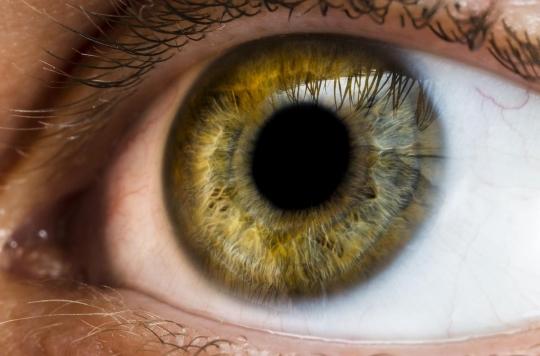
The larger the pupils, the higher the cognitive abilities.
- The relationship between pupil size and cognitive abilities is the same regardless of age.
- This relationship would be explained by the activity of the locus coeruleus, a cerebral area which would ensure the connection between cerebral regions distant from each other so that they can work together.
The eyes are the only visible part of the brain. Consequently, observing them makes it possible to give indications, as certain researchers have recently shown, who have suggested that the size of the pupils informs about the level of confidence of the interlocutor. In new research, published March 10 in the journal Science DirectAmerican scientists from Georgia Institute of Technology argue that the pupils could also determine the intellectual level.
A first study with the same conclusions in 2016
This isn’t the first time researchers have investigated the correlation between eyes and intelligence. Already in 2016, they revealed, after conducting reasoning, attention and memorization tests, that people with larger pupils have higher cognitive abilities. They even found that the difference in pupil size between the people with the highest test scores and those with the lowest scores was large enough to be detected with the naked eye. After publishing their results in the journal Cognitive Psychology, their work has been widely criticized. Surely, the researchers launched new experiments to prove their results.
For this new work, the researchers recruited more than 500 people between the ages of 18 and 35. They used a eye tracker, or eye tracker, to measure the diameter of the pupils. This tool captures the reflection of light off the pupil and cornea using a high-precision camera to determine where and how a person is looking. The first measurements were made while participants stared at a blank computer screen for a few minutes. Then, the other measurements were taken while the participants conducted a series of cognitive tests. The researchers were careful to keep the light low so that the light didn’t cause their pupils to narrow. These tests aimed to measure three different components of intelligence: fluid intelligence, or the ability to reason when faced with new problems; working memory, the ability to remember information over a period of time; and attention control, the ability to stay focused despite possible distractions and interference.
The locus coeruleus, a key brain area
The results suggested that the larger the pupil the participants had, the higher their score on the fluid intelligence test and attention control. The correlation with working memory was less marked. Furthermore, the researchers found that pupil diameter decreased with age but that the relationship between pupil size and cognitive abilities was the same regardless of age.
For the researchers, these results validate those of their previous study and consolidate their suggestion of the link between pupil size and intelligence. According to them, this would be linked to the activity of the locus coeruleus, a subcortical nucleus of the brain, located in the brainstem. This area contains a very large number of neural connections with the rest of the brain and would ensure the connection between cerebral regions far from each other so that they can work together. This coordination involves the release of norepinephrine, a substance that acts both as a neurotransmitter and as a hormone. This regulates perception, attention, learning and memory. Moreover, this process is also involved in certain emotions (stress, fear, anxiety) or in the sleep-wake cycle.
The size of the pupils would reveal better regulation and coordination of cerebral activity by the locus coeruleus. This better coordination being an indicator of improved cognitive performance, it is through this that the size of the pupils would be indicative of fluid intelligence and attention control. The researchers stress that further studies are needed to clarify this link.
.