The thymus is a gland often considered useless in adults, yet it actually plays an important role in immune health and cancer prevention, contradicting previously held beliefs.
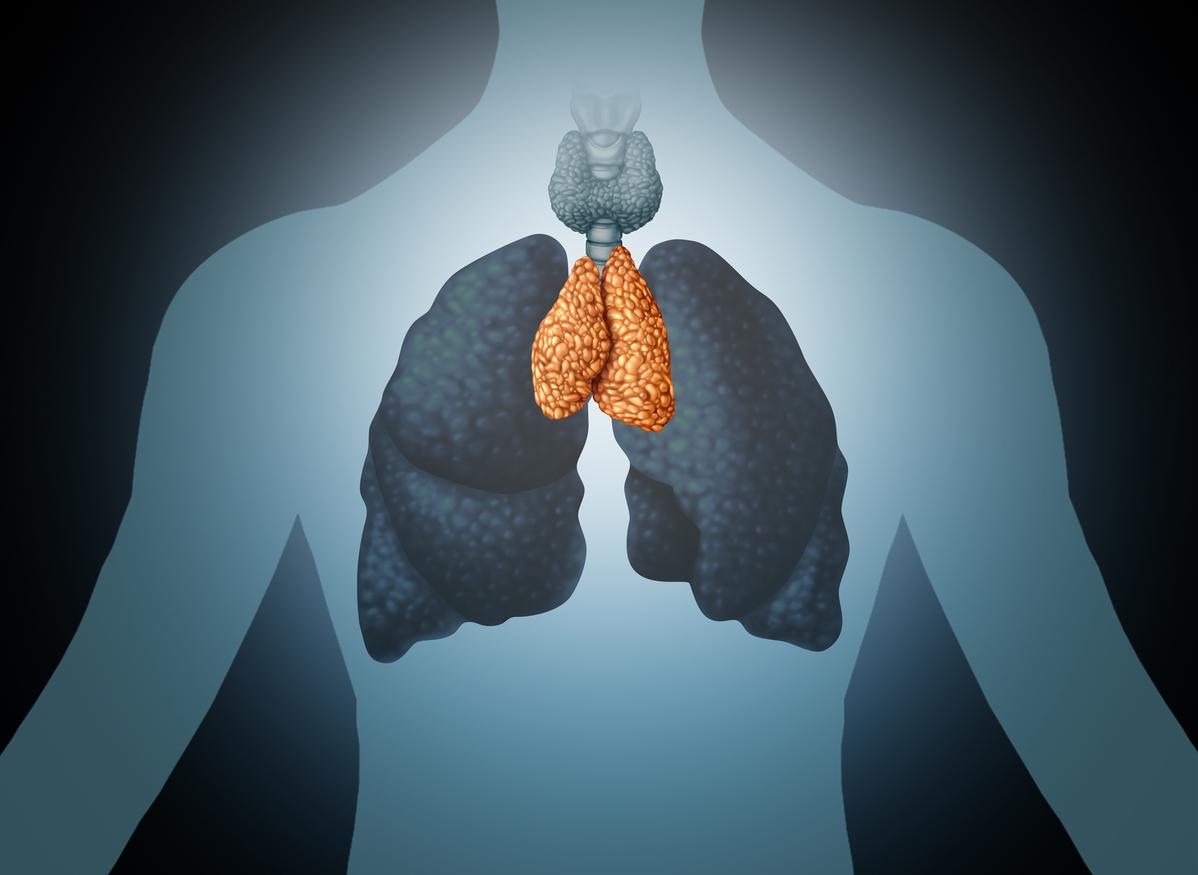
- Previously, scientists thought that the thymus, a gland located at the top of the chest, was only useful in children.
- Now a study has shown that this organ plays a role in adult immunity, particularly in the prevention of cancers.
- Removal of the thymus affects T-cell production.
The thymus is a gland located in the upper part of the thorax, it is known to play a crucial role in the development of the child’s immune system. Until now, many doctors believed that this organ was no longer useful in adulthood, as it atrophies over time. However, a 2023 study, published in Tea New England Journal of Medicine, advances knowledge by demonstrating that the thymus is involved in cancer prevention as well as overall health.
The risk of Cancer is increased by the absence of thymus
To reach these conclusions, the scientists examined the records of 1,146 adult patients whose thymus had been removed during surgery. They compared them to other people who had undergone similar operations but whose organ had been preserved. The results showed that patients who no longer had a thymus had a risk of death almost three times higher than those whose thymus had been preserved. Specifically, they were more likely to develop cancer, with a risk twice as high as others. A more modest increase in autoimmune diseases was also observed.
“This study demonstrates how vital the thymus is in maintaining adult health.”explained Dr. David Scadden, Gerald and Darlene Jordan Professor of Medicine at Harvard University and Professor of the Department of Regenerative and Cell Biology-strains in a press release.
Thymus removal may affect T cell production
“The magnitude of mortality and cancer in patients who underwent thymectomy was the biggest surprise to me.”the first author wondered. Kameron Koosheshin the same press release. “The more we dug, the more we found: The results suggested to us that the absence of the thymus appears to disrupt fundamental aspects of immune function.“
Although the causes of this increase in cancer and other health problems are not yet clear, the study authors concluded that removing the thymus disrupts the immune system. In particular, they noticed an effect on the rates of T lymphocytes, also called T cells.
“In a subgroup of patients in whom T cell production was measured, those whose thymus had been removed had lower production of new T cells, including helper and cytotoxic T cells. These patients also had higher levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines – which are small proteins associated with autoimmunity and cancer – in their blood.”scientists note.
The results of this study open up new research perspectives in the field of immunology and the fight against cancer.