Colin, tuna, merlan, dorade, salmon … Fish have many nutritional qualities. But when is it possible to introduce them into the plate of an infant? Explanations.

- Fish is a privileged source of omega-3 fatty acids, some of which are essential to the development and functioning of the nervous system and contribute to the prevention of cardiovascular disease.
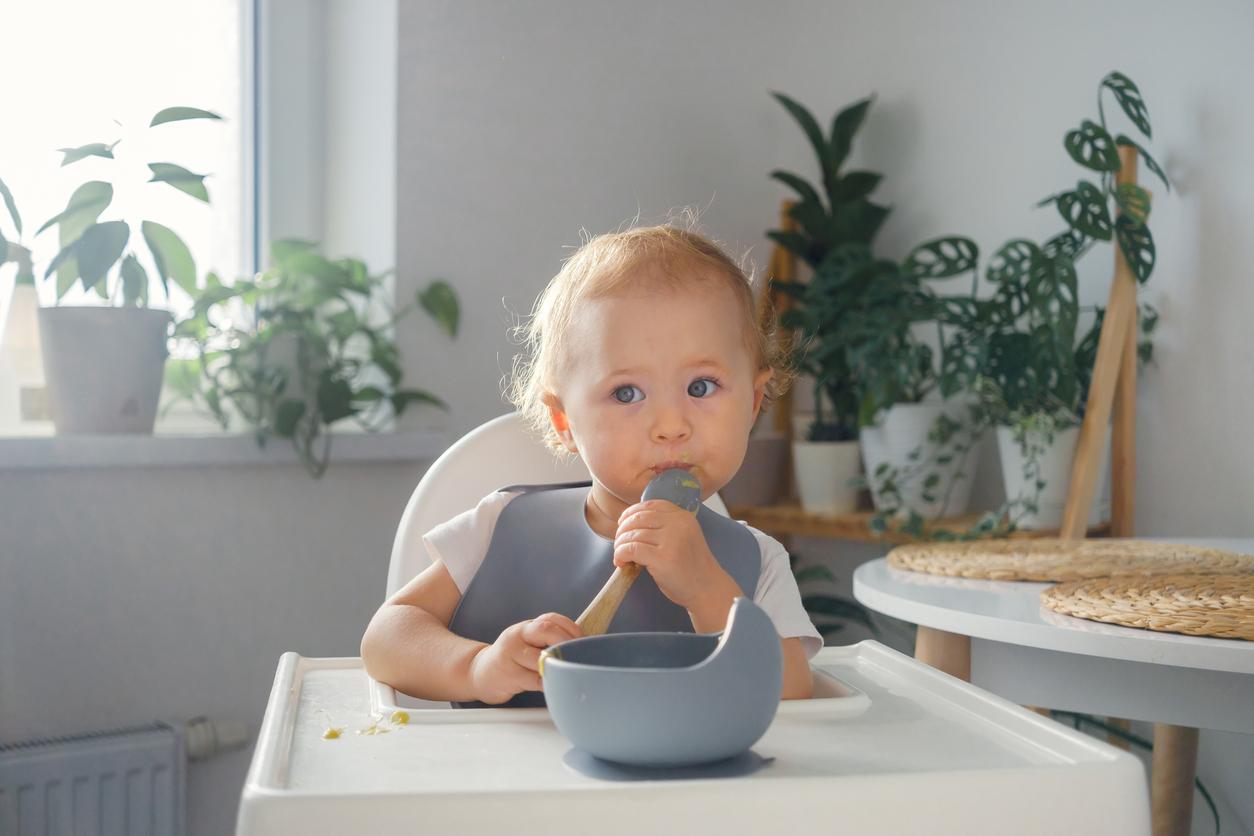
- When a baby starts the food diversification period between 4 and 6 months, he can eat fatty or lean, fresh or frozen fish.
- These foods, which must be cooked, mixed or finely crushed, should be given to an infant twice a week.
The fish are sources of protein, minerals such as phosphorus, iodine, zinc, copper, selenium and fluorine, but also vitamins A, D, E essential to health. Also known for its omega-3 fatty acids, these foods, in particular those that are fatty, are essential to the development and functioning of the nervous system and contribute to the prevention of cardiovascular disease. Given these benefits, it is interesting to give fish to your baby, who begins the period of food diversification at the earliest after the age of 4 months over and at the latest at the age of 6 months. As a reminder, this step is to introduce solid foods into the food of the breastfed baby or receiving milk for infants. It gradually leads to a family food around the age of 1 to 2 years.
From what age can an infant consume fish?
“There is no particular order to respect to introduce the different food groups between 4 and 6 months: vegetables, fruits, poultry, fish, meat, eggs, pulses (lentils, beans, chickpeas, etc.) , starchy foods (pasta, rice, semolina, even complete bread), dairy products. noted Health insurance. Thus, fish can be offered, for the first time, to a child from the age of four months.
What fish favor?
After The Ministry of Healthall fish agree that they are fatty or lean, fresh or frozen. However, breaded fish are excluded from the diet of a baby at this age. The health authorities advise regularly varying fish species, as some may contain pollutants present in the environment, including dioxins, PCBs or methylmercure, and must therefore be avoided or limited up to 3 years. “PCB and dioxins are preferentially found in the most fatty fish such as eels, as well as in certain organic fish such as barbeau, bream, carp or catfish. Methylmercide is found in wild predatory fish like tuna , monkfish or sea bream “, report ANSES.
How much can a baby eat?
The eating site Bouger recommends offering fish to a baby from time to time and then more regularly as the latter grows. “Give fish to your infant 2 times a week by varying the species. Do not exceed 10 g of meat or fish (i.e. 2 teaspoons)”, specifies health insurance. Regarding the preparation, it is recommended to cook this food well to avoid a risk of food toxi-infection and toxoplasmosis. At the beginning, it is necessary to mix or finely crush the fish.