The skin is a reflection of your microbiota, it “represents” your general condition. You are depressed, stressed, tired: it will show on your skin. As well as the way you eat… If it is often said that drinks influence the state of your mine, this is also the case for what you eat. Dermatologist Marie-Estelle Roux answers our questions.
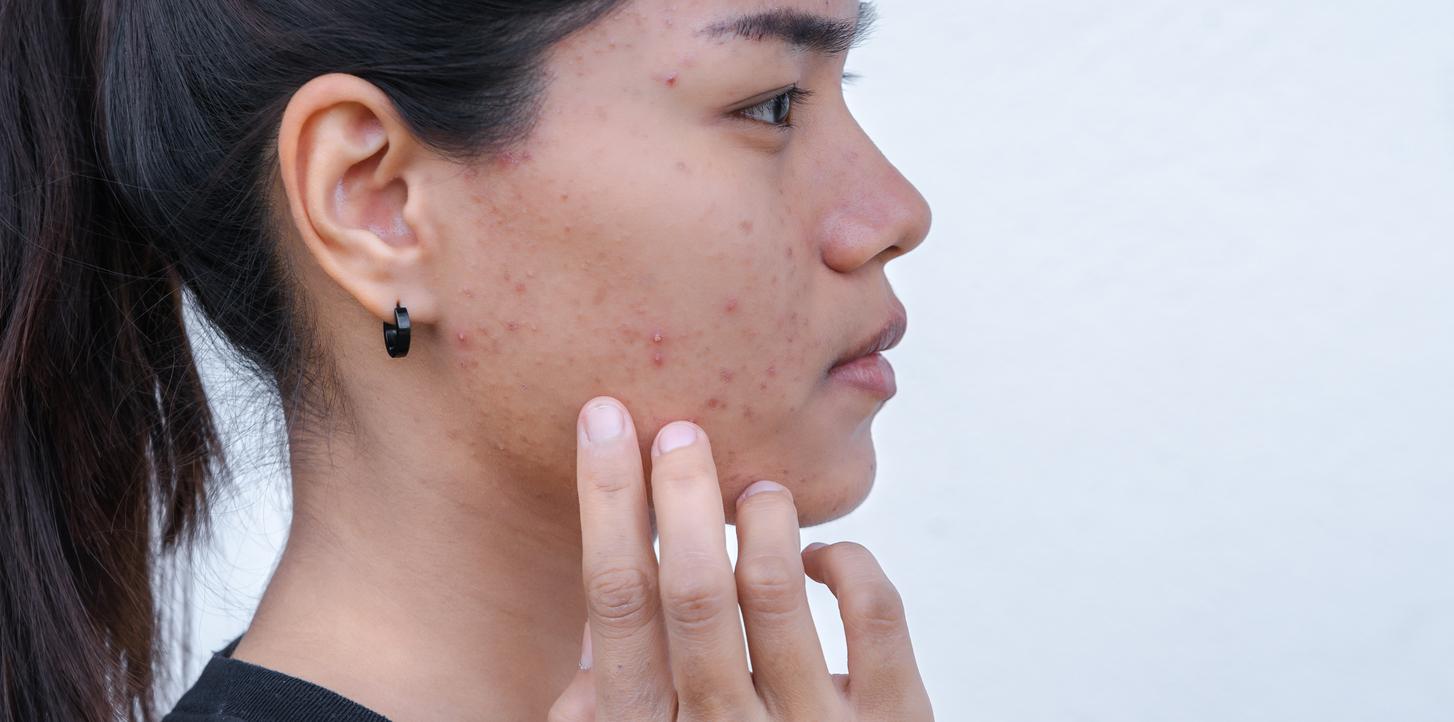
Oily skin with spotty tendency: foods to avoid?
What should be limited as much as possible is sugar consumption in generalor all foods with a high glycemic index, i.e. foods that go trigger rapid and significant insulin secretion, insulin being the hormone which makes it possible to store sugar. Foods with a high glycemic index are essentially refined sugars (those added to preparations), and refined cereals (white flours). It is also not recommended to drink milk in large quantities, and alcohol which are acne triggers.
Eating fatty, sweet, salty… An impact on the skin or a myth?
Food and skin are intimately linked. So a bad diet, an unbalanced diet, will inevitably have a negative influence on the skin. But it’s not a small gap from time to time that will change the condition of the skin. It’s more the way we eat in general, and on the long term.
Are oleaginous dried fruits really good for the skin?
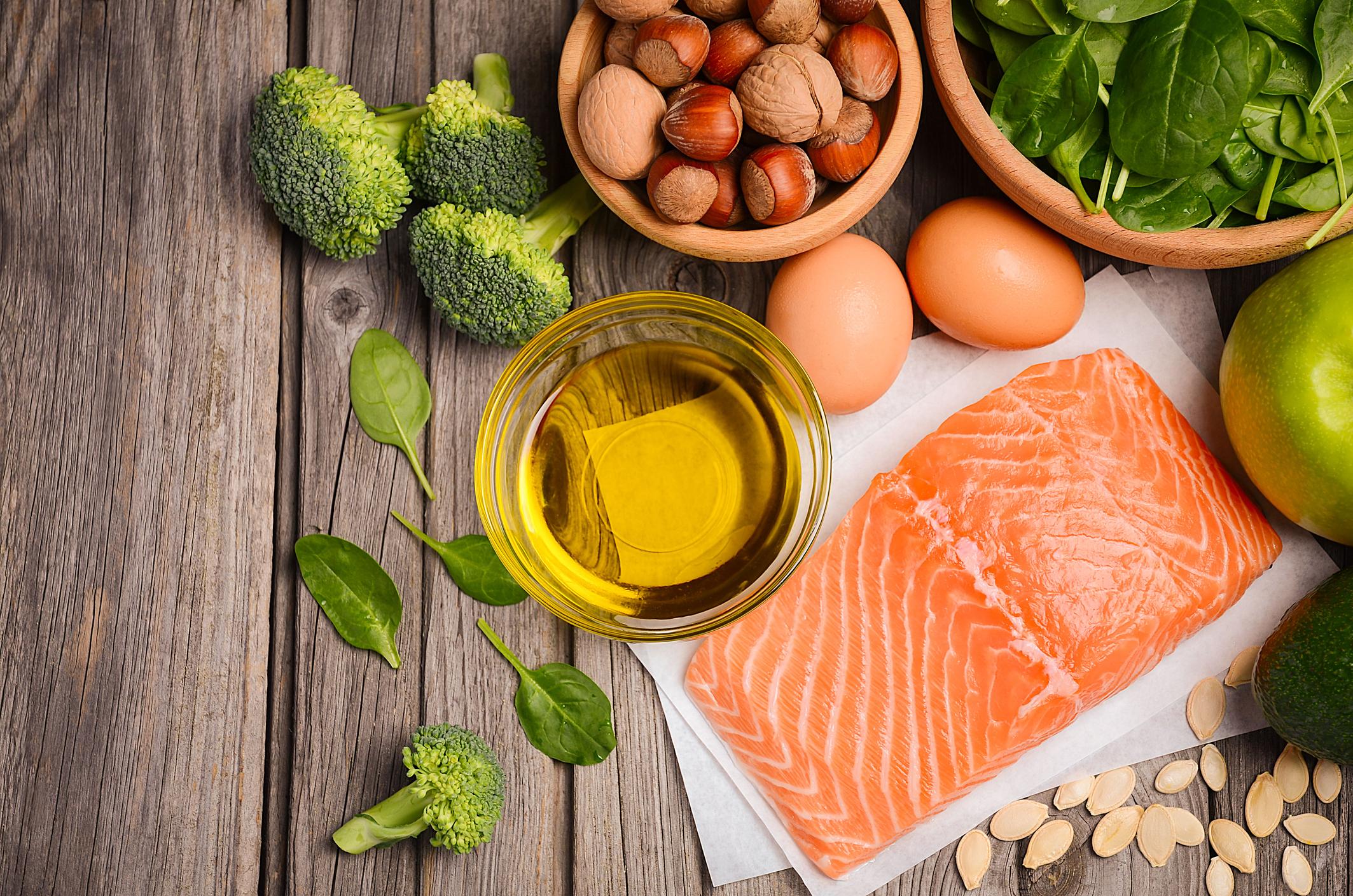
The oleaginous dried fruits are very low in sugar and rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids, in particular omega 3 and omega 6, which are good for health. They have a moisturizing and anti-inflammatory effect on the skin.
Are fruits good for the skin?
Fresh fruits are good for health in general, and for the skin in particular, we can only recommend them. In effect, they are rich in essential vitamins. Yes, they contain sugar, but in the form of fructose, not glucose. Fruit sugar has a lower glycemic index than refined sugar, which is added to preparations.
Are there foods that are more concentrated in collagen than others?
Collagen is a good protein for the skin: it gives it firmness, elasticity, allows it to renew itself properly. There are few collagen-rich foods (egg yolk, fish skin) but rather foods that can stimulate the natural production of collagen by our body: foods rich in amino acids, vitamins A, C, E, minerals (zinc, silicon, sulfur).
- Vitamin A : beta-carotene and retinol, in carrots, apricots, but also fatty fish…
- Vitamin C : in fruits (kiwi, red fruits…) but also cabbage…
- Vitamin E : in seeds, oilseeds…
- Proteins : certain amino acids are beneficial for the skin: spirulina, lysine (egg yolk), glycine and proline (in meat)
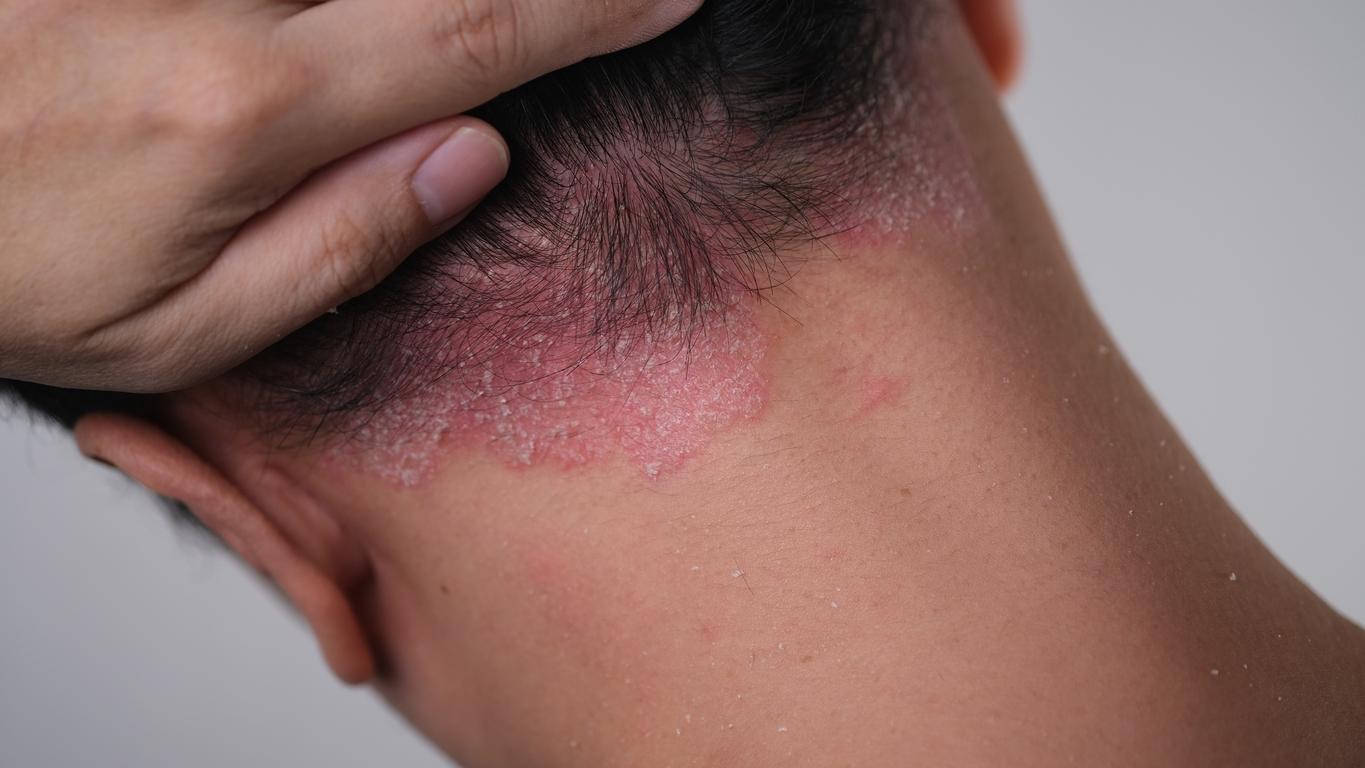
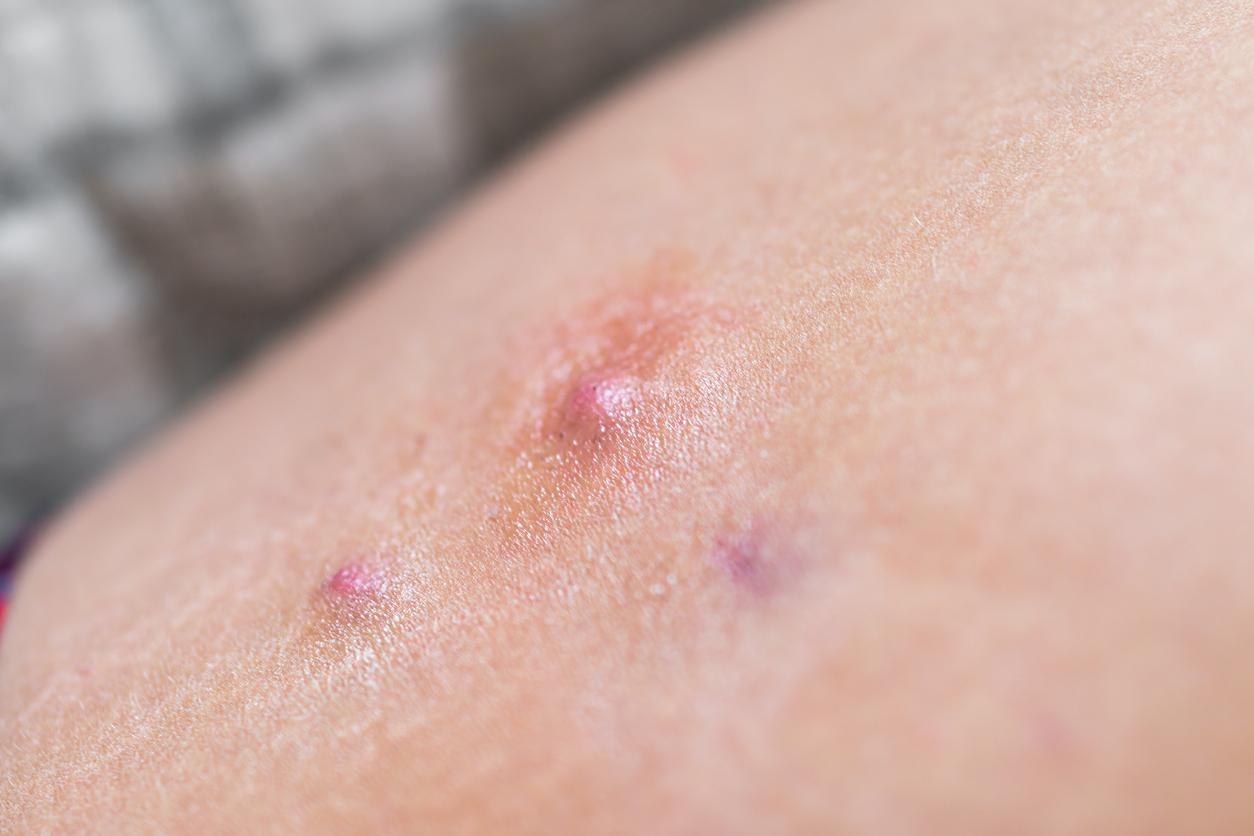
Eczema or psoriasis: are there trigger foods?
Eczema and psoriasis are inflammatory dermatoses. So the pro-inflammatory foods can aggravate or even trigger flare-ups : these are foods with a high glycemic index. Generally sugars, refined cereals. Alcohol plays a very important harmful role for these dermatoses.
Read also:
- What is vitiligo, the disease that bleached the prime minister’s beard?
- Eczema, allergies, excess sun, psoriasis: how to tell the difference?