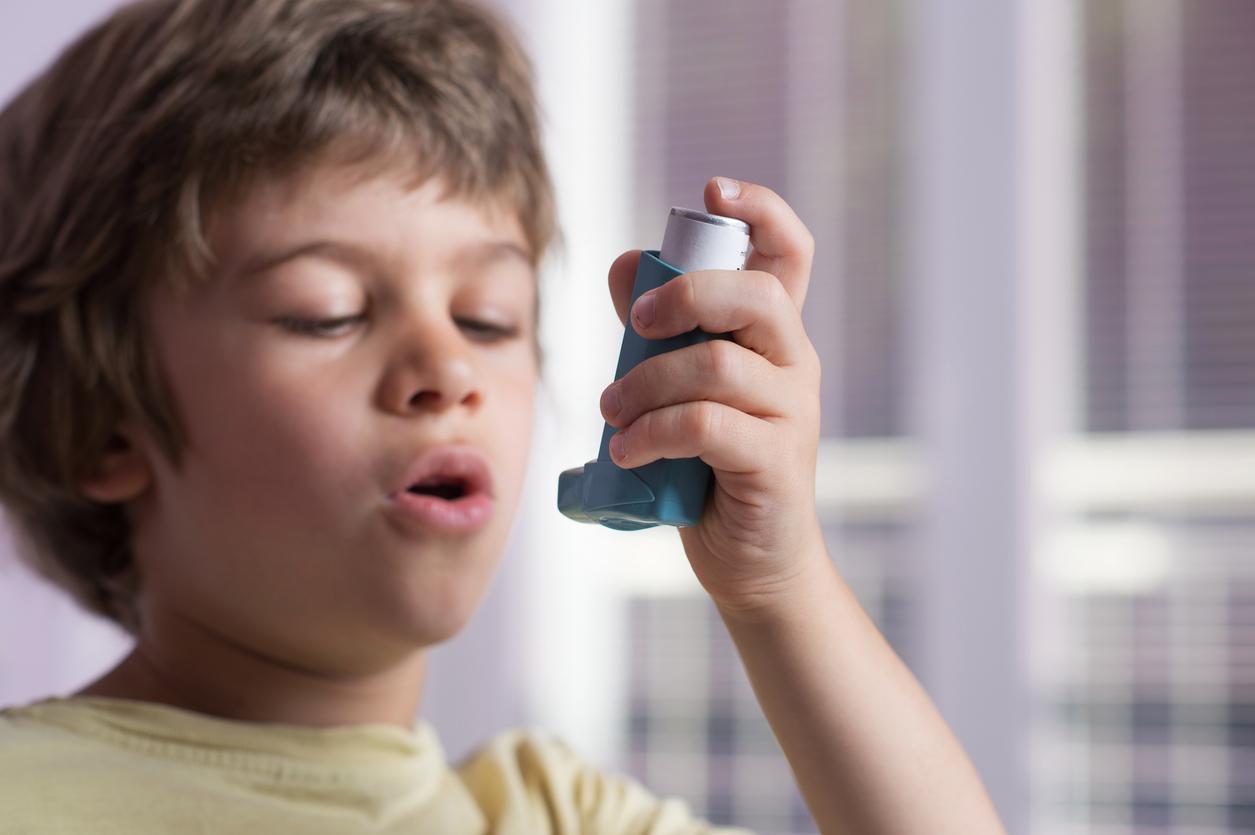
The Swiss laboratory Roche is working on the development of a drug for moderate to severe asthma, which fights this respiratory disease in a new way. This medicine, quilizumab, works by inhibiting an inflammatory protein called immunoglobulin E (IgE) linked to asthma. The drug simply prevents it from producing new inflammatory molecules.
A new clinical study has been published in the journal Science Translational Medicine showing that the drug can be administered to people with asthma safely. In addition, a single dose of the drug was sufficient to reduce respiratory discomfort for four weeks.
Research is still in its early stages and the drug still has a long way to go before it is administered. But these initial results are encouraging because quilizumab has an innovative approach that is unlike any existing drug for treat asthma.
Some people with asthma or certain allergies, such as hay fever, have higher levels of an antibody protein called immunoglobulin E (IgE) in their blood. The IgE protein is found on the surface of some cells and causes them to react in the presence of allergens such as pollen and dust mites. The result is inflammation of the airways and asthma symptoms such as wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath.