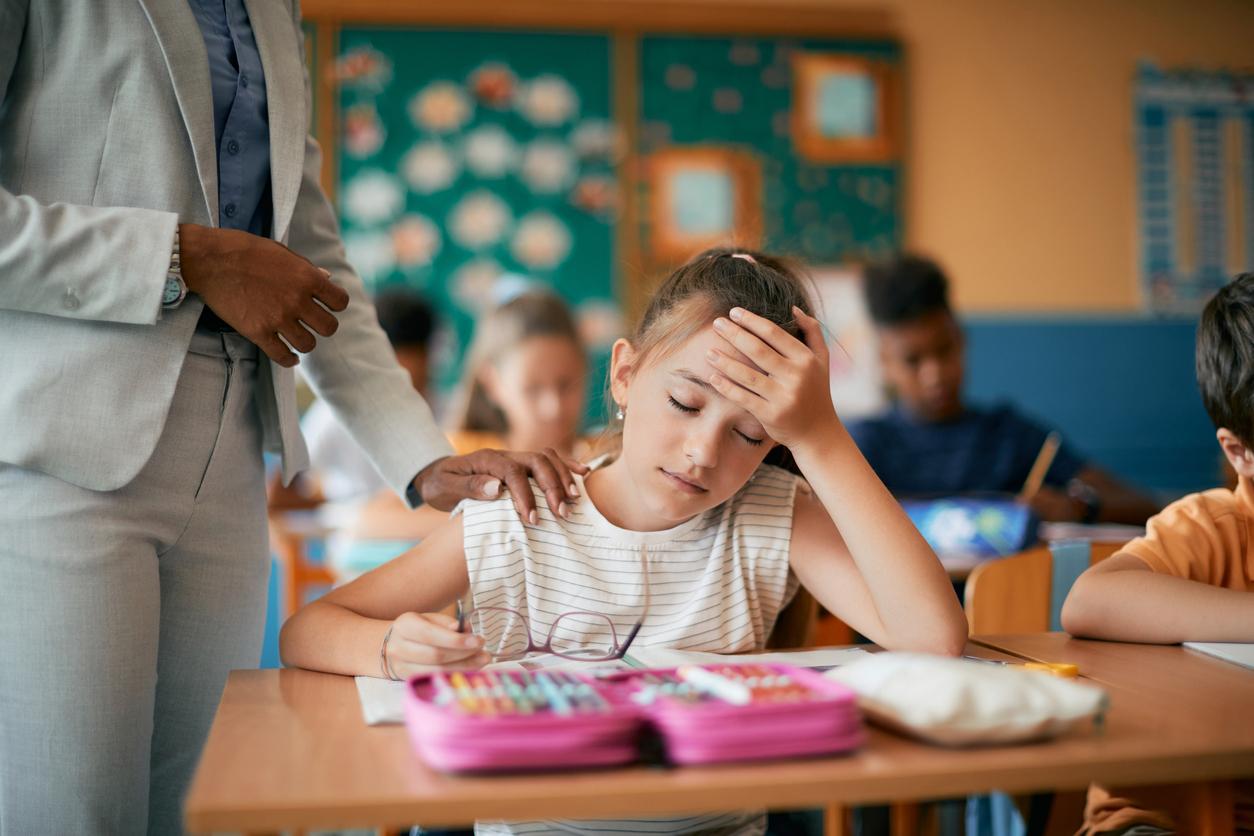
A case of tuberculosis has been detected in an adult caring for children in a school in Caumont-sur-Aure (Calvados). A screening must be organized for the 250 schoolchildren in the coming days.
- An adult fell ill with tuberculosis in Caumont-sur-Aure (Calvados)
- Since the 1970s, public policies implemented to fight tuberculosis have gradually reduced the disease, which affected 4,000 people in 2020.
Tuberculosis, a real scourge at the end of the 18th and beginning of the 19th century, has not disappeared. This infectious disease was detected in a man who took care of children during after-school hours. It is caused by a mycobacterium, Koch’s bacillus, which is transmitted through the air.
many signs
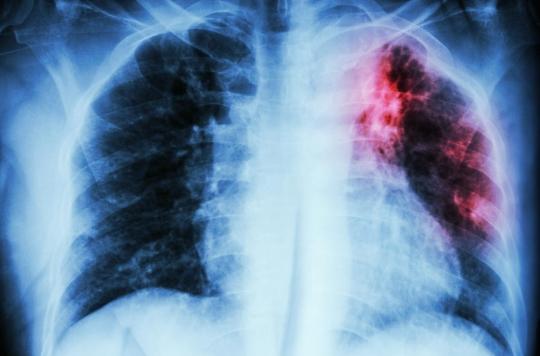
Tuberculosis most often affects the lungs but sometimes also affects other organs. It is a disease transmissible by air, by dispersion of droplets of bronchial secretions, from a contagious patient, particularly when he coughs.
The symptoms of tuberculosis are not specific: it can be fever, weight loss, night sweats. It can give many signs: the most suggestive are prolonged cough.
Differences in symptoms with Covid-19
Both Covid-19 and tuberculosis cause respiratory symptoms, such as cough and shortness of breath and both cause fever and general weakness. But one of the major differences between these two diseases is the time it takes for the first symptoms to appear: several weeks or even longer for tuberculosis, unlike a few days for Covid-19. Also, in the case of tuberculosis, the symptoms gradually set in. The number of tuberculosis cases declared in 2020 is down 10% in connection with the Covid-19 pandemic, according to Public Health France.
responsible germ
The diagnosis of tuberculosis is ensured by examinations which highlight the responsible germ on samples (by microscopic examination, culture or gene amplification test). Other examinations such as x-rays and scanners look for lesions caused by the disease. As there are many possible locations, other imaging or biopsy tests are sometimes necessary.
Screening in people who have no symptoms or have not noticed them, is based on certain tests and examinations: clinical examination, chest X-ray, bacteriological examination of sputum (sputum) and/or gene amplification tests .
Vigilance remains essential
Although the disease is less and less frequent, vigilance is still required with regard to the proliferation of bacterial strains resistant to usually effective treatments.
The obligation to vaccinate children and adolescents was suspended in 2007, in favor of a strong recommendation to vaccinate the children most exposed to tuberculosis. The Centers for the Fight against Tuberculosis organize screenings for those most at risk.
.