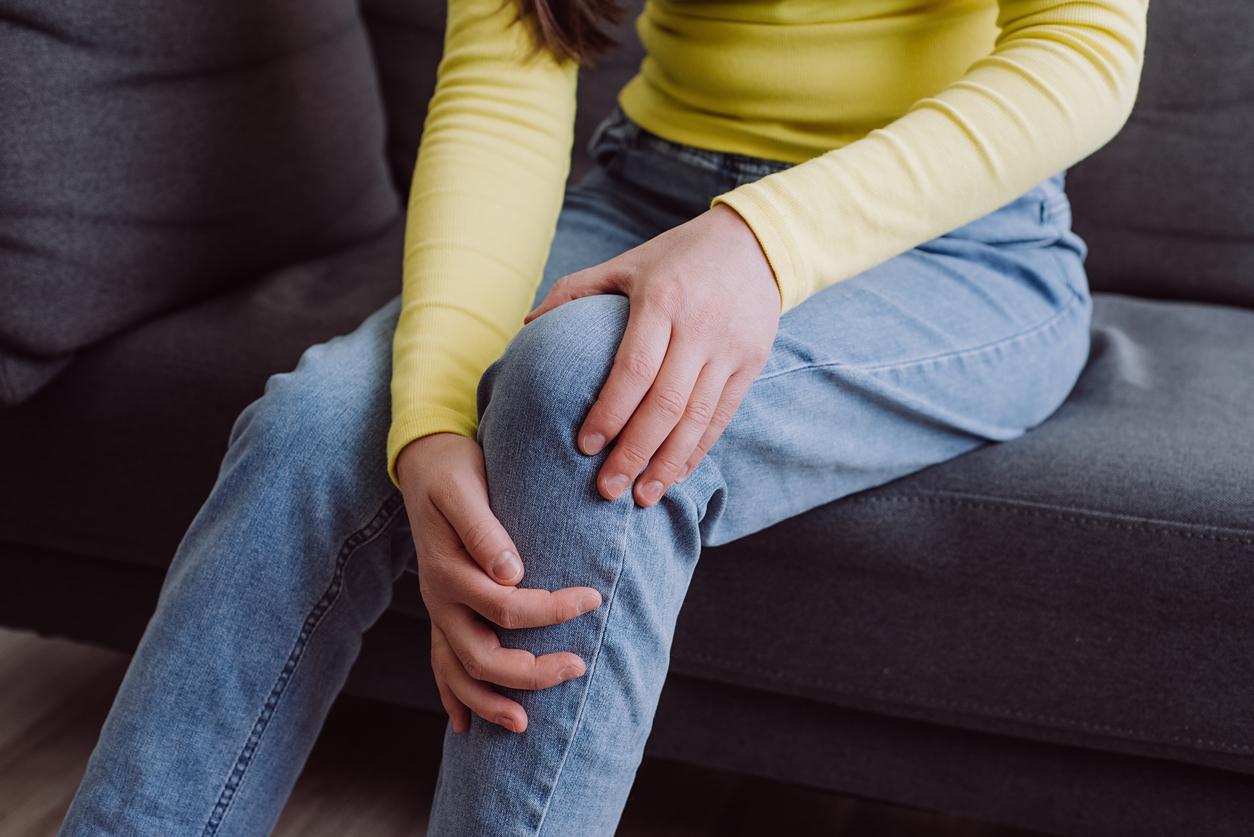
South Korean researchers have succeeded in developing a treatment for polyarthritis based on nanoparticles that helps relieve symptoms and prevent new inflammatory flare-ups.

- A team of South Korean scientists has developed a new solution for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
- The researchers placed cerium oxide nanoparticles (CNPs), known to have antioxidant properties, on nanovesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCNV).
- This “cocktail” helps to immediately combat the symptoms of the disease and avoid new inflammatory flare-ups in the long term.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease characterized by inflammation of the joints, but also significant production of cytokines and imbalances in the immune system. Together, these create a cycle of worsening symptoms and inflammatory flare-ups.
“Essentially, the ideal treatment for rheumatoid arthritis should not only provide immediate relief of inflammation and symptoms, but also address the root cause by restoring the immune system to its normal, balanced state”writes the South Korean researcher in a press release Sagang Koo. To achieve this objective, the scientist and his team had the idea of using nanoparticles.
Arthritis: nanoparticles with antioxidant properties to reduce inflammation
Their new treatment for polyarthritis involves placing cerium oxide nanoparticles (PCN)known to have anti-oxidant properties, on nanovesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCNV). Tests were carried out on mice suffering from the inflammatory disease to evaluate the effectiveness of this cocktail. Rodents, treated with the association NCP-MSCNV, better recovered compared to those treated only with the PCN where the MSCNV.
In detail, the results showed that cerium oxide nanoparticles were capable of cleaning excess reactive oxygen species in joints affected by polyarthritis. In addition, they managed to induce the polarization of macrophages M1 (inflammatory cell) in M2 (cell involved in remodeling and repair processes), ce which helps to obtain relief from inflammation and symptoms. THE stem cells Mesenchymal cells, in turn, also played a key role in promoting the production of regulatory T cells, which resulted in long-term immune tolerance.

Nanoparticles and polyarthritis: a combined approach for better treatment
“In short, this approach aims to bridge both innate and adaptive immunity to achieve both short-term pain relief, as well as to convert the tissue environment into a state immuno-tolerant to prevent recurrence of symptoms”write the authors in their communicated.
Another encouraging element of this work for people suffering from rheumatoid arthritis: data suggest that symptom improvement can be achieved after only a single dose treatment.
However, additional research will be necessary before this approach based on cerium nanoparticles can be considered as a treatment option.