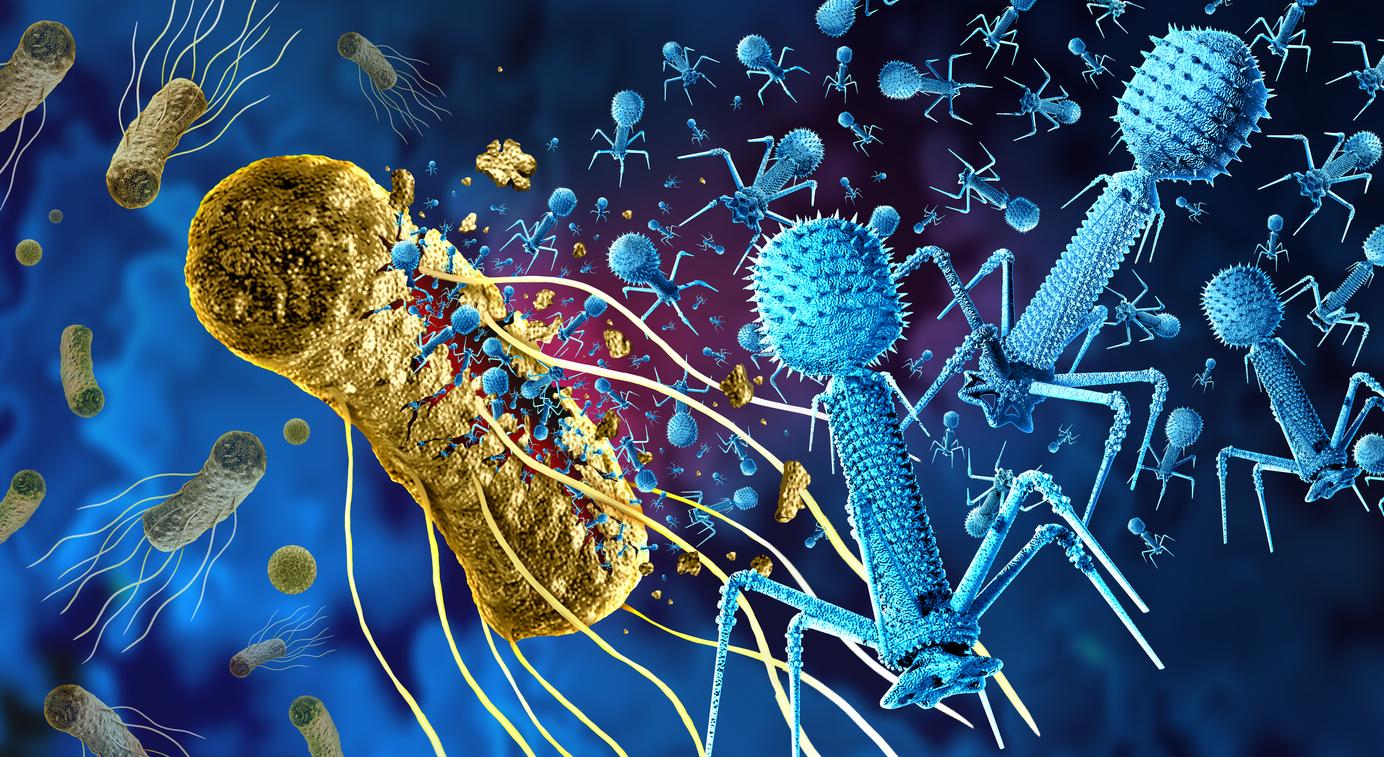
An ancestral care technique, phage therapy, came to the end of a staphylococcus aureus which threatened a French patient with a leg amputation.
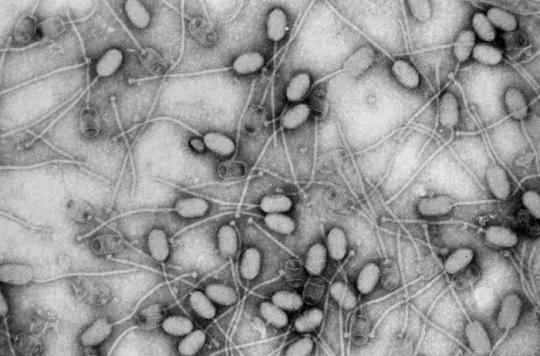
At a time when resistant bacteria are decimating Europe, the story of Christophe, told in The Parisian, is instructive. Displacing antibiotics that have become ineffective, phage therapy came to the end of a golden staphylococcus which threatened the leg of this fifties.
An ancestral treatment technique
“As a result, the cocktail of antibiotics that I received continuously no longer worked; it slipped on me like water on an oilcloth”, says the patient, struggling with an open wound since the age of nine. . After 49 operations, a doctor finally talks to him about amputation. Desperate, Christophe then hears about phage therapy. Practiced in particular in Georgia, this ancestral treatment technique consists of using bacteriophage viruses (also simply called phages) to treat certain infectious diseases of bacterial origin.
Treated on the spot, it will take barely 15 days for Christophe to get rid of his staphylococcus aureus and gradually regain the use of his leg. “It took me a long time to land, to lean on it, to tell myself that I could go out with my dogs, watch the little birds sing”, says the ex-patient, who is discovered in passing five bacteria multiresistant.
“Growing Phages”
“We must develop phages at all costs. Sorry, but today we are in deep shit, the bacteria are becoming super-strong,” he concludes. An objective that Christophe intends to achieve thanks to his new association Phages without borders. About twenty patients resistant to antibiotics have already left for Georgia via his intermediary.
While in 2014 a report on antibiotic resistance predicted that by 2050, antimicrobial resistant infections could become the leading cause of death worldwide, causing 10 million deaths per year, a new study published in the review The Lancet Infectious Diseases makes an equally alarming finding. According to researchers, antibiotic-resistant bacteria caused the death of 33,000 people in 2015 within the European Union. “The burden of these infections is comparable to that of the flu, tuberculosis and HIV/AIDS combined,” the scientists worry.
Design alternative treatments
Hence “the urgency of taking antibiotic resistance into account as vital health data for patients and the need to design alternative treatments for patients who have other diseases and who are vulnerable due to weakened immune defenses or age”.
.