Genes that increase the risk of Alzheimer’s
There are many forms of dementia, some rare forms are hereditary. There are dozens of genes that increase your risk of Alzheimer’s disease. What is the chance that you will also have to deal with dementia if this disease runs in your family?
There are as many as 50 diseases in which dementia is one of the symptoms. The most common are Alzheimer’s, Vascular Dementia, Lewy Body Dementia, and Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD).
Risk Factors
Usually dementia is not hereditary. There are hereditary forms of dementia, but they are rare and usually start around the age of 50 or 60 and sometimes much earlier. However, there are dozens of genes that can increase the risk of Alzheimer’s. One of these is the Apo-E gene – variants of this that increase the risk of Alzheimer’s occur in 16 percent of the Dutch.
The biggest risk factor is age. Furthermore, damage to the heart and blood vessels increases the risk of dementia, so smoking, high blood pressure, obesity in middle age and type 2 diabetes are also risk factors.
Family
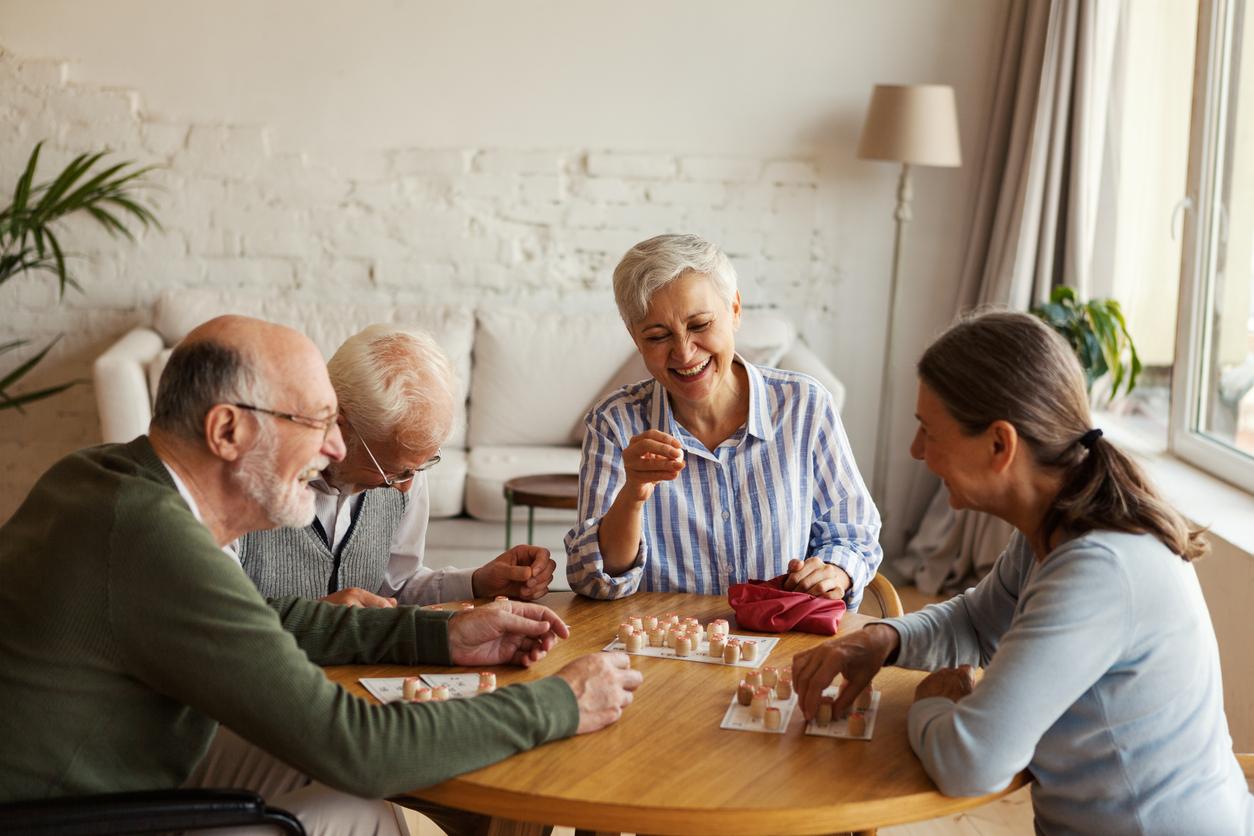
What are the chances of you getting dementia if it runs in your family? About a quarter of all Alzheimer’s patients have at least one family member with Alzheimer’s. Someone with a parent, brother or sister who got it after the age of 65 has a few percent more chance of dementia. In about 1 in 1600 families with Alzheimer’s there is a hereditary form at a young age.
FTD is much more often hereditary, in as much as 25-40 percent of cases. If one of your parents has hereditary Alzheimer’s disease or FTD, there’s a 50 percent chance that you will get it too. Vascular dementia is probably less often hereditary than Alzheimer’s. Lewy Body Dementia is almost never hereditary.
Genetic testing
There are commercial tests for a number of genes that slightly increase the risk of Alzheimer’s, such as Apo-E, and for three genes that cause hereditary Alzheimer’s, and a test that can predict some forms of hereditary FTD.
If one of the parents, brothers or sisters has been diagnosed with a dominant genetic form of dementia, you are eligible for such a test. The same applies if someone has become demented at a young age (before the age of 60 to 65) or is a child, brother, sister or parent of someone with dementia at a young age, and if at least three family members have become demented at such a young age in at least two generations. .
Those who carry certain gene variants have a slightly increased risk of getting Alzheimer’s. You can reduce that risk by adjusting your lifestyle.
Sources):
- Plus Magazine