What is the role of perspiration? Why doesn’t it always smell good? Does diet play a role? When does sweat become a problem?

- On average, an adult loses between 0.5 and 1 liter of sweat every day.
- When it is not a problem, sweating can also be a solution: by analyzing the chemical composition of sweat, it would be possible to determine the state of health of a person, according to a recent study.
Perspiration is a reflex and unconscious phenomenon that is good for us: we sweat to cool and regulate the body so that it does not exceed the ideal temperature of 37°C, for example when we play sports or we have a fever. This is called “thermoregulation”: when the brain – an area called the hypothalamus – is alerted to excessive heating, it sends a nervous signal to the sweat glands, located in the skin, which will then secrete the sweat. By evaporating through the pores, it will cause the body temperature to drop.
Perspiration does not have an odor in itself
The sweat glands, also called sweat glands, number 3 to 4 million and are divided into two categories. Eccrine sweat glands are located all over the body but especially the forehead, back, hands and feet. They are primarily responsible for the fact that we sweat every day on average between 0.5 and 1 liter of sweat, a liquid composed of 99% water, minerals and proteins/lipids evacuated by the body. In addition to regulating the temperature, the eccrine glands also help moisturize the skin and eliminate certain toxins.
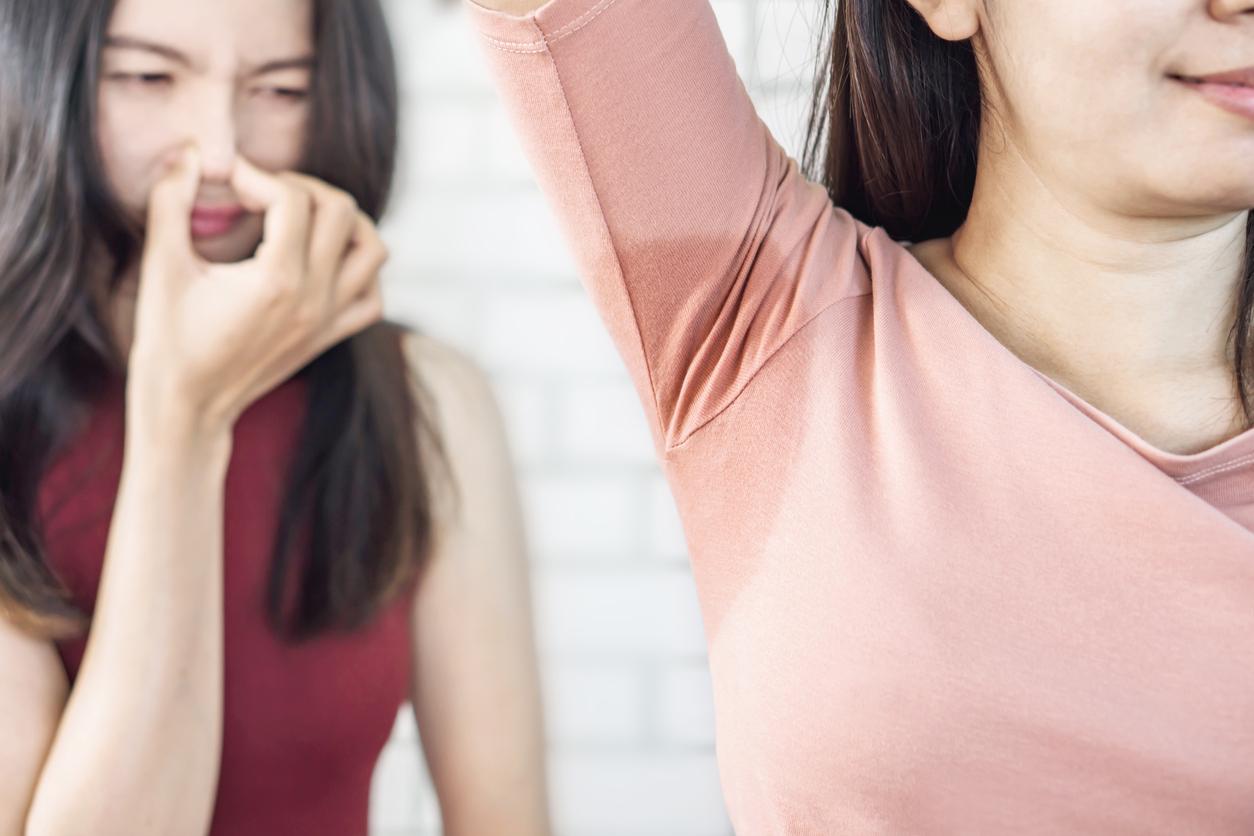
The apocrine sweat glands have nothing to do with thermoregulation: they are stimulated by emotions, stress, concentration. They appear at puberty in the armpits and genitals especially, poorly ventilated and hairy areas of the body. It is their sweat, which is more acidic and greasy, which is responsible for the dubious perfumes of perspiration. But contrary to popular belief, sweat itself is odorless: it is the bacteria in our skin that feed on the organic compounds in sweat and then release the gases responsible for this unpleasant odor. The longer we let them do (i.e. the less we take a shower), the stronger the smell becomes…
Hyperhidrosis, up to 10 liters of sweat per day
If the influence remains at the margins, the smell of perspiration can vary depending on what one ingests. A diet rich in protein (meat, eggs, etc.) would make it more oily and smelly, just like garlic, onions, certain spices or even alcohol. But in order not to “smell”, the first thing to do is to avoid the proliferation of bacteria by having a healthy lifestyle: wash daily (at least the private parts, and if possible with a neutral pH soap), wash your clothes regularly… In terms of wardrobe, it is better to prefer cotton or linen because synthetic materials promote perspiration.
Indispensable, sweating can become a health problem when it is excessive. Some people can sweat up to ten liters in case of fever, intense physical effort or high heat. We speak then hyperhidrosisa pathology that affects about 2% of the world’s population and nearly one in five American adolescents (17%), sometimes with serious consequences on social life, according to a recent study by theInternational Hyperhidrosis Society. In this case, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist who will determine the cause (obesity, diabetes, hyperthyroidism, menopause, certain medications, etc.) and propose an appropriate treatment.