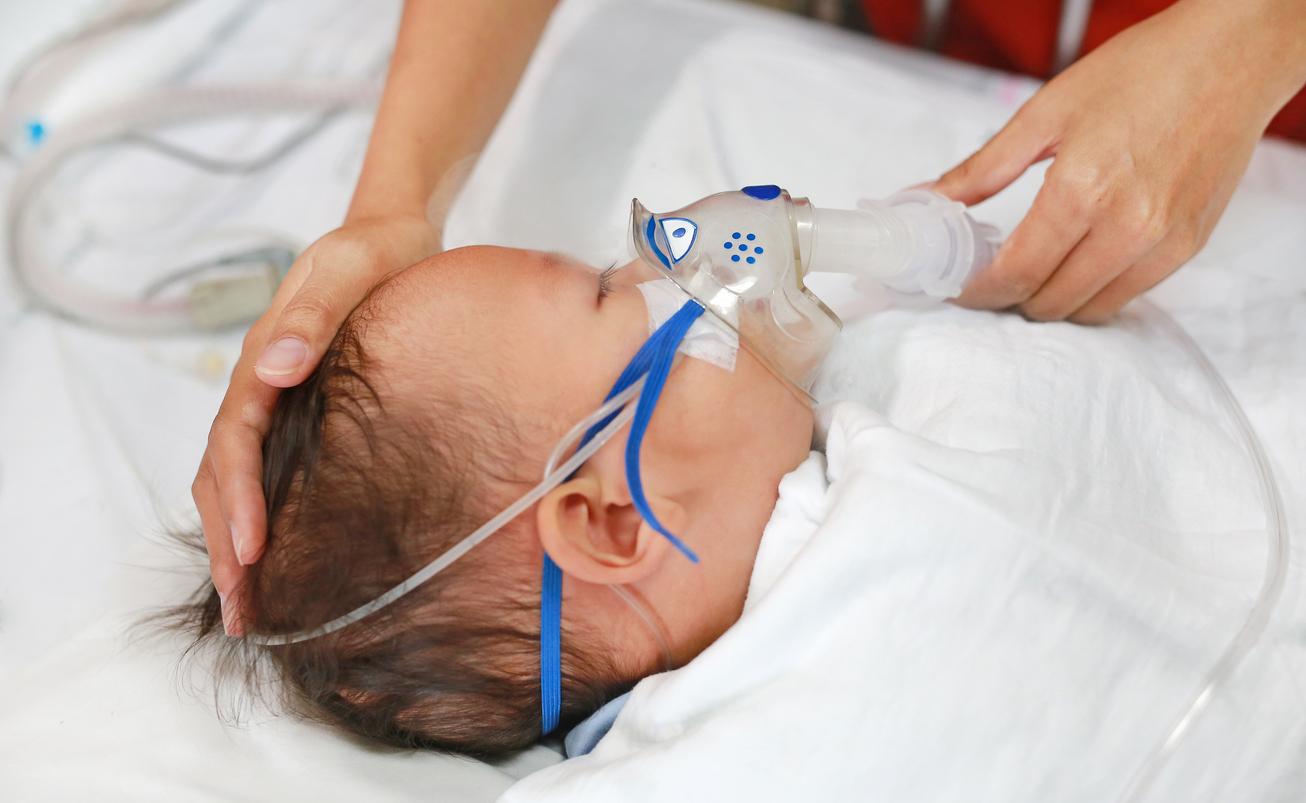
The new preventive treatment against bronchiolitis is available from this Friday, September 15 for infants born after February 6, 2023.
- All infants born after February 6, 2023 will be able to receive preventive treatment against the bronchiolitis virus.
- This treatment, called Beyfortus, must be administered to infants during their first season of circulation of the bronchiolitis virus.
- Each year, 30% of infants under 2 years old are affected by bronchiolitis.
For the first time, the Beyfortus is available in France. This is a preventive treatment against the main virus responsible for bronchiolitis, the Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV). The serum, administered as a single injection into the thigh muscle, is intended for infants born after February 6, 2023.
Preventive treatment against bronchiolitis
The active substance in this treatment is nirsevimab, a monoclonal antibody. This one “binds to a protein called “F protein” on the surface of RSV, noted the European Medicines Agency (EMA). When nirsevimab binds to this protein, the virus becomes unable to enter the body’s cells, particularly those in the lungs. This helps prevent RSV infection.”
Beyfortus is the first preventive treatment against bronchiolitis authorized for all infants, and not just those at risk as was the case with the other existing treatment, Synagis. According to High Authority for Health (HAS)“the duration of protection conferred by nirsévimab (Beyfortus®) is at least 5 months” and it can be administered to “newborns and infants during their first season of RSV circulation”.
For this year, only infants born after February 6, 2023 will benefit if they are “considered not exposed to RSV during the previous epidemic season”. Finally, Beyfortus must be administered before the start of the epidemic.
Bronchiolitis, a risky disease for infants
“Bronchiolitis occurs in the form of epidemics in autumn from October and in winter, can we read on the website of health insurance. It frequently affects infants aged 2 to 8 months. Each year in France, 30% of infants under 2 years old are affected.”The symptoms are difficulty breathing – rapid, wheezing – and coughing.
In general, bronchiolitis is a benign illness. However, in epidemic periods, this is the 1st cause of hospitalization and referral to pediatric emergencies. Certain infants are also at greater risk of serious illness: those less than two months old, born prematurely, with fragile lungs, suffering from heart disease or an immune deficiency, exposed to passive smoking, etc.
“This season (2022-2023), the epidemic was characterized by very high intensity, almost twice higher than the average values of reference epidemics“, note Public Health France. There were 73,262 visits to the emergency room for bronchiolitis and 26,104 hospitalizations after visits to the emergency room for bronchiolitis.
This new preventive treatment is therefore a “a major breakthrough”, according to the Minister of Health, Aurélien Rousseau.