On the occasion of the 72nd world day of leprosy patients, let’s untangle the true of the false on this shame disease which still affects very many people in the world.

- Each year, more than 200,000 people are affected, a new case every three minutes, according to WHO figures.
- Contrary to popular belief, which lead thousands of people to be excluded from health care and education, leprosy is not a very contagious disease. Indeed, its transmission is made by close and prolonged contact (several months) with an infected and untreated person.
- There is no leprosy vaccine, but since 1981, the processing protocol recommended by WHO has been polychemotherapy (PCT), composed of three antibiotics (Dapsone, Rifampicin and Clofazimine): from the first take, the sick are no longer contagious.
Stigmatized, excluded from health care or even education for the youngest, people affected by leprosy have a double penalty with the difficulties of the disease and on the other, the sometimes ruthless look of people lacking in knowledge. “” “It has often been considered a hereditary disease, a curse or a punishment of God“, evoked The Raoul Follereau Foundation.
How does this infectious disease, certainly the oldest of humanity, still continues to wreak havoc? What are the symptoms? Is it so contagious? Why does doctor answers all these questions.
Lepre is present in more than 120 countries
Leprosy is classified in the group of neglected tropical diseases (MTN) by The World Health Organization. Like leishmaniasis, Chagas disease or dengue, this condition mainly affects poor populations living in wet and hot climates. Each year, more than 200,000 people are affected, a new case every three minutes, according to WHO figures. The organization recalls that the disease is still present in more than 120 countries -145 according to the Raoul Follereau Foundation which specifies that the official figures “are underestimated as the disease is sometimes neglected in certain countries concerned and the patients who are difficult to reach”. The most affected countries are Brazil, India and Indonesia, with a number of new cases reported above 10,000 in 2019. Thirteen other countries (Bangladesh, Ethiopia, Madagascar, Mozambique, Myanmar, Nepal, Nigeria, Philippines, Philippines, Philippines, Philippines Democratic Republic of Congo, Republic-United Republic of Tanzania, Somalia, Sudan from the South and Sri Lanka) are also particularly affected, with between 1,000 and 10,000 new cases in the year according to these same data.
Leprosy is not a very contagious disease
Contrary to popular belief, which lead thousands of people to be excluded from health care and education, leprosy is not a very contagious disease. Indeed, its transmission is made by close and prolonged contact (several months) with an infected and untreated person. It is caused by the presence of bacilli called Mycobacterium leprae which are transmitted from one human to the other by air, through droplets and nasal or oral secretions. “” “Leprosant is therefore not transmitted by occasional contact: it is therefore quite possible to speak face-to-face or to sit with an infected person, without risk of contagion”, Insists Malta’s order.
An incubation period of at least 5 years before the first symptom
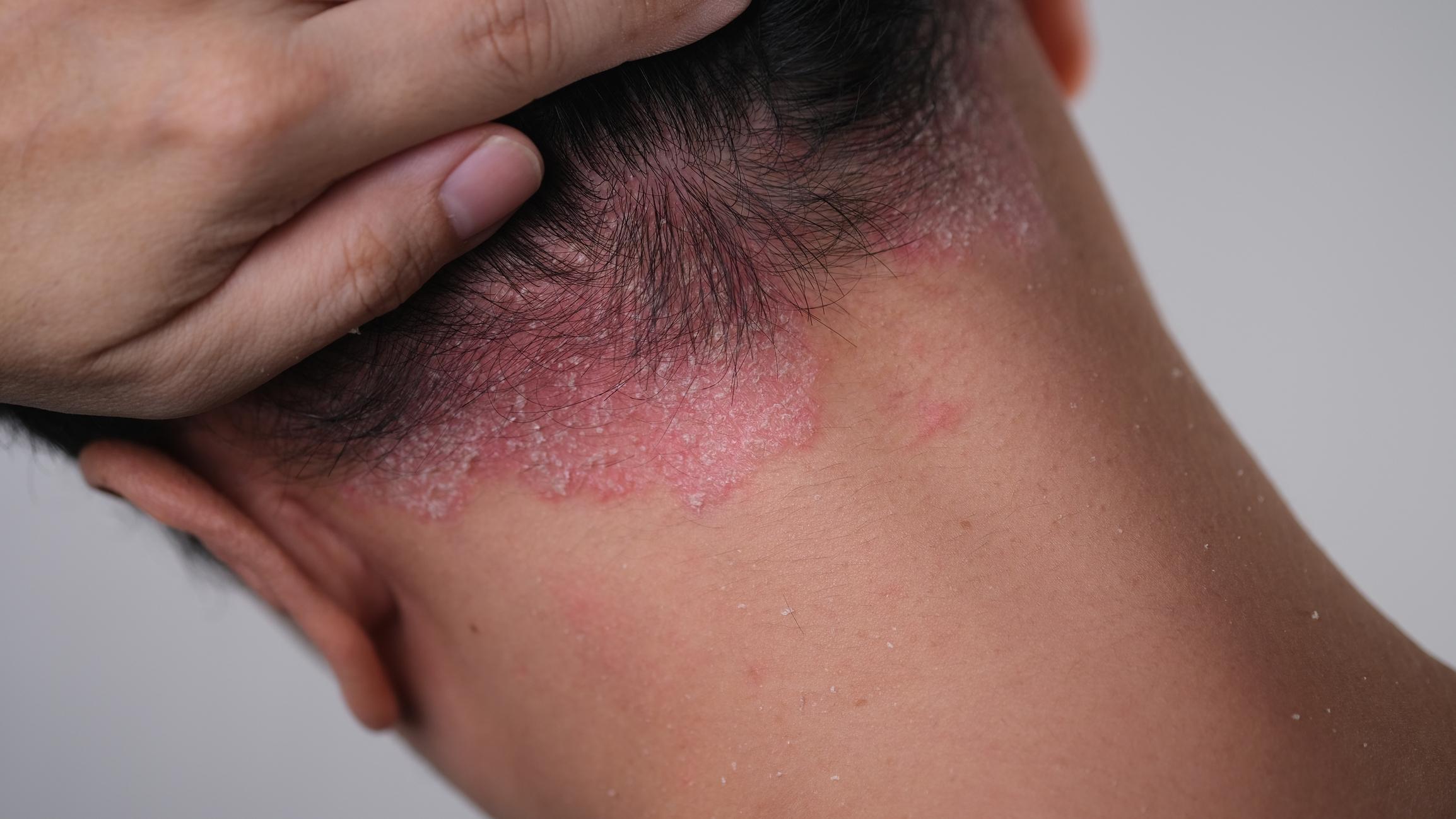
“” “The leper bacillus multiplies very slowly: the incubation period of the disease is 5 years on average, but the symptoms can sometimes appear until 20 years“, explain The Pasteur Institute. The most common signs are skin lesions that can manifest in several ways. In general, the first visible symptom is an insensitive task on the skin. There are also neurological symptoms (numbness and tingling, muscle weakness, etc.), eye symptoms (decrease in tears’ production, cornea ulcers, etc.) and respiratory symptoms (nasal congestion, nose bleeding, etc.) which can gradually appear if the disease is not treated in time.
A clinical diagnosis of Hansen’s disease
The diagnosis of leprosy, or Hansen’s disease, is based on a clinical examination, with possible laboratory tests for certain difficult cases. “” “The diagnosis of leprosy is based on the presence of at least one of the following pathognomonic signs”, Details the WHO:
- A manifest loss of sensitivity on an area of the pale (hypopigmented) or reddish skin;
- thickening or enlargement of a peripheral nerve, accompanied by a loss of sensitivity and/or a weakness of the innervated muscles;
- Detection under the microscope of bacilli in a skin smear.
Depending on the diagnosis, the doctor can determine the type of leprosy affecting the infected person:
-paucibacillaire: one to five skin lesions which are insensitive, without proven presence of bacilli in the skin, skin,
-Multibacillary: more than five insensitive skin lesions or nervous involvement (neuritis alone or neuritis accompanied by several skin lesions) or the proven presence of bacilli in the skin, regardless of the number of skin lesions.
“” “There is also a 3rd form of leprosy, called borderline leprosy, which combines the symptoms of the other 2 forms. Ultimately, it tends to get closer to one of them”, Adds the order of Malta.
3 antibiotics to treat leprosy
There is no leprosy vaccine, but since 1981, the treatment protocol recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) has been polychimotherapy (PCT), composed of three antibiotics (Dapsone, Rifampicin and Clofazimine). From the first PCT, patients are no longer contagious. The sooner the treatment, the better it prevents nerve, paralysis and mutilation damage. “” “Paucibacillaire leprosy can be healed in 6 months and multibacillary leprosy in 12 months”Indicates the Pasteur Institute.
The climate crisis impacts the monitoring of lepers
The Raoul Follereau Foundation warns against the impact of climate change on the detection and monitoring of patients. In Chad, for example, one of the poorest countries in Africa, the population is particularly victim of the increasingly frequent climatic hazards, forcing the populations to move, making all the more difficult screening and monitoring of sick.