According to the Institute for Public Health Surveillance, the French overseas departments, Nord-pas-de-Calais, Haute-Normandie and Picardy have the highest rates of premature death linked to cardiovascular pathologies.

With nearly 15,000 annual deaths, cardiovascular disease is the third leading cause of premature death in our country. If the level of death has fallen by nearly 22% over the last decade, significant regional disparities persist, indicates a study published today in the Weekly Epidemiological Bulletin (BEH) of the InVS.
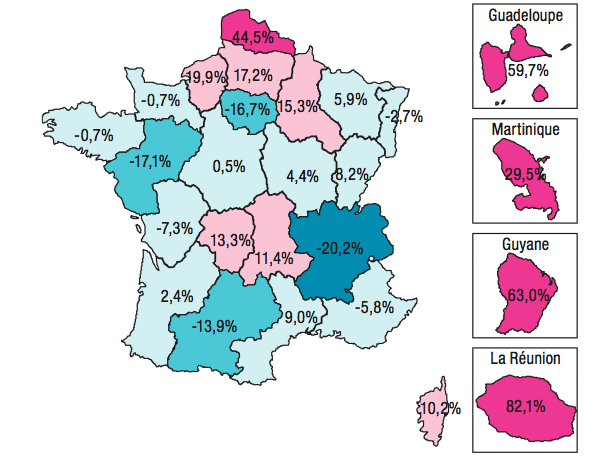
According to the analysis of the national causes of death databases for 2008-2010, for all cardiovascular pathologies, the French average is 25.7 premature deaths. Compared to this national level, the highest differences are observed in the Nord-pas-de-Calais (+ 44.5%), Haute-Normandie (+ 19.9%) and Picardy (+ 17.2%) regions ).
In the overseas departments, the rates of premature cardiovascular excess mortality are soaring: from + 29.5% in Martinique to 82.1% in Reunion. Conversely, several regions show rates lower than that of the national average, this is the case of Rhône-Alpes (-20.2%), Pays-de-la-Loire (-17.1%) , Ile-de-France (-16.7%) and Midi-Pyrénées (-13.9%).
Social determinants
For the authors of the study, its strong regional variations are directly linked to the unequal distribution of risk factors in our territory (age, income level, arterial hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, obesity, tobacco, alcohol, etc.) coupled with the variability of the health care offer and the quality of care depending on the region.
Geographical differences in mortality are also linked to the impact of social inequalities depending on the region. Thus, Nord-pas-de-Calais, Picardy, Champagne-Ardenne, Lorraine, Haute-Normandie, Languedoc-Roussillon and the overseas departments, which have the highest rates of beneficiaries of complementary universal health coverage (CMU-C), also present an excess premature cardiovascular mortality.
Regional levels of premature cardiovascular mortality
compared to the national average
Source : InVS
.