Nearly 1,300 cases of dengue fever have been confirmed in the north, west and south of Reunion since January 1, 2018, Public Health France announced on Thursday. What is dengue fever? And what are the preventive measures?

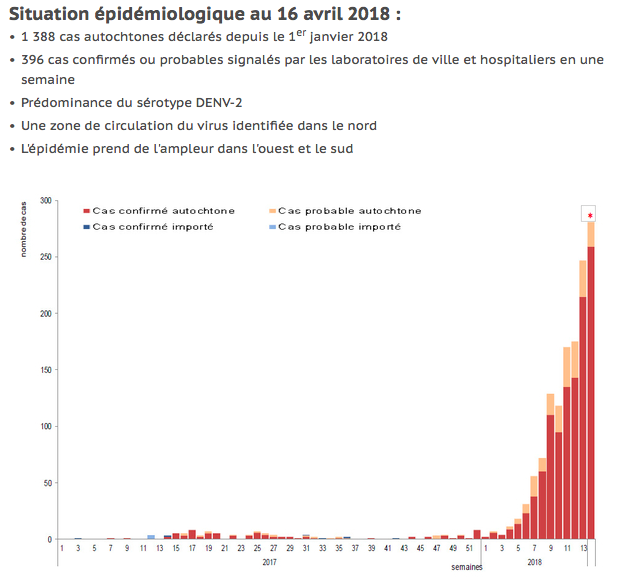
“After an unusual circulation of the virus during the austral winter of 2017, the number of dengue fever cases has gradually increased (in Reunion, editor’s note) since the start of 2018, with an intensification in February”, announces this Thursday Public Health France. Nearly 1,300 cases have been identified in the north, west and south of the island.
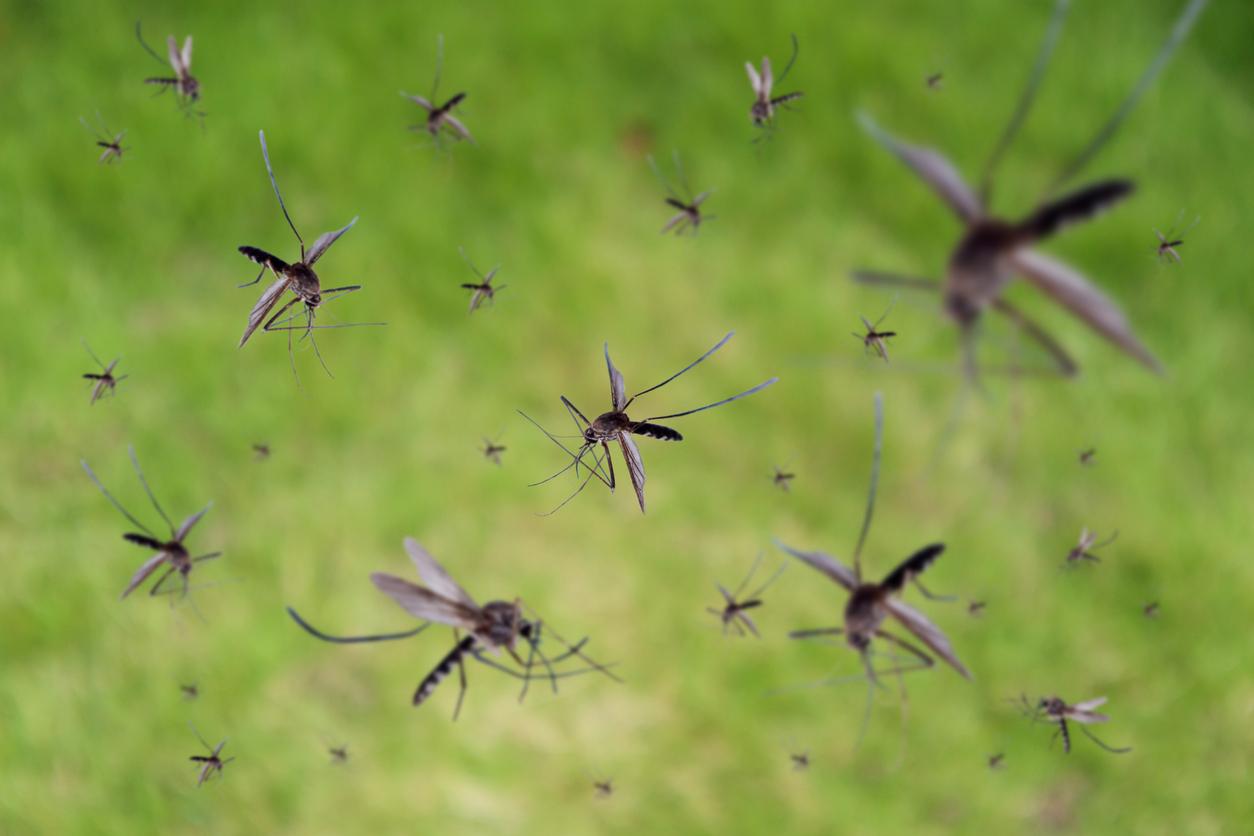
Dengue fever, also called “tropical flu”, is a tropical haemorrhagic fever linked to an arbovirus, transmitted by a mosquito of the genus Aedes. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates the number of annual cases worldwide at 50 million, including 500,000 cases of “haemorrhagic” dengue, i.e. which are fatal in more than 2.5% of cases. . Dengue fever is initially present in tropical and subtropical areas of the world.
Escalation risk
On March 26, 2018, the prefect of La Réunion declared the level “low intensity epidemic” against arboviruses. But the epidemic could intensify in the weeks to come, in particular because few people are immune to it: “only 3.1% of blood donors, tested for dengue in 2008, had antibodies against the virus”, specifies Public Health France.
Two forms of dengue fever
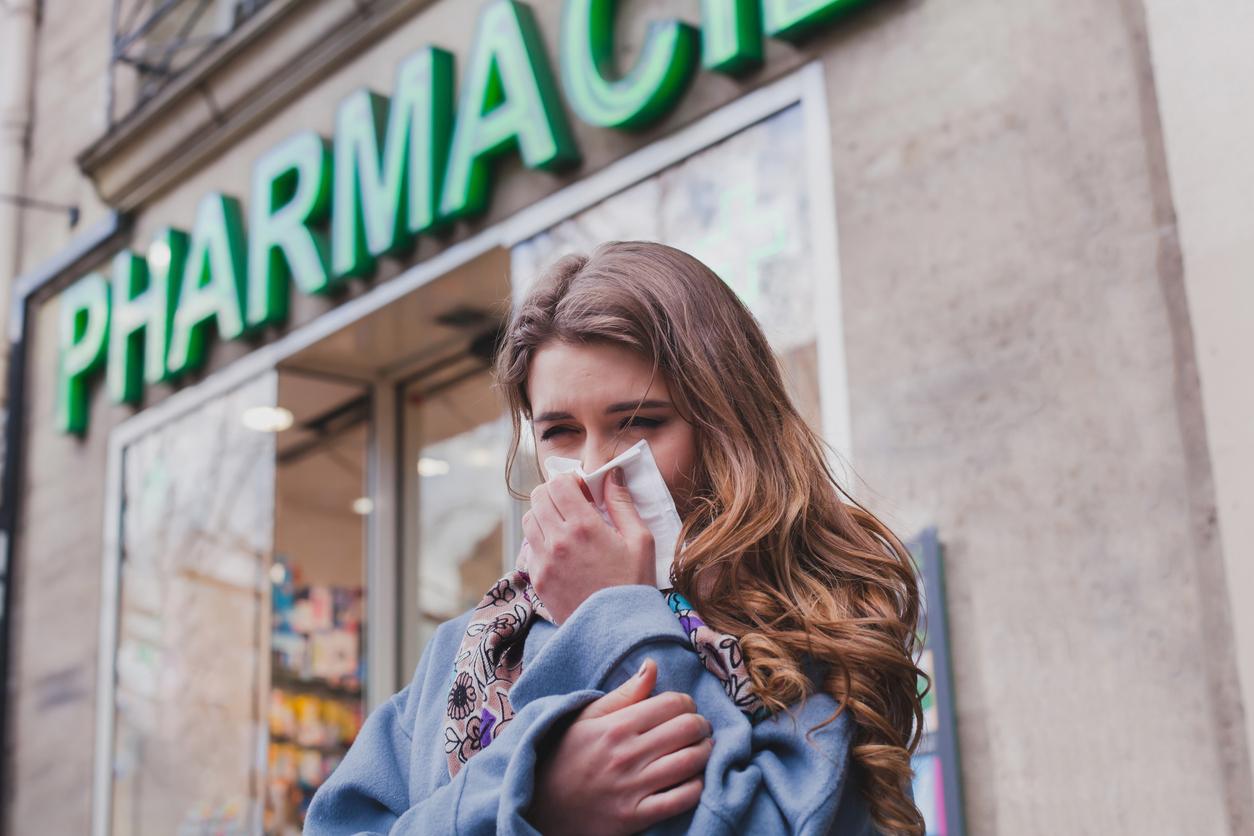
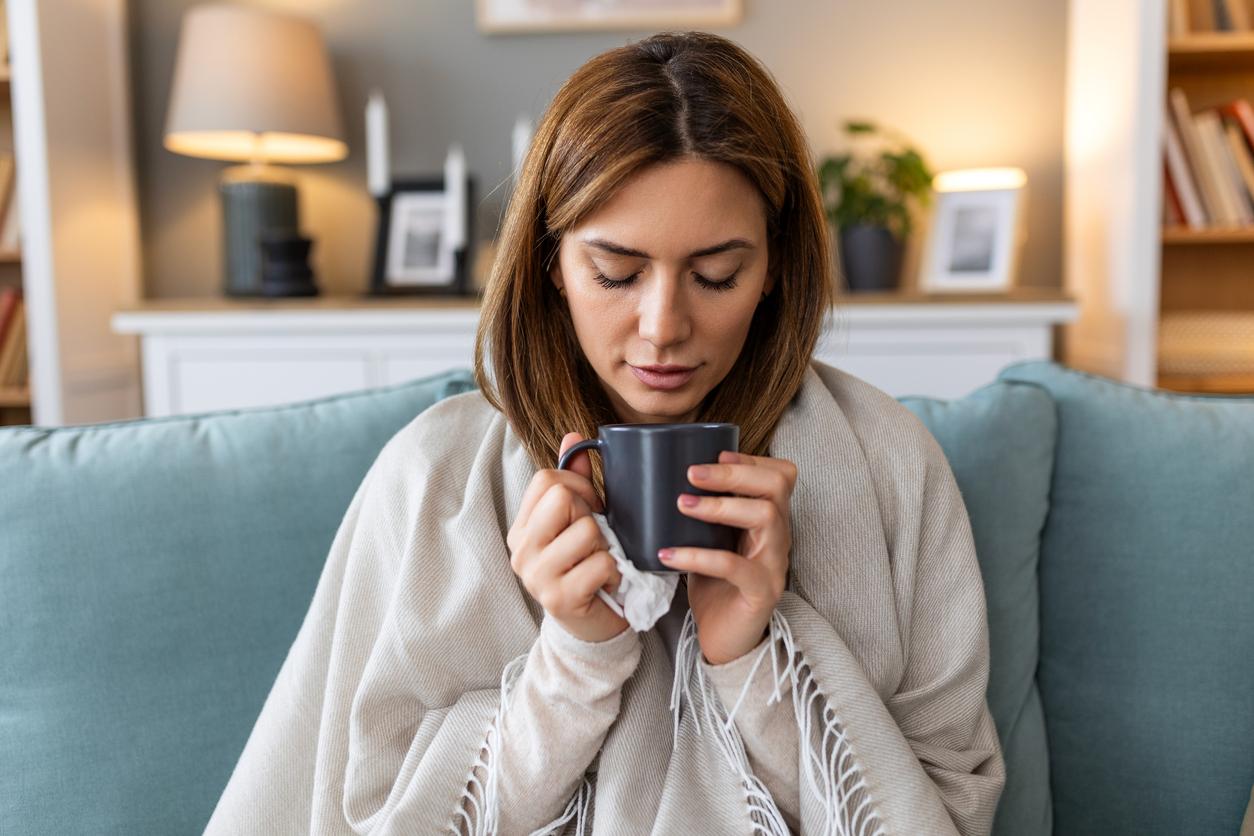
classic dengue fever manifests itself suddenly after 2 to 7 days of incubation by a high fever with headache, nausea, vomiting, joint and muscle pain and a rash like that of measles. A brief remission is observed after 3 to 4 days, then the symptoms intensify, conjunctival hemorrhages, nosebleeds or bruises may occur, before regressing rapidly after a week and a convalescence which may last Several weeks.
dengue hemorrhagic fever which represents approximately 1 to 2.5% of cases, is extremely severe: the fever persists and multiple gastrointestinal, cutaneous and cerebral haemorrhages occur. In children under fifteen in particular, a state of hypovolemic shock can set in, cause abdominal pain and cause death if the patient is not resuscitated. There is no specific treatment for the virus.
Preventive measures to adopt
Public Health France recalls that it is necessary “to eliminate water containers around your home and waste that promote breeding sites (empty saucers, small containers, respect waste collection days, etc.). Protect yourself mosquito bites (diffusers, repellents, covering clothing, mosquito nets, etc.). Consult your doctor if symptoms of the disease appear and continue to protect yourself from mosquito bites”.
.