes mixed with blood or phlegm, cramps, fever, etc.), avoid being in contact with fragile people such as the elderly, infants, pregnant women or people suffering from respiratory or heart diseases.
.