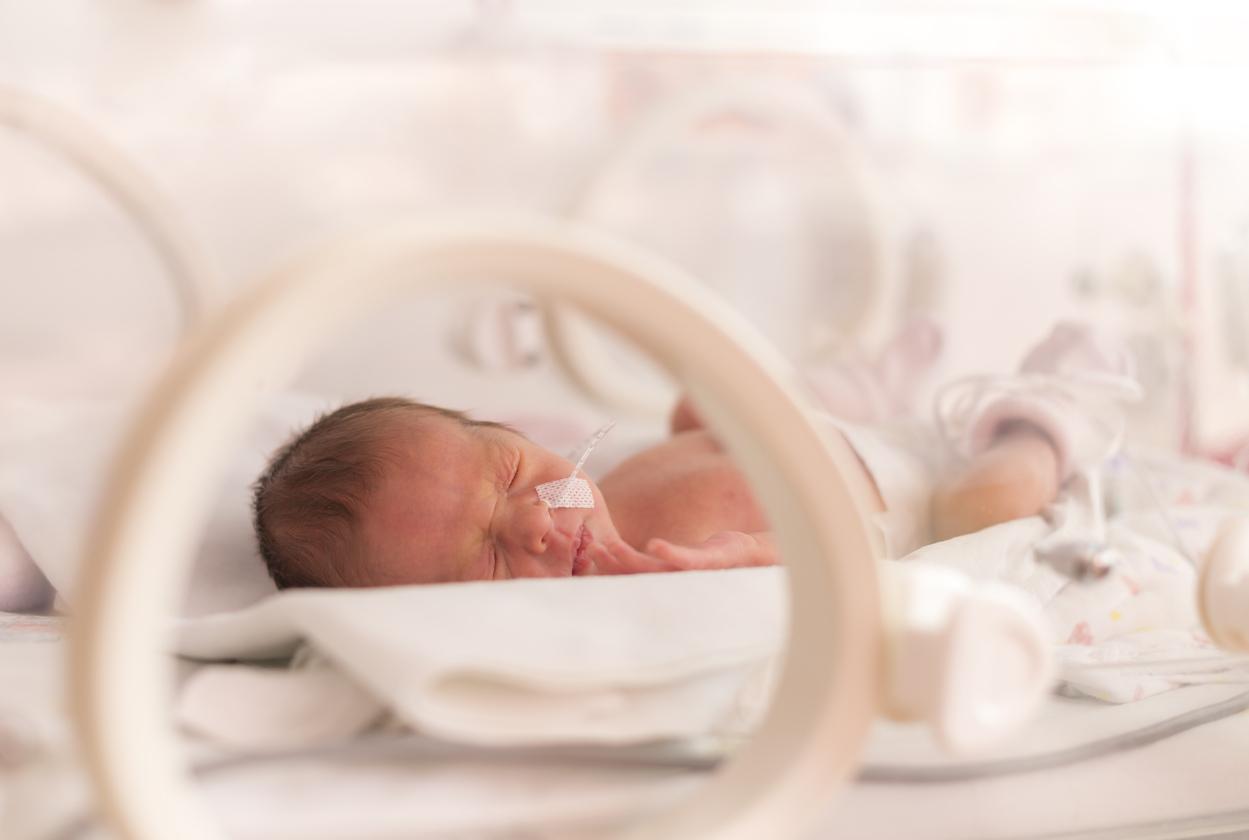
Every year, 55,000 children are born prematurely in France. An earthquake for which parents are rarely prepared. This arrival (too) early interrupts development in utero. If the organs are present (heart, brain, digestive tract and ductus arteriosus), they are still immature. Management depends on the stage of prematurity and the general state of health. Development is not set in stone, it is unique to each child’s brain.
What are the levels of prematurity?
- A premature birth occurs before 37 weeks of amenorrhea (SA), i.e. 8 and a half months of pregnancy.
- Average prematurity corresponds to a birth between the 32nd and 36th SA (7 to 8 months of pregnancy).
- Extreme prematurity: birth between the 28th and 32nd SA (6 to 7 months of pregnancy).
- The extreme prematurity : birth before 28 weeks (within 6 months of pregnancy).
Up to 2 years: monitor motor problems
In April 2021, the French Epipage 2 survey, led by Inserm, delivered its conclusions on the consequences of prematurity in babies born between 5 and 7.5 months of pregnancy. The greater the prematurity, the more the children present with neurodevelopmental disorders. Whatever the degree of prematurity at birth, more than a third of the children showed so-called minor difficulties.
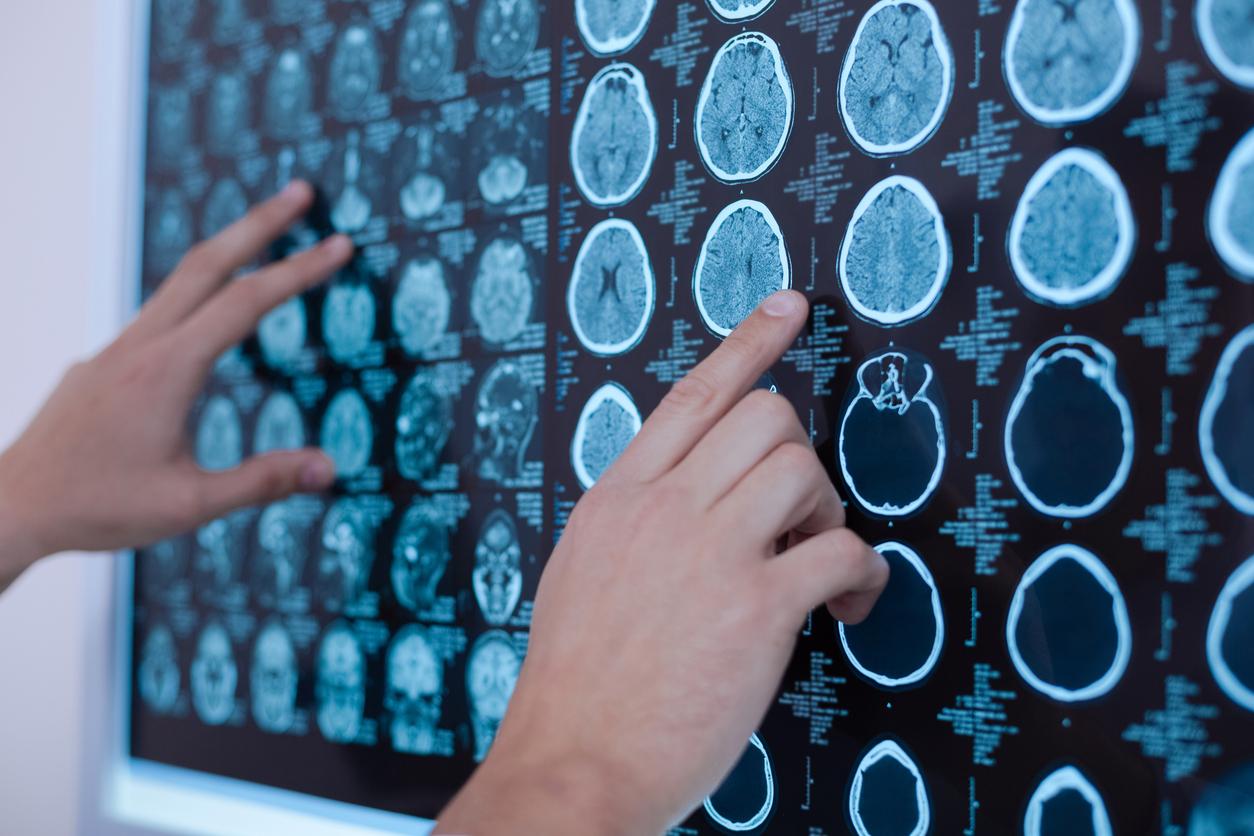
Neuromotor, sensory, cognitive development, so many areas scrutinized over the years in these children born too early. “A child born prematurely is especially at risk of cognitive impairment. This study sheds light on the difficulties faced by these children at the age of 5 1/2 years. Up to 2 years, it is particularly necessary to monitor the appearance of motor problems. Over the years, the number of cerebral palsy decreases” summarizes Pr Jean-Christophe Rozé, president of the French Society of Neonatology, professor of pediatrics at the University of Nantes and head of the pediatric resuscitation and neonatology department at the CHU.
Up to 6 years: consultations every year
During the first two years, consultations are scheduled every two to four months, then every year until six years. Obviously, this duration is adapted to the state of health of the child and to his needs. The medical team monitors growth, development, and ensures that there are no disorders. A follow-up with a psychomotrician thus makes it possible to accompany the premature child in his psychomotor development (fine motor skills, coordination, etc.). A speech therapist can work on language disorders, eating disorders, etc.
“This follow-up is organized differently depending on the region. There are perinatal networks made up of private practitioners and hospital practitioners who guide and support parents. In our Grandir ensemble network, we include private doctors”,welcomes Professor Rozé.
This network has set up a rapid questionnaire of 20 questions intended for teachers to assess children. The Center for Early Medico-Social Action (CAMSP) also has the task of detecting certain disorders and treating them. These centers offer a multidisciplinary follow-up generally addressed to the most fragile children. Each network operates differently, the neonatology team remains best able to indicate the resource person. It is also possible to rely on the Maternal and Child Protection (PMI). Concerning the financial support in the regional networks, there is no homogeneity at the national level.
Our expert : Pr Jean-Christophe Rozé, President of the French Society of Neonatology
Read also :
- Fewer premature births during confinement
- Very premature babies: the survival rate continues to increase