How to reconcile the desire for children and chronic illness?
- Endometriosis is a chronic disease that can lead to fertility problems.
- Diagnosis and treatment of endometriosis have made significant progress, but challenges remain.
- Comprehensive and personalized care is essential to improve the quality of life of women suffering from endometriosis and infertility.
Endometriosis, a chronic disease that affects many women, is often associated with fertility problems. While the link between these two conditions is well established, the exact mechanisms remain partly unknown.
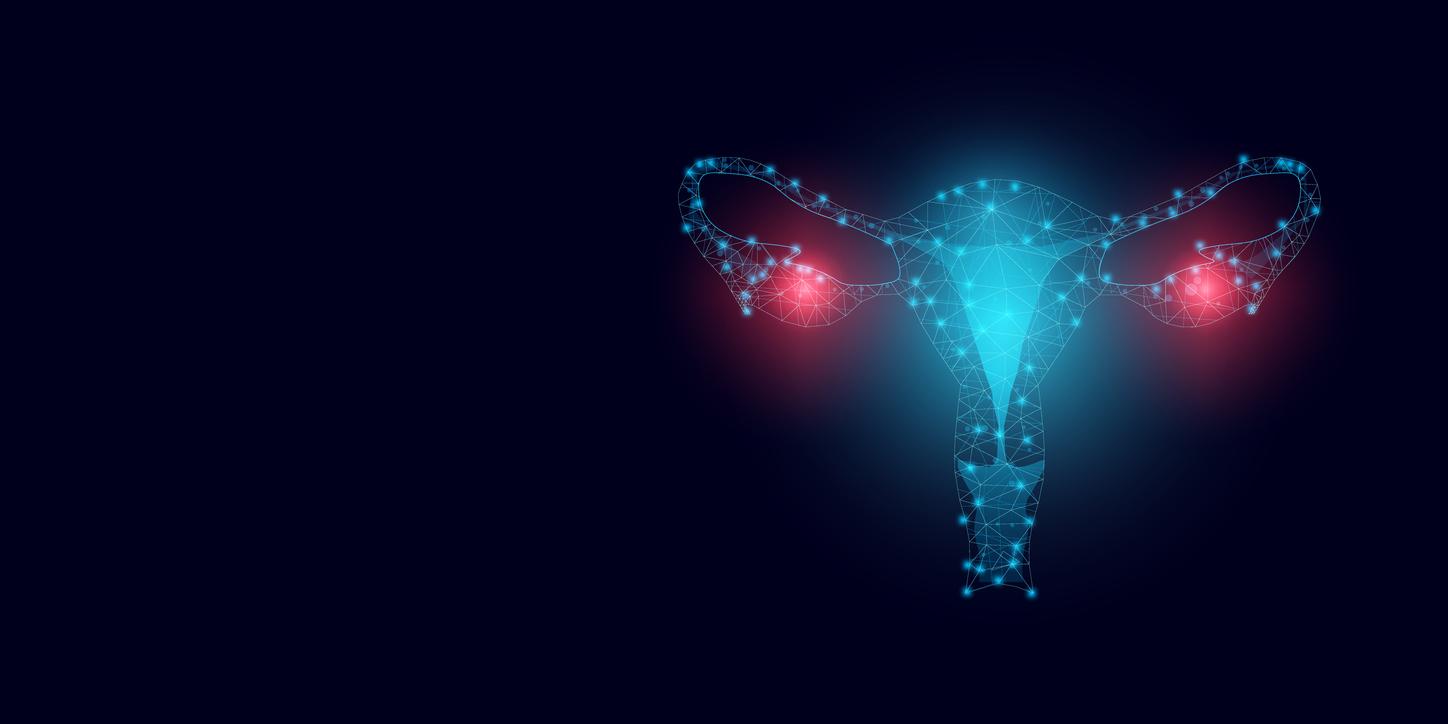
Endometriosis is characterized by the presence of tissue similar to that which lines the inside of the uterus (the endometrium) outside of it. These endometriosis foci can develop in the ovaries, fallopian tubes, peritoneum or other pelvic organs. These tissues, under the influence of female hormones, tend to bleed and cause inflammation, which can lead to chronic pelvic pain, heavy and painful periods, as well as digestive problems.
Endometriosis and infertility: a complex link
The link between endometriosis and infertility is multifactorial. Several mechanisms can explain this association:
• Blocked fallopian tubes : Adhesions related to endometriosis can obstruct the tubes, preventing the egg and sperm from meeting.
• Altered egg quality : Chronic inflammation associated with endometriosis can impair egg quality and reduce the chances of fertilization.
• Difficulties with embryo implantation : Endometriosis foci can change the environment of the uterus and make implantation of the embryo more difficult.
• Pelvic pain : Chronic pain associated with endometriosis can have a significant psychological impact and affect couples’ quality of life, making sexual intercourse difficult.
Advances in the diagnosis and treatment of endometriosis
In recent years, significant progress has been made in the diagnosis and treatment of endometriosis:
• Improving medical imaging techniques : Pelvic MRI allows endometriosis lesions to be visualized with great precision, thus facilitating diagnosis.
• Development of new medical treatments : New drugs, such as angiogenesis kinase inhibitors (AKIs), are being investigated to reduce the growth of endometriotic lesions and improve symptomatology.
• Minimally invasive surgery : Surgical techniques have improved considerably, allowing endometriosis lesions to be removed more precisely and less invasively.
• Medically assisted procreation (MAP) : ART techniques, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), make it possible to circumvent infertility problems linked to endometriosis.

The challenges to be met
Despite these advances, many challenges remain:
• Early diagnosis : The diagnosis of endometriosis often remains late, due to non-specific symptoms and a lack of awareness among health professionals.
• Personalized treatments : There is no single treatment for endometriosis, and management must be individualized based on the severity of the disease and each woman’s symptoms.
• Prevention : The exact causes of endometriosis remain unknown, making it difficult to implement effective preventive measures.
• Psychological support : Endometriosis can have a significant impact on women’s quality of life and requires appropriate psychological support.
Endometriosis is a complex disease that requires multidisciplinary care. Research continues to advance to better understand the mechanisms of this disease and develop new therapeutic strategies. Women suffering from endometriosis and infertility must benefit from appropriate medical and psychological support to improve their quality of life and achieve their motherhood project.