The mpox virus, formerly called monkeypox, is causing more and more cases in the Democratic Republic of Congo. The World Health Organization is warning of a risk of spread beyond its borders.

- The Democratic Republic of Congo is facing a major epidemic of mpox, monkeypox.
- The World Health Organization fears international spread.
- The disease, of viral origin, is transmitted through sexual intercourse, kissing and touching.
A number of cases never reached for a year in the Democratic Republic of Congo which is facing a major epidemic of mpox, formerly called monkeypox. According to a report from the World Health Organization (WHO), published on November 23, 12,569 cases were recorded between 1er January and November 12, 2023 in 22 of the country’s 26 provinces. 581 people died. “This is the highest number of cases ever reported for a year, some in geographic areas that have never previously reported cases of monkeypox, including Kinshasa, Lualaba and South Kivu.”notes the WHO in a communicated.
WHO warns of risk of spread of monkeypox
The organization specifies that the cause of this spread of the virus is unknown at the moment. The cases concern men as well as women and children. The WHO fears an even greater spread because “capacity to respond to monkeypox remains limited in the country“. Screening by PCR test is very low in this African state and although a vaccine exists, no campaign has been put in place.
“There appears to be a significant risk of monkeypox spreading to neighboring countries and around the world.“, warns the WHO. This risk is linked to several factors: among people who contracted the disease through sexual contact, several have traveled outside the country and cases have been recorded in the Republic of Congo, also called Congo Brazzaville. “The introduction of clade I MPXV into different sexual networks that could have links between them could facilitate and amplify the spread of this clade of the virus which has always been more virulent.completes the organization.
DRC: what is mpox, responsible for more than 12,000 cases in the country?
In fact, mpox is a disease of viral origin: it is transmitted by touch, kissing and oral, vaginal and anal sex. “More rarely, the disease can also be transmitted by respiratory droplets and during contact with contaminated equipment.“, specifies the organization. It notes that most cases involve gays, bisexuals and other men who have sex with men infected through sexual contact. “Although the 2022-2023 outbreak has disproportionately affected these populations, it is important to emphasize that anyone who comes into close, prolonged contact with an infected person or their contaminated personal belongings can contract monkeypox.”warns Dr. Richard Pebody, who leads the high-risk pathogens team at WHO/Europe.

Mpox: how is monkeypox treated?
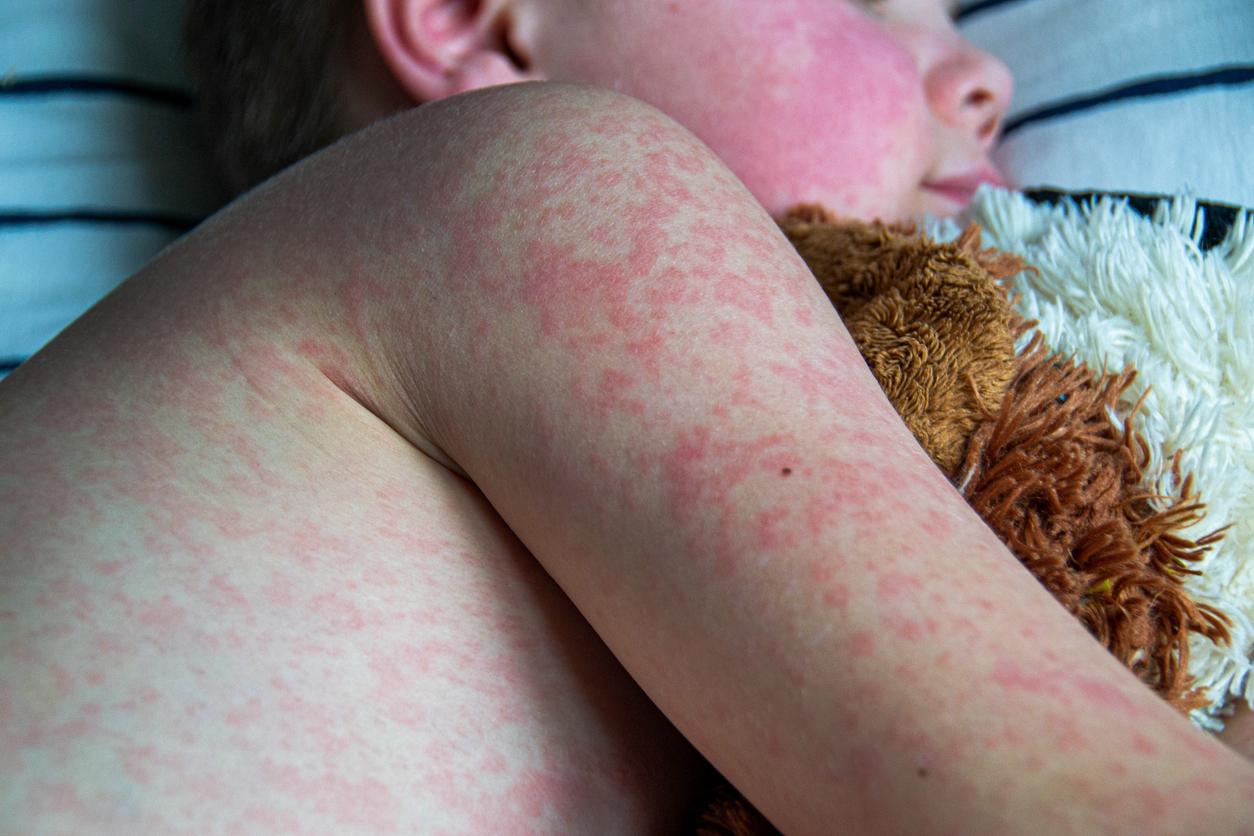
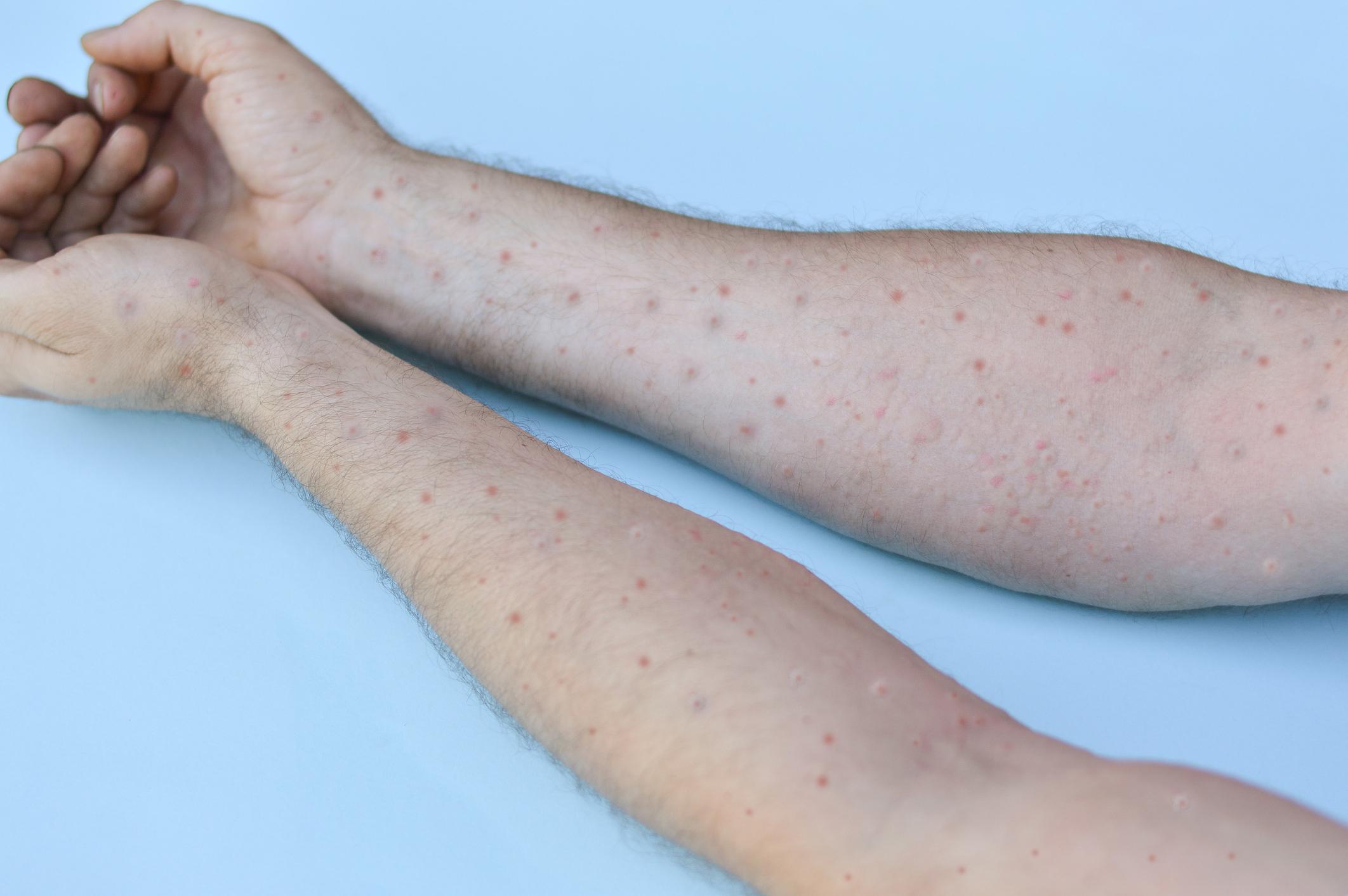
Infected people develop the first symptoms between 6 and 13 days after being exposed to the virus. The most common symptoms are skin rashes evolving from blisters to blisters, notes the WHO. These can be accompanied by fever, muscle pain, headaches or even lymph nodes. In most cases, symptoms disappear spontaneously within two to three weeks. “The disease can worsen and even become fatal, particularly in young children, pregnant women and immunocompromised people, such as those whose HIV is poorly controlled.alerts the organization.
In France, since July 2022, preventive vaccination has been offered to people most exposed to the virus: the Ministry of Health cites “men who have sex with men, trans people with multiple sexual partners, sex workers and professionals working in places of sexual consumption“. In the event of exposure, the vaccine can also be administered between 4 and 14 days after the risky contact.