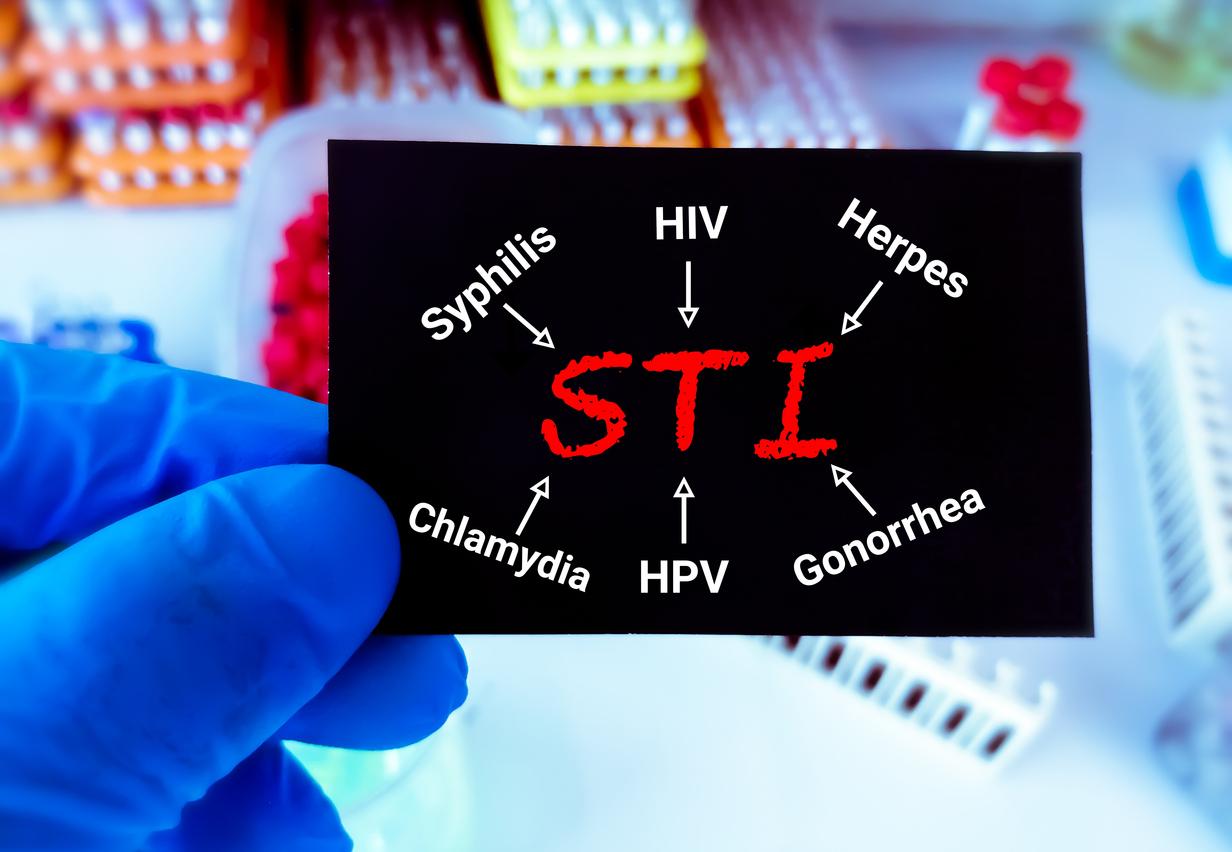
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that 700,000 people worldwide die from drug-resistant infections each year. These infections include gonorrhea, a common sexually transmitted infection that causes infection of the genitals, rectum and throat, and which increasingly resistant to antibiotics.
Some strains of the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae are currently not cured due to the lack of alternative treatments.
Effective on 146 bacteria samples out of a total of 149
British researchers at Imperial College London have lab tested an antibiotic recent, closthioamide, in gonorrhea samples. After collecting 149 samples of N. gonorrhoeae from hospital patients with infections in the throat, urethra, cervix and rectum, they found that a very small amount of closthioamide was effective in 146 of these samples. .
Although it is necessary to test this new antibiotic on animals and humans before claiming victory, the researchers believe that closthioamide could represent a crucial step in the fight against gonorrhea. Their study was published in the journal Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy.
Read also :
A daily mouthwash for gonorrhea?
STIs: what are the risks of transmission according to sexual practices?