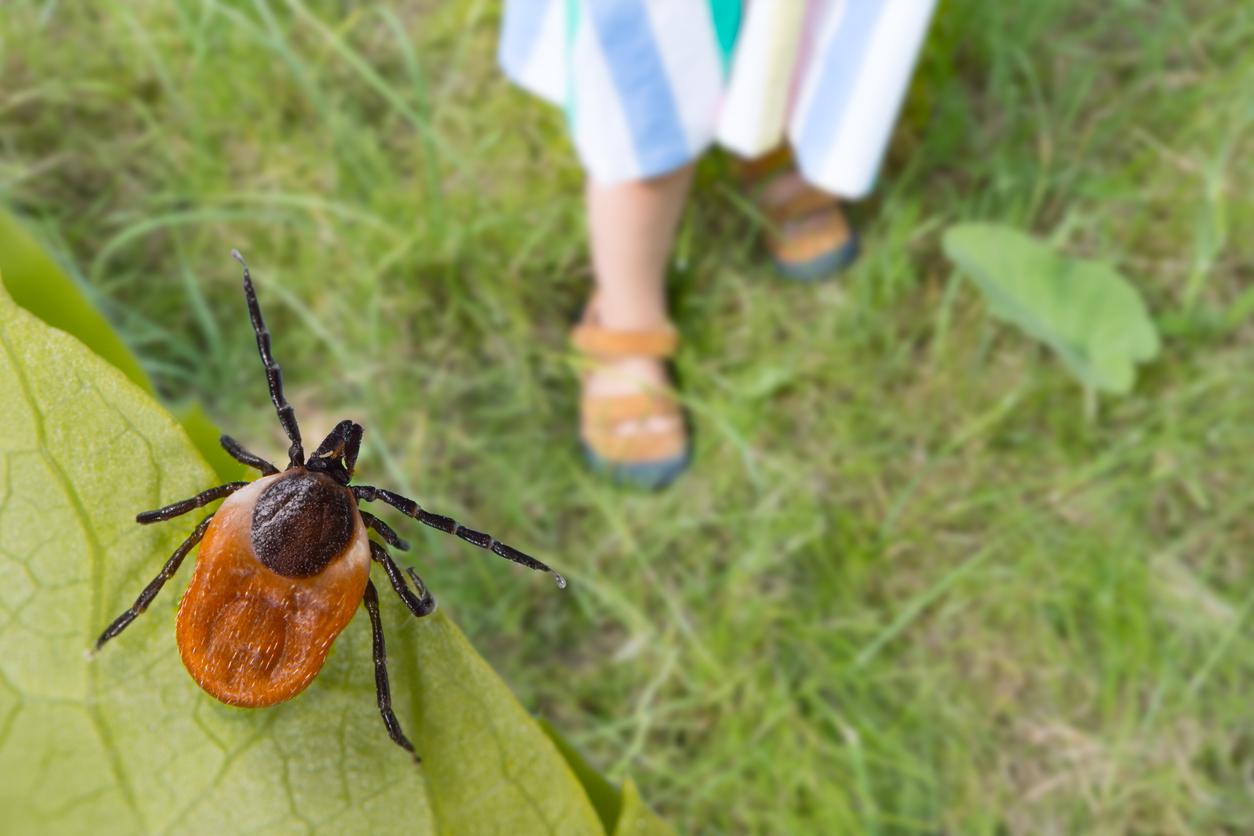
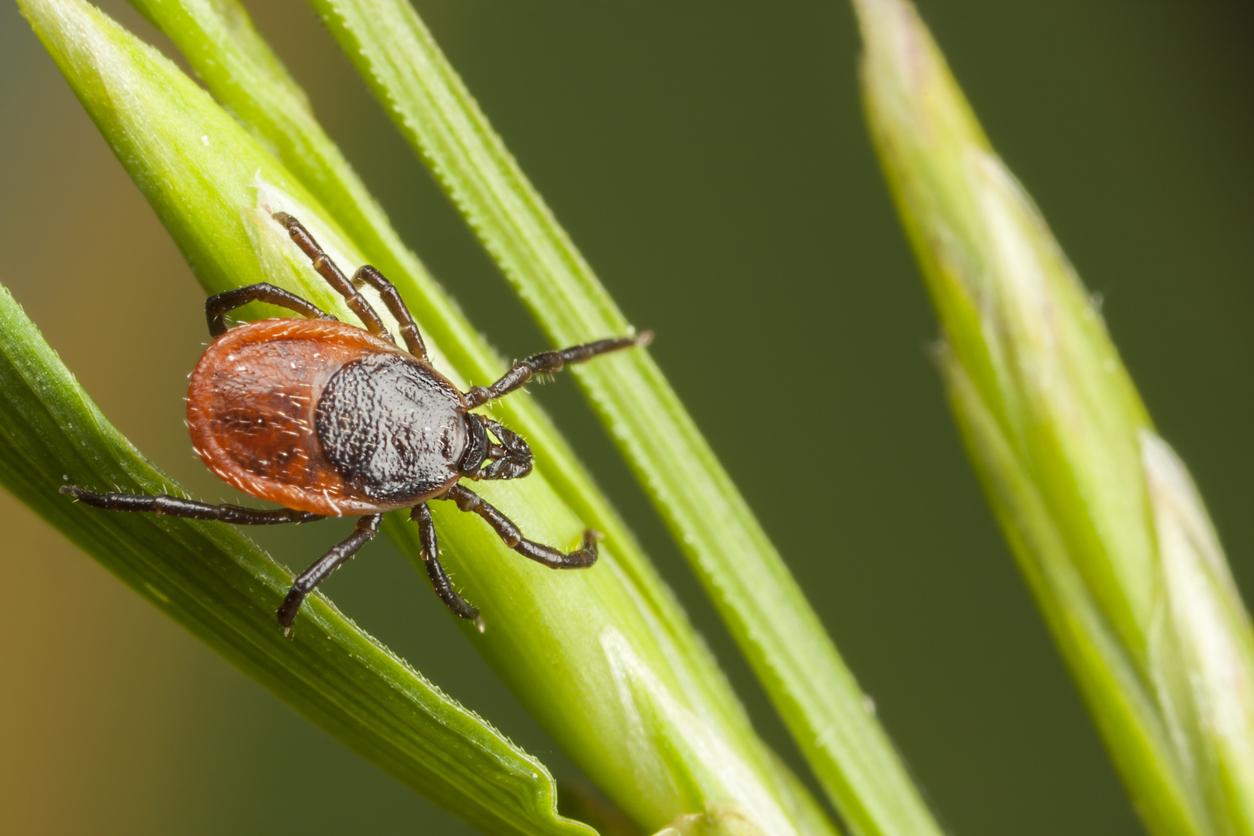
The Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus is transmitted by giant ticks, present in the South of France. It usually triggers flu-like symptoms, but some people can develop severe forms.

- The Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus has been detected on giant ticks in the South of France.
- Infected people initially show flu-like symptoms, but the disease can lead to bleeding.
- According to the World Health Organization, the case fatality rate is between 10 and 40%.
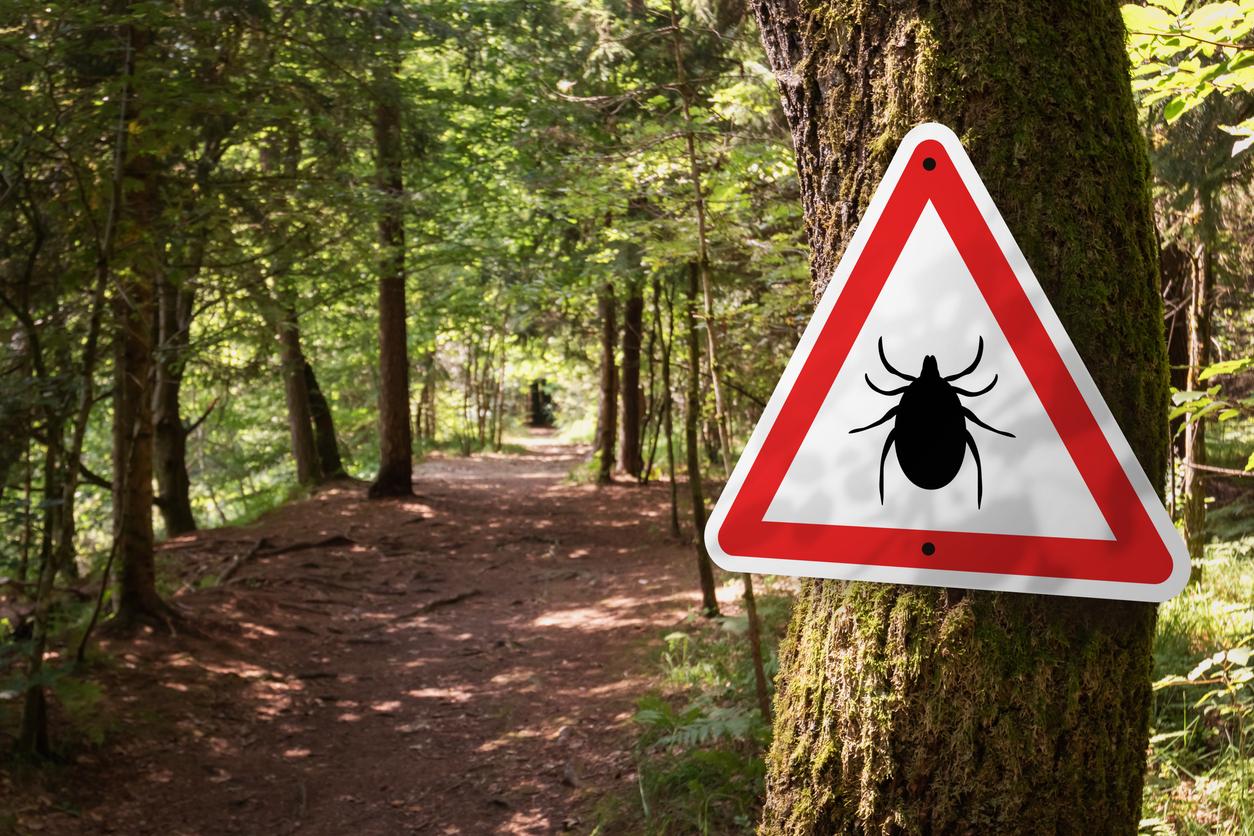
Protect yourself from ticks! Since last fall, the Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus has been detected in so-called giant ticks, of the species Hyalomma marginatum. “No human cases have been diagnosed in France to date, warned Public Health France last May. However, the risk of contamination has now been demonstrated, as Hyalomma ticks infected with the virus are present in the south of France.“These insects have been established in Corsica for many years and for about ten years on the entire French Mediterranean coast.
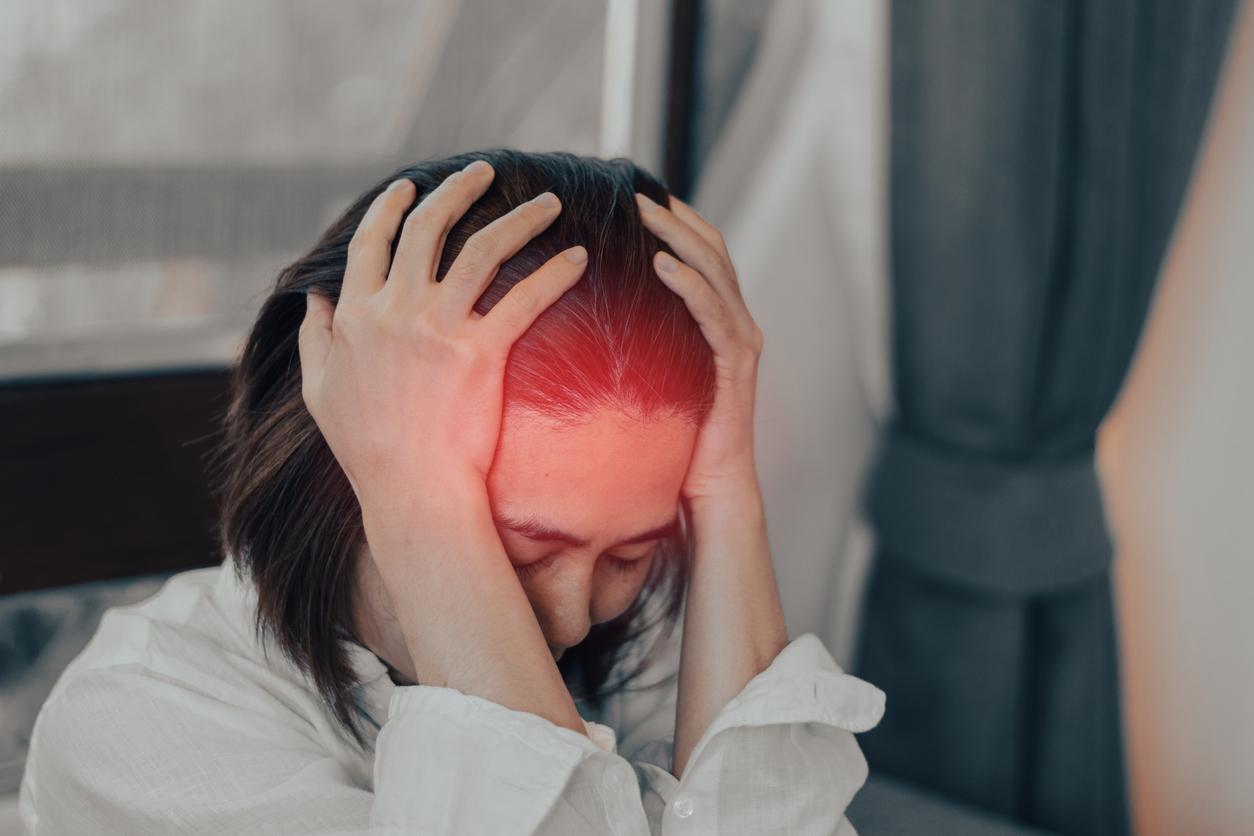
Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever: flu-like symptoms in less severe cases
If bitten by a tick of this species, there is therefore a risk of contamination by Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever.Infection with this virus is, in most cases, mildly symptomatic, but it can also cause illness with severe or even fatal forms.specifies thePastor InstituteThe first symptoms appear between five and seven days after contamination and are similar to those of flu: muscle pain, dizziness, fever, stiff neck, headache, sensitivity to light.Sometimes there is nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain and sore throat at the beginning, followed by sudden mood swings and confusion.”note theWorld Health Organization. After a few days, some people may also experience depressive symptoms or a form of weariness.
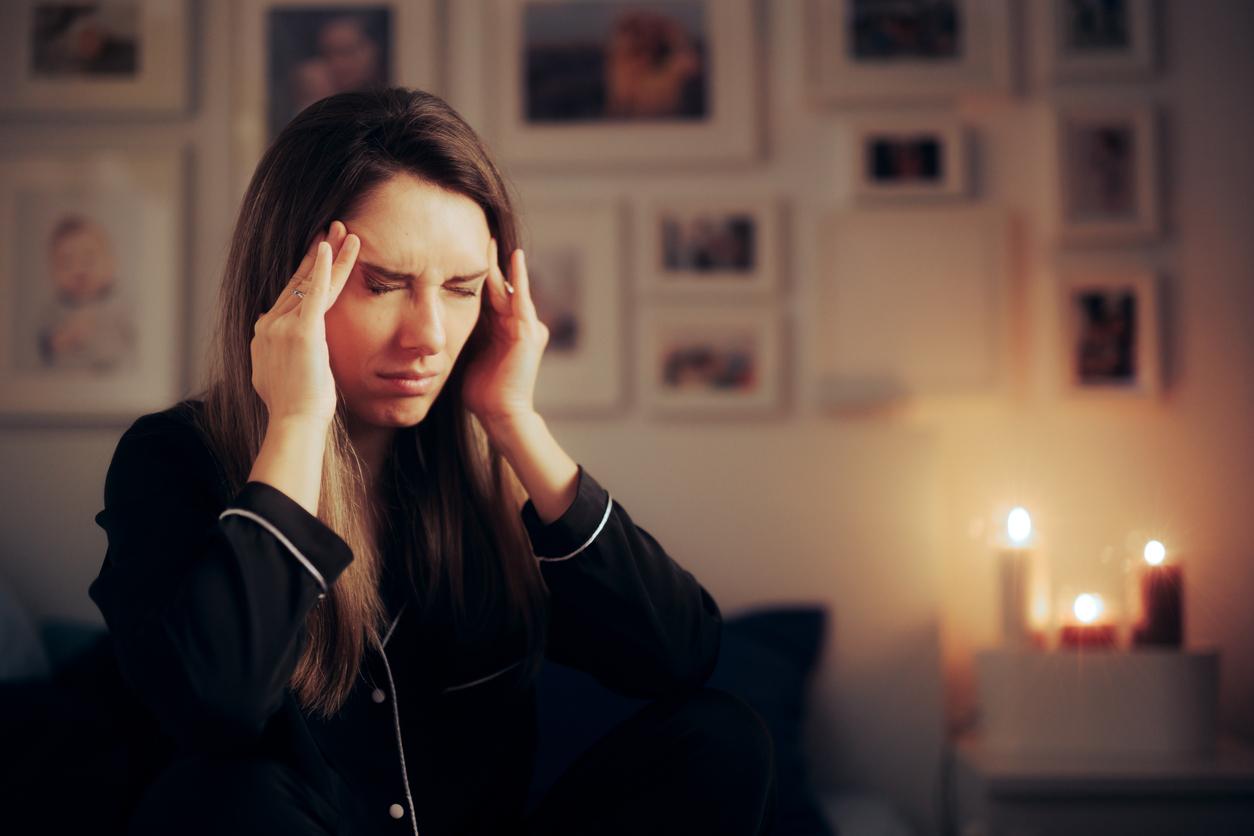
Risk of hemorrhage and death in severe forms of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever
In the most severe cases, the disease causes hemorrhages and rapid deterioration of kidney and liver function, and even lung function. According to the World Health Organization, when it takes this form, the pathology is fatal in 10 to 40% of cases.For those who recover, general condition begins to improve nine to ten days after the onset of symptoms.”estimates the Pasteur Institute.
How to treat Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever?
In case of contamination, treatment consists of managing the symptoms.An antiviral drug, Ribavirin, has been proposed to treat patients when symptoms appear but its effectiveness is still debated.he says.
The organization reminds that there is no vaccination to protect yourself. To reduce the risk of contamination, preventing bites is the best solution.
If you go out into the forest or potentially infested areas, you must:
- wear long, light-colored clothes;
- use repellents on skin and clothing;
- Check the skin regularly for ticks.
Once the insect is on the skin, it is important to remove it gently, ideally with suitable tweezers, called a tick remover, and to disinfect the area properly afterwards.