Regular consumption of lentils helps reduce fasting total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels.
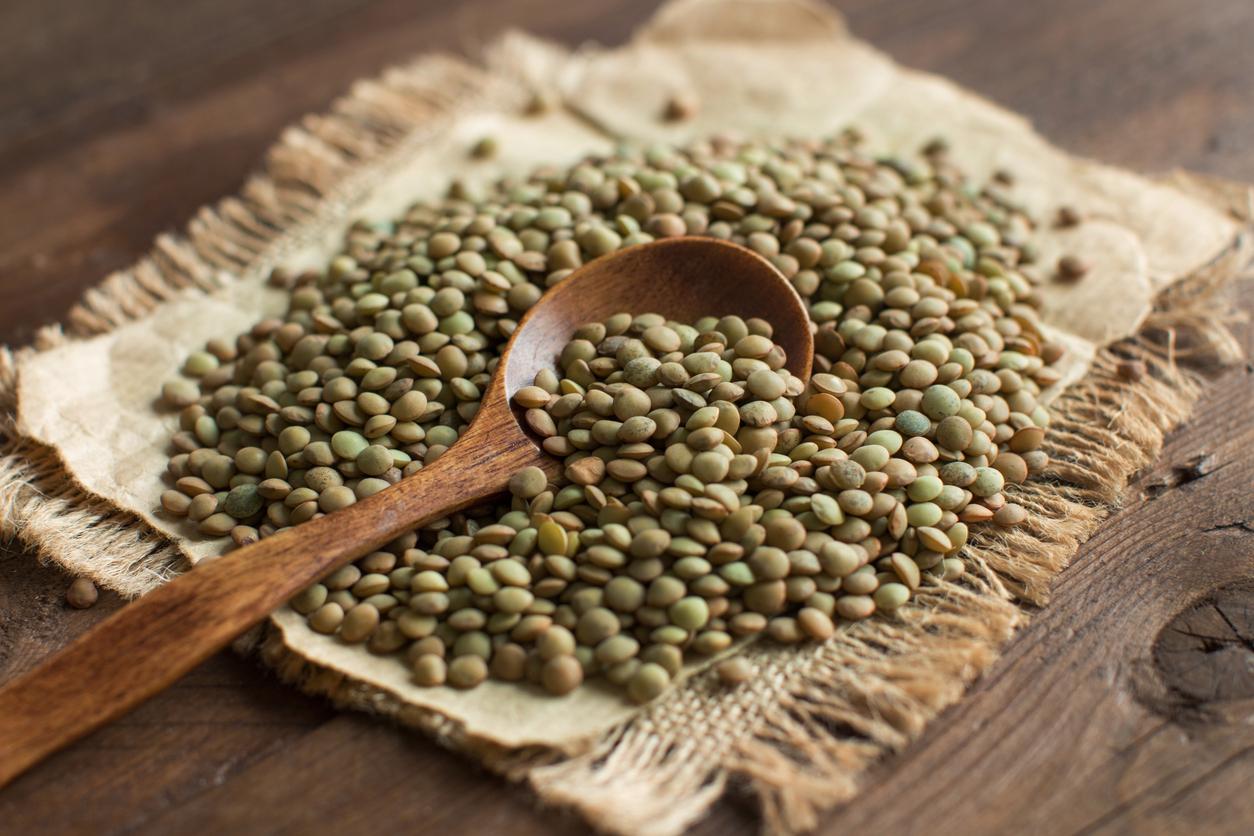

- Eating lentils daily in people at higher risk of developing metabolic disease may reduce fasting cholesterol levels.
- It would also improve postprandial glycemia and systemic inflammatory responses.
- This diet did not cause any gastrointestinal upset.
They are high in fiber and protein. Lentils have many health benefits, including the potential to improve metabolic health. In one study, scientists at Montana State University (USA) sought to assess the impact of lentil meals on fasting and postprandial measures of glucose and lipid metabolism and inflammation.
Lower cholesterol through regular consumption of lentils
To carry out the work, the team recruited 38 overweight and obese adults, with an average age of 47, a body mass index (BMI) of 34.4 kg/m2 and a large waist circumference. For 12 weeks, the participants had to eat a meal containing 980 or 0 grams of cooked green lentils every lunchtime. During the follow-up, the volunteers had to answer questions about their gastrointestinal symptoms and satiety once a week. Blood samples were also taken fasting and every hour for five hours after the meal to assess blood markers.
The results, published in the journal Nutrientsshowed that increasing average daily lentil consumption led to higher total fiber intake. After consuming these legumes for 12 weeks, fasting total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels decreased. In addition, long-term lentil consumption improved postprandial glucose and inflammatory responses to a high-fat meal. “Gastrointestinal disturbances did not differ between groups and all symptoms were reported as ‘not present’ or ‘mild’ during the intervention period,” can be read in the research.

What are the mechanisms involved?
According to the authors, these observations can be explained by the fact that fibers bind to bile acids, preventing their return to the liver and stimulating the production of hepatic bile acids. “The body replenishes liver cholesterol levels through absorption of blood cholesterol, which lowers serum cholesterol levels.” Another mechanism by which lentils likely contributed to lowering serum cholesterol is through saponins, which are bioactive compounds that regulate lipid metabolism and prevent cholesterol absorption. Regular consumption of lentils may also reduce total saturated fat intake, a dietary component that increases cholesterol levels.