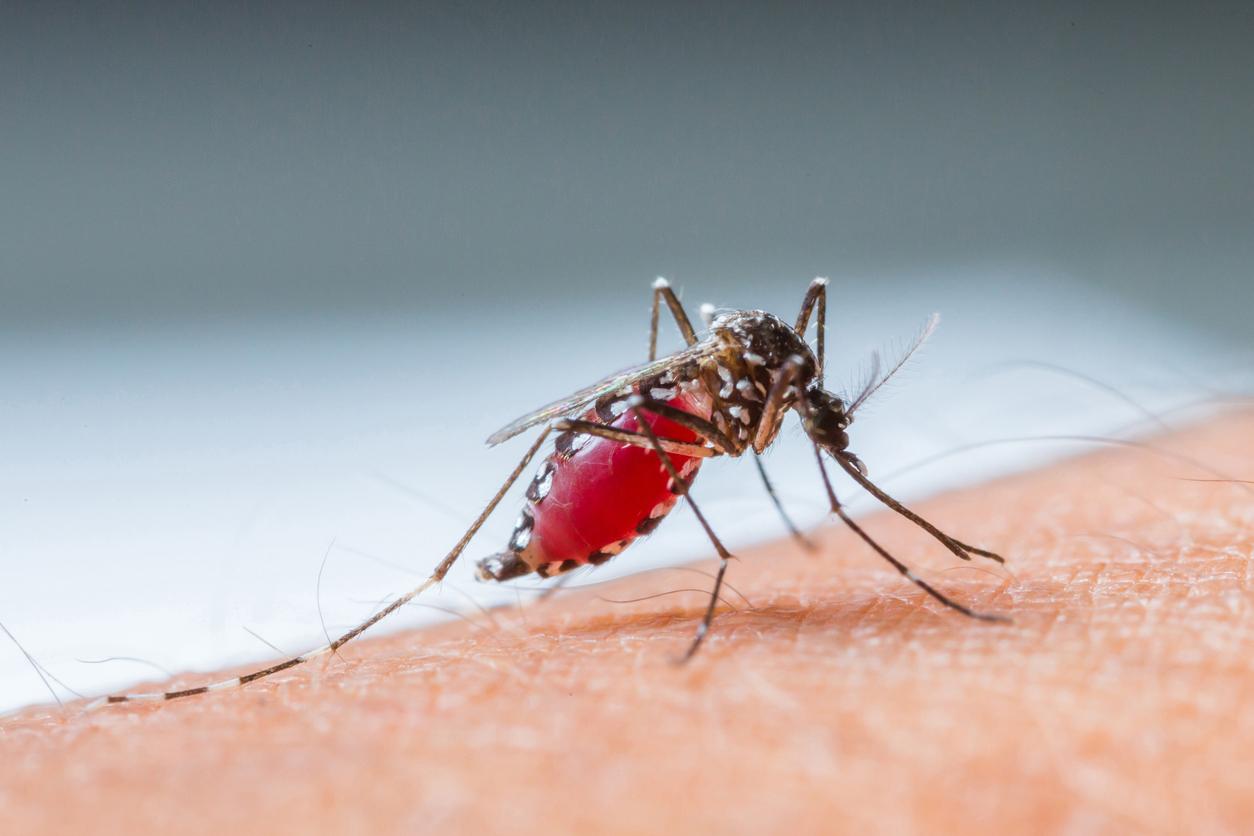
Researchers from the Institut Pasteur and the World Health Organization are worried: they have discovered a case of Japanese encephalitis in Africa. The infection is aptly named since it is normally present only in Asia. It is therefore the first time that the virus has been observed in another territory, more precisely in Angola, in a patient who has never traveled outside his country.
The study, published in The New England Journal of Medicine, reveals that the man contracted both yellow fever and Japanese encephalitis. Two diseases transmitted by two different mosquitoes, from the Flaviviridae family (the same family that transmits dengue fever or Zika).
Infectious diseases spread
For scientists, this infection could be an isolated case, but the risk of the virus appearing in Africa or other territories should not be excluded. Globalization and increased trade between Asia and Africa, or other regions of the globe are associated with the greater spread of infectious diseases. Vector mosquitoes present in Angola or host animals could also promote the spread of the infection, with a risk for the population.
According to the Institut Pasteur, serological surveillance studies should therefore be carried out to estimate the proportion of the population exposed to the virus. And if necessary, organize the fight against the disease, for example by deploying a vaccination campaign.
Read also
Learn more about disease-carrying mosquitoes
Mosquitoes: the right strategies to keep them away
How to protect yourself from mosquitoes