An American study conducted by researchers at the University of Southern California highlights the direct consequences of obesity and overweight on knee osteoarthritis.
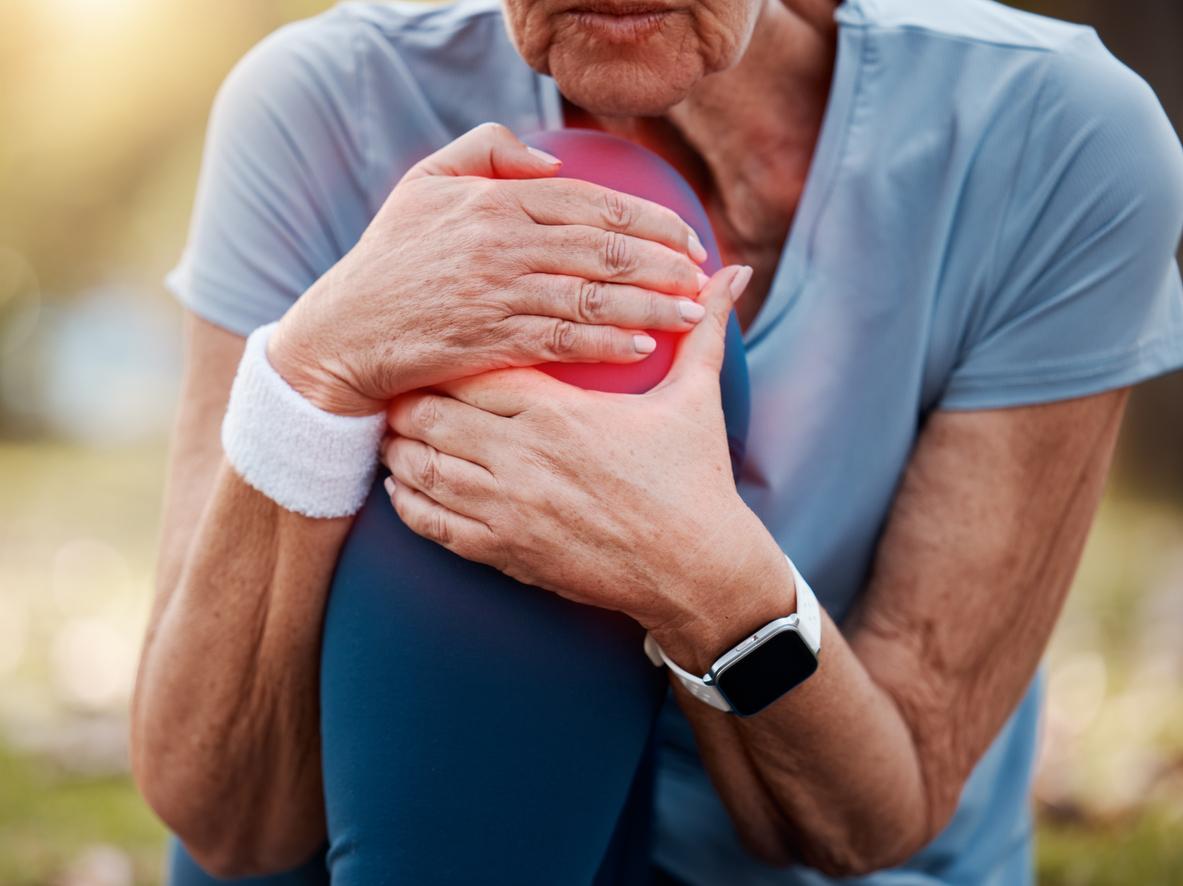

- Knee osteoarthritis affects 30% of people over 65.
- It is caused by the deterioration of the cartilage and leads to pain and loss of mobility.
- Avoiding weight gain is the first treatment for this debilitating disease.
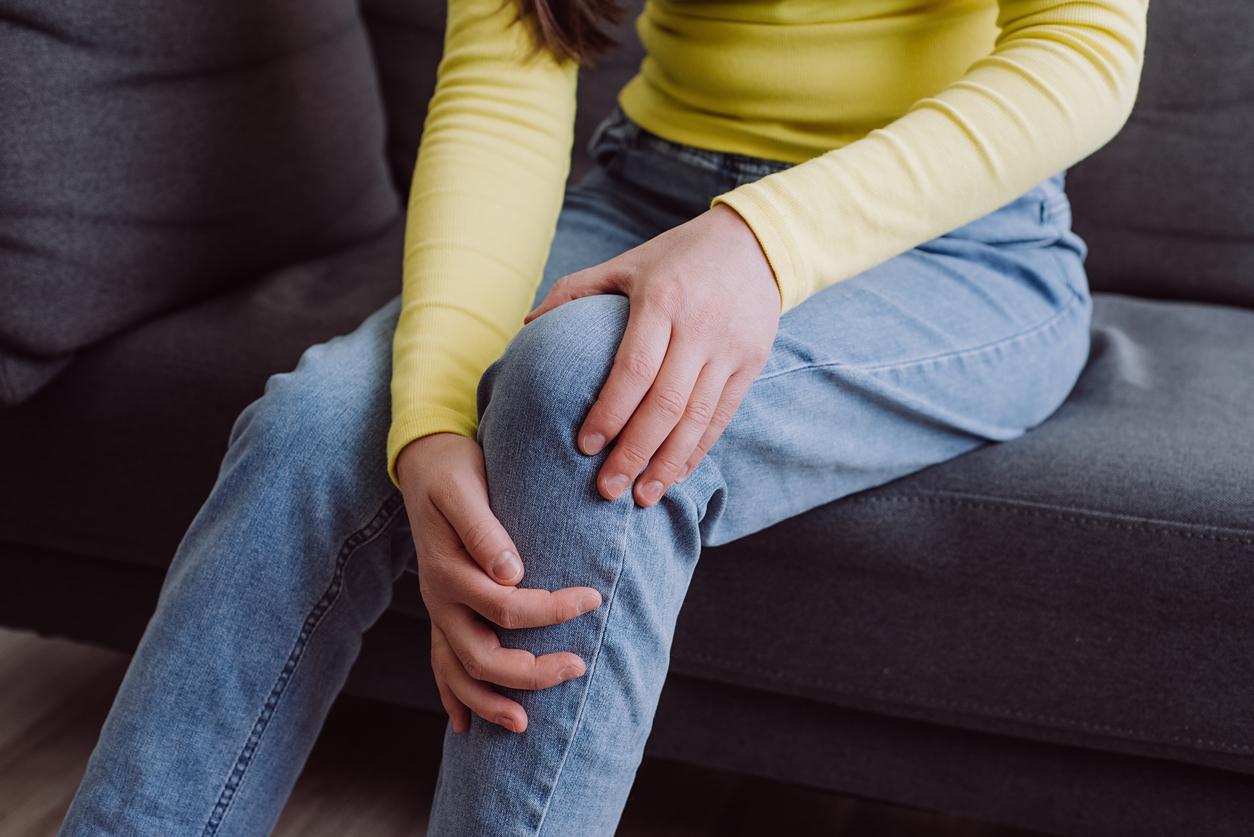
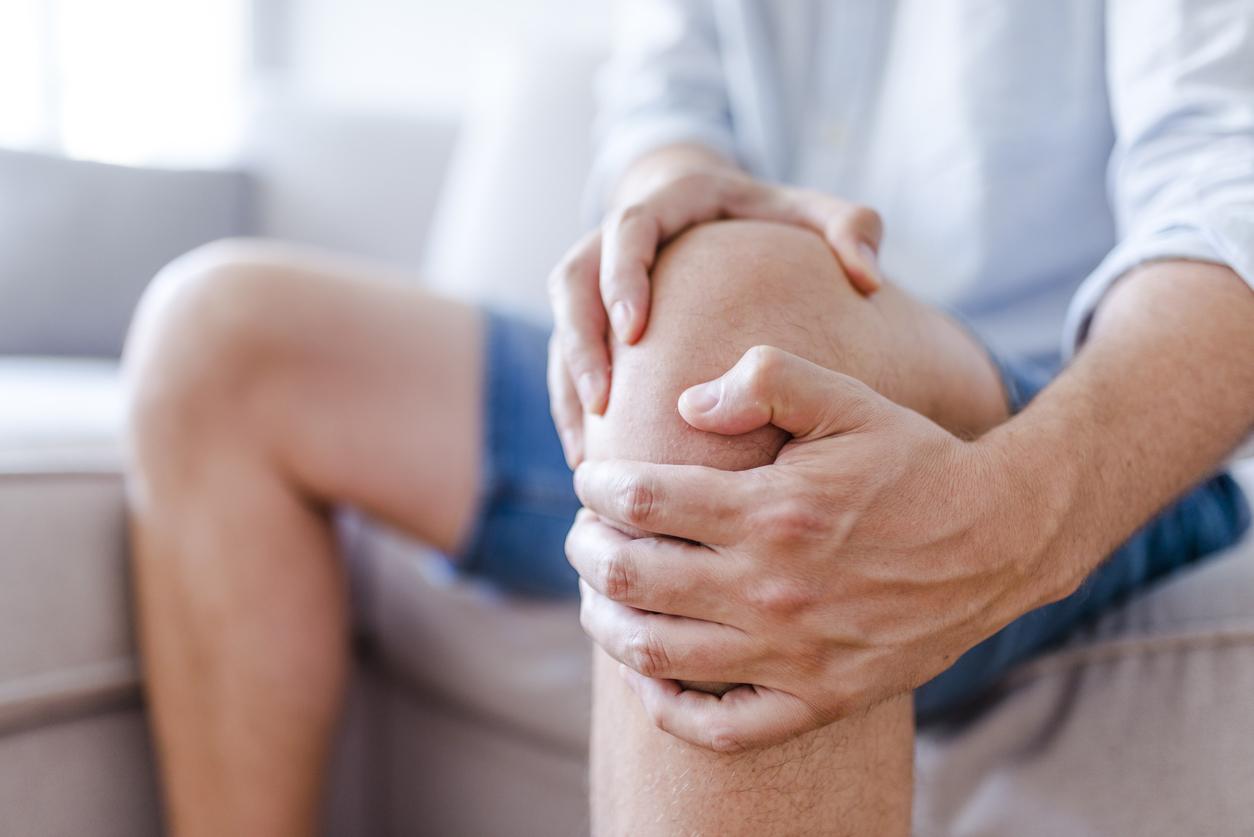
Osteoarthritis of the knee is a disease that affects 30% of people over the age of 65. This disease is very debilitating since most of the body weight rests on the knees. Concretely, osteoarthritis of the knee is caused by a deterioration of the cartilage of the joint. One or both knees may be affected. When cartilage deteriorates with age or as a result of trauma, it leads to severe pain and loss of mobility.
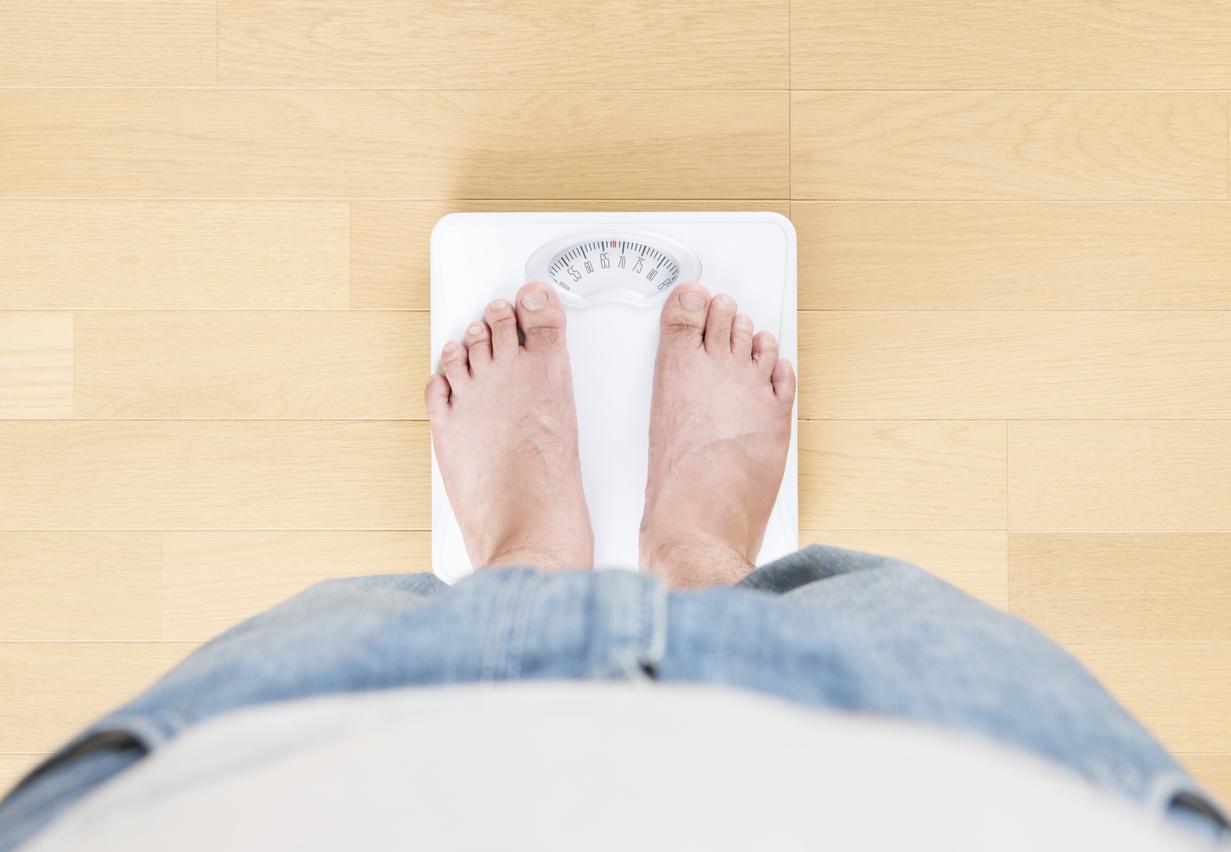
Weight gain makes symptoms worse
Led by researchers at the University of Southern California, a new study made it possible to observe the evolution of osteoarthritis of the knee over a period of four years. The results reveal that obesity and even being slightly overweight can have direct consequences on knee osteoarthritis. Participants who gained more than 5% of weight have a risk of worsening osteoarthritis increased by 29%. Conversely, weight loss reduces the pain associated with this disease. Weight gain and obesity are therefore correlated with an increase in pain.
Chronic pain and loss of mobility
People with knee osteoarthritis can suffer from chronic pain, which occurs especially when walking or when standing. The knees can also be swollen as a result of the synovial inflammation that accompanies osteoarthritis. People with knee osteoarthritis may also experience joint stiffness, which makes movement difficult. The lack of mobility that comes with this condition can also isolate sufferers socially, preventing them from participating in activities they previously enjoyed.
Weight loss is the most effective treatment
There are several treatments to relieve the pain associated with knee osteoarthritis, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or viscosupplementation, which consists of injecting hyaluronic acid into the joint. However, weight loss is considered one of the most effective treatments for relieving pain and slowing disease progression. A healthy, balanced diet can help keep weight gain to a minimum. Regularly engaging in gentle physical activity, such as walking or swimming, can also help strengthen the muscles around the knee joint, which can help reduce pain and improve mobility.