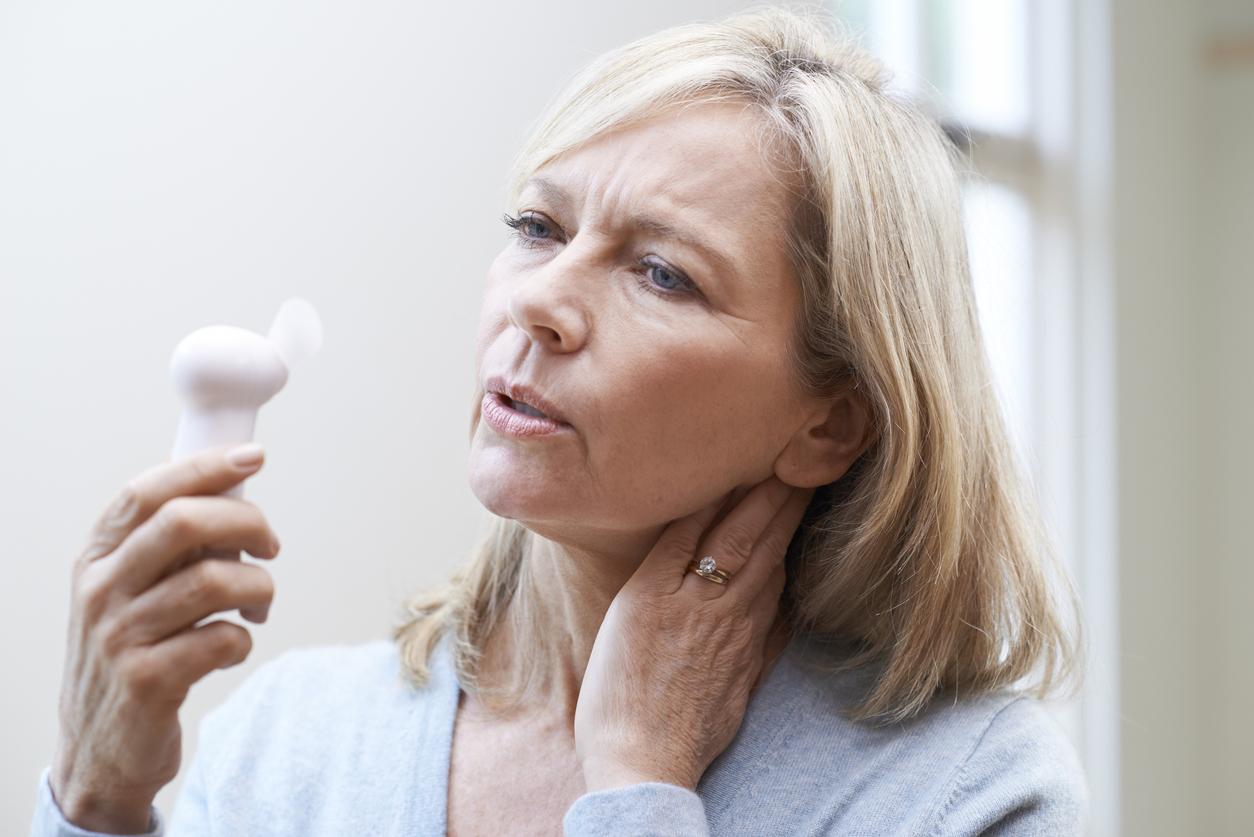
A new British study claims that Covid-19 disease is responsible for dizziness and hearing problems, ranging from hearing loss to tinnitus.
The list of symptoms of the coronavirus is starting to get long. The main serious symptoms of SARS-COV-2 are mainly fatigue, loss of taste or smell, and breathing problems. But according to a new study published in the journal International Journal of Audiology, three new manifestations would emanate from Covid-19: hearing loss, tinnitus and dizziness.
A prevalence of hearing loss of 7.6% and that of tinnitus at 14.8% for patients infected with Covid-19
To complete their study, British scientists from the University of Manchester and NIHR Manchester Biomedical Research Center (BRC) performed a review of 56 other studies linking hearing and vestibular problems. They gathered data from 24 of these studies to confirm the recurrence of these three symptoms in the context of a SARS-COV-2 infection. They reported that the prevalence of hearing loss was 7.6% and that of tinnitus 14.8% and that of dizziness 7.2%. “ There is an urgent need for a clinical study and careful diagnosis to understand the long-term effects of Covid-19 on the hearing system. It is well known that viruses such as measles, mumps and meningitis can cause hearing loss, but little is known about the hearing effects of the Sars-CoV-2 virus “explained Kevin Munro, professor of audiology at the University of Manchester, head of hearing health at BRC Manchester and co-author of the study.
Further research is needed
However, the study’s authors are tempering their research findings, as the data used is based primarily on patient-reported symptoms and not on hearing tests. “The reported quality rating does not reflect the overall quality of the evidence as almost all studies used uncontrolled designs and may be subject to confounding factors, measurement errors, and selection and information bias. . […] There is a need for high-quality studies that provide a comprehensive assessment of audio-vestibular function in COVID-19 and controls. These studies should include measures of impairment (pure-tone audiometry), hearing difficulty (laboratory speech in noise and self-assessment), as well as objective measurements to identify the location of any dysfunction ” say the British researchers of the study.