Thrombosis is manifested by the formation of a blood clot in a vein. This condition must be treated quickly to reduce the risk of complications. What are the symptoms to identify?

- Venous thrombosis is responsible for one in four deaths worldwide.
- Deep phlebitis can lead to a pulmonary embolism, an obstruction by a blood clot of a pulmonary artery or one of its branches.
Every year, World Thrombosis Day is celebrated on October 13. For ten years, a global awareness campaign has been conducted by the International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISTH) to warn of the signs of the disease.
What is venous thrombosis?
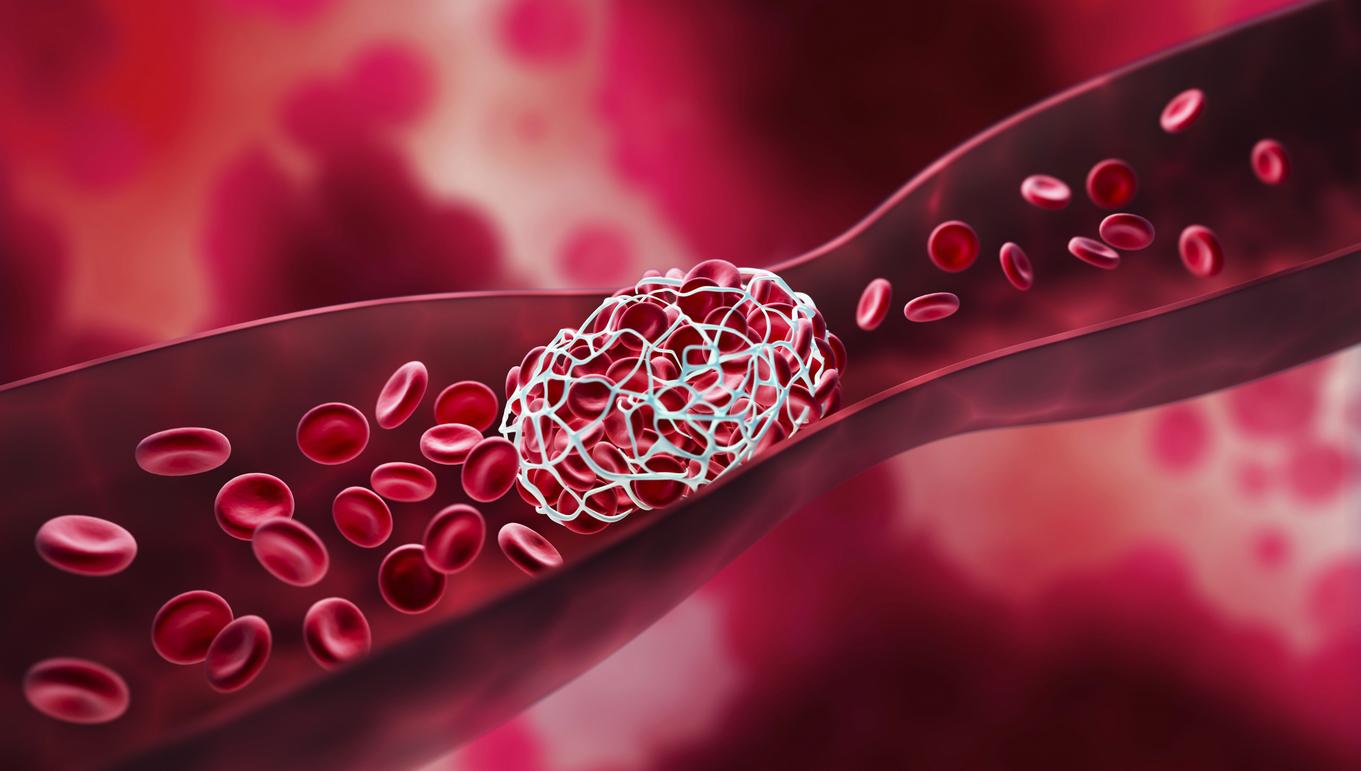
In France, there are 50,000 to 100,000 annual cases of thrombosis. Also called “phlebitis”, it is characterized by the formation of a blood clot in a vein. In a majority of cases, it affects the lower limbs, especially the calves.
“During phlebitis, the clot can form in a superficial vein, a small vein located between the skin and the muscles (saphenous vein). In this case, it is a superficial phlebitis also called ‘paraphlebitis’ or ‘periphlebitis’. It is benign, unless it is associated with deep vein thrombosis, which should always be sought”Explain Ameli Healththe health insurance platform.
Deep vein thrombosis is caused by the formation of one or more clots in a deep vein that can travel through the bloodstream and lodge in the lungs. A pulmonary embolism, an obstruction of a pulmonary artery or one of its branches, can then occur.
What are the symptoms associated with phlebitis?
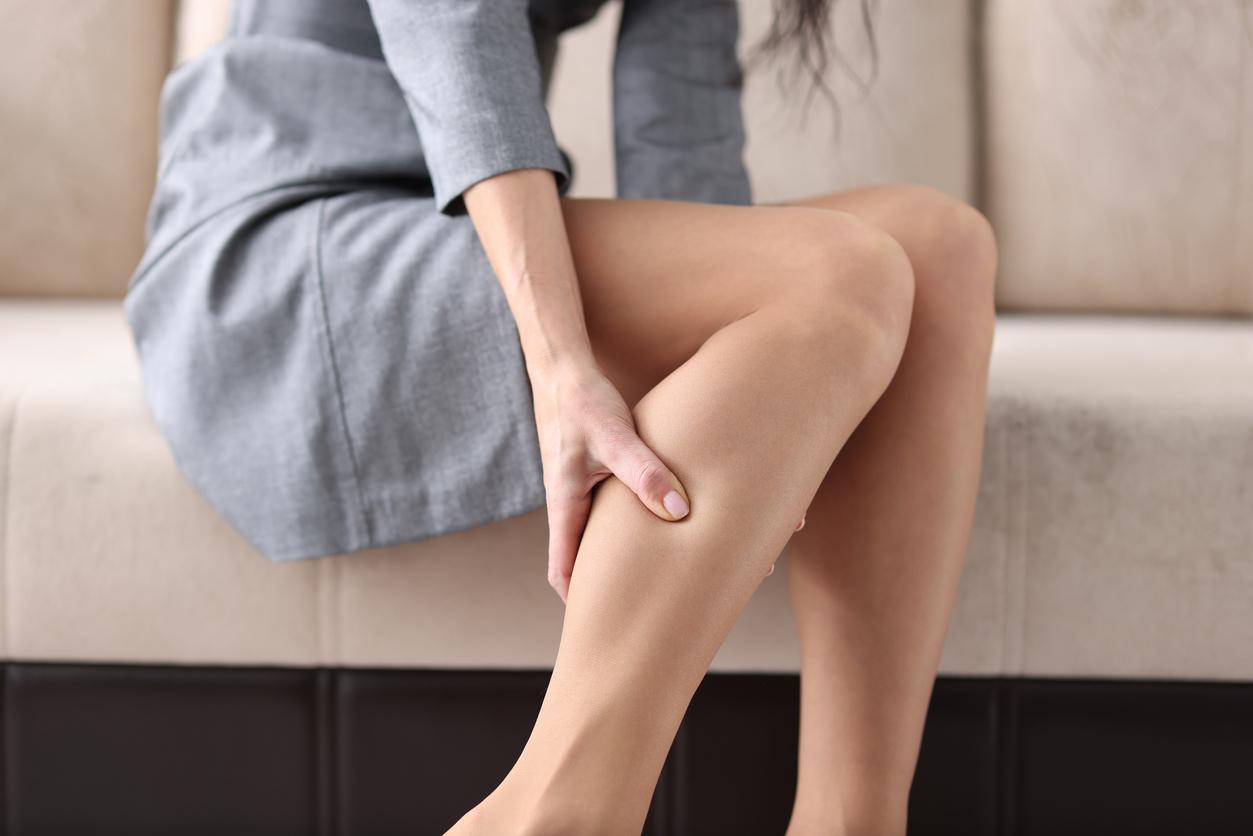
Superficial phlebitis usually causes pain as well as redness in the affected area. Paraphlebitis is usually located at the level of a varicose vein that looks like a hot red cord.
Symptoms of deep vein thrombosis are more distinctive compared to those of superficial phlebitis. We identify in particular:
- calf pain that may spread to the whole leg. This manifestation is present in 60% of cases and can lead to a feeling of heaviness in the leg;
- calf edema which may be associated with hardening and swelling of the calf up to the thigh. A bluish/purple color in the region concerned can reach this limb;
- an increase in skin temperature which results in skin that is warmer to the touch
In some cases, venous thrombosis is asymptomatic. It can be diagnosed during a medical check-up for another pathology. “Blood clots are often overlooked because their symptoms can resemble those of many other diseases (…) It is absolutely crucial that healthcare professionals and the general public know the signs, symptoms and risk factors so that clots blood are treated as quickly as possible”, said Professor Beverley Hunt, Chair of the World Thrombosis Day Steering Committee and international expert in thrombosis and haemostasis, in a press release.
Thrombosis: how to treat phlebitis?
The International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISTH) states that blood clots are “the underlying cause of heart attacks, strokes and deep vein thrombosis (DVT), the three leading causes of cardiovascular death”. It is therefore essential and urgent to treat superficial phlebitis which can develop into deep vein thrombosis.
For superficial phlebitis, the doctor may recommend anticoagulant treatment administered subcutaneously. A venous compression by a bandage can also be performed. The objective is to eliminate the risk of occurrence of deep vein thrombosis and to treat paraphlebitis to limit recurrences.
“When the thrombosis superficial vein disease of the lower limbs is associated with deep vein thrombosis, it is the treatment of the latter which is followed”, can we read on Ameli Santé. In case of deep phlebitis, treatment with anticoagulants should be started quickly. It thus makes it possible to avoid the increase in the size of the clot and its displacement which can be responsible for a pulmonary embolism.