A team of researchers has developed a new test to quickly diagnose food allergies, particularly to peanuts, with 95% accuracy.

- Researchers have developed a new test to diagnose food allergies, particularly to peanuts, with 95% accuracy.
- This test, called Hoxb8 MAT, simulates the allergic reaction in the laboratory using mast cells and serum from patients, which prevents them from consuming the allergen.
- Faster and more accurate than current methods, it could reduce diagnostic errors and be easily adapted to other types of allergies.
Diagnosing food allergies could become much simpler and safer thanks to a new method developed by researchers at the University of Bern, Switzerland. This innovative test, which reproduces the allergic reaction in the laboratory, has shown diagnostic accuracy “exceptional” in clinical trials in children and adolescents with peanut allergies. The results were published in the journal Allergy.
Simulate the allergic reaction without consuming the allergen
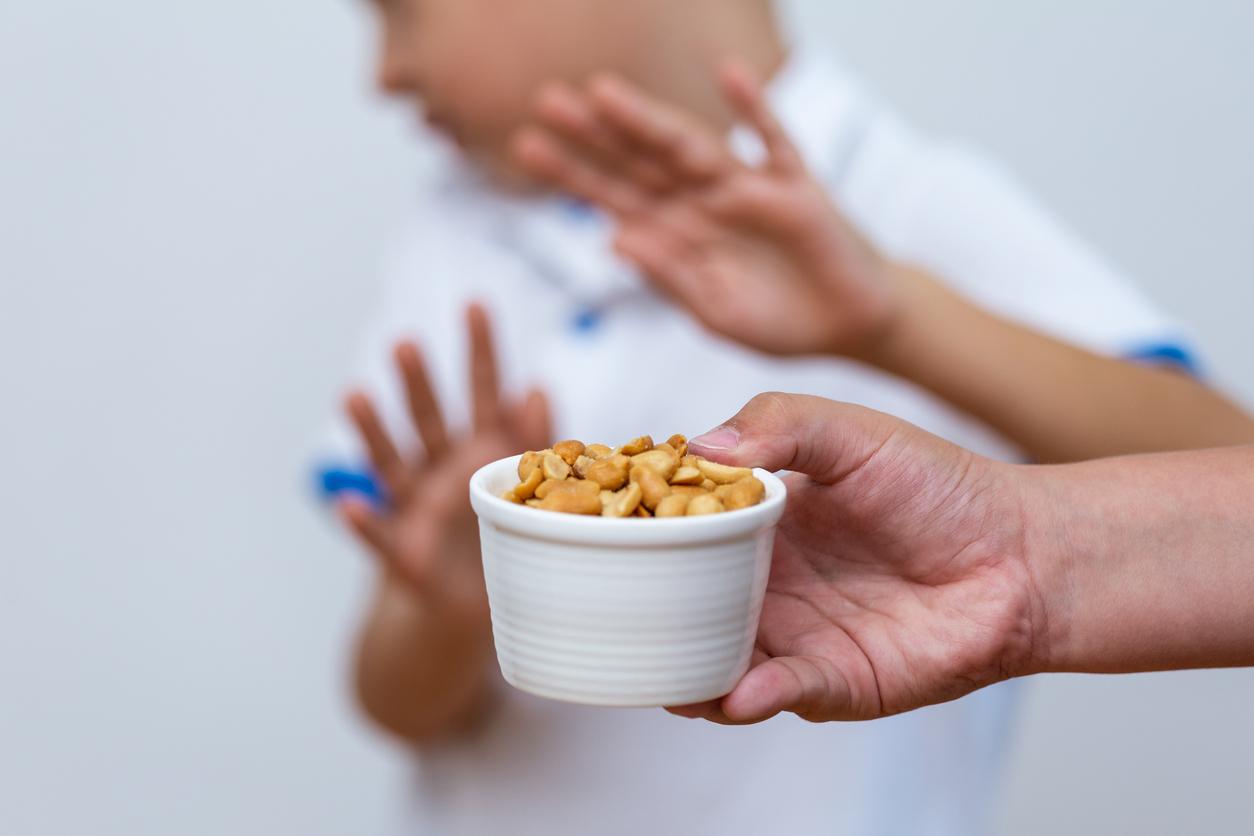
Food allergies represent a major public health problem, affecting up to 10% of the population in some countries, mainly young children. Peanut allergy is one of the most common and deadly. Current tests, where patients consume the allergen under medical supervision, remain the gold standard for establishing a diagnosis, but they are risky and complex to implement. As for skin or blood tests, used in addition, they are not precise enough and lead to diagnostic errors.
The new test, developed in 2022, is based on the activation of mast cells, immune cells involved in allergic reactions. Called “Hoxb8 mast cell activation test” or Hoxb8 MAT, it involves culturing mast cells in the laboratory, then putting them in contact with the blood serum of allergic patients. The mast cells, after binding to the antibodies present in the serum, are stimulated by the allergen – in this case peanut extract – and react as if they were in the patient’s body. This technique makes it possible to simulate the allergic reaction without the patient needing to consume the allergen.

95% diagnostic accuracy for peanut allergy
Experimented on serum samples from 112 children and adolescents with peanut allergies, the test showed “a diagnostic accuracy of 95%”greatly outperforming other existing clinical methods, according to a press release. It was not only more precise, but also “more representative of the true allergic reaction” of the patient.
The great advantage of the Hoxb8 MAT test lies in its speed and simplicity. “All samples could be processed within two days”explain the researchers. Not to mention that this new method reduces false negatives and is based on easily storable serum samples, making it easier to implement on a large scale.
Although the study focused on peanut allergies, the authors believe this technology could be easily adapted to other types of allergies.