In Savoie, 14 cases of human immunodeficiency virus contamination, with the same viral strain, were detected.
- The Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes Regional Health Agency (ARS) reported that 14 people were infected with the human immunodeficiency virus in Savoie.
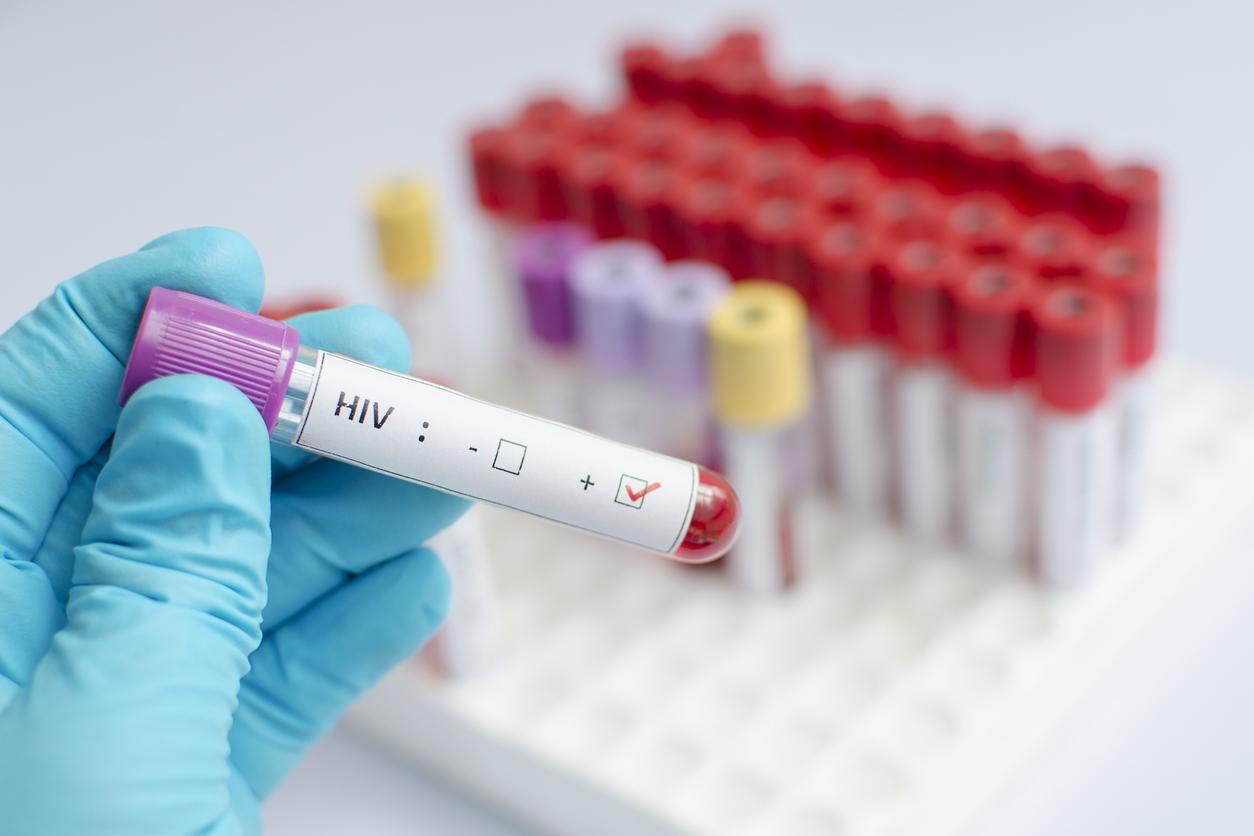
- The same viral strain was detected in the affected patients and investigations confirmed that some cases were linked.
- Faced with this “unusual situation”, the agency reminds that it is important to use a condom and to get tested regularly.
A “unusual situation”according to the Regional Health Agency (ARS) Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes. On December 9, the latter reported that between April and November 2024, fourteen people were infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), which weakens the immune system and causes AIDS. According to the infectious diseases departments of the region’s hospitals, the same viral strain was identified in the patients concerned. Investigations helped confirm that some cases were linked.
“From the beginning of November, health professionals in Savoie were alerted to the situation so that, in the event of the slightest doubt, they would offer their patients the opportunity to be tested, particularly in the event of unprotected sex. Local associations, specializing in prevention and sexual health, have also been informed and are particularly active in the field in order to raise awareness among the population (out-of-home operations, screenings, etc.). can we read in the press release.
Condom use and testing to protect yourself from HIV
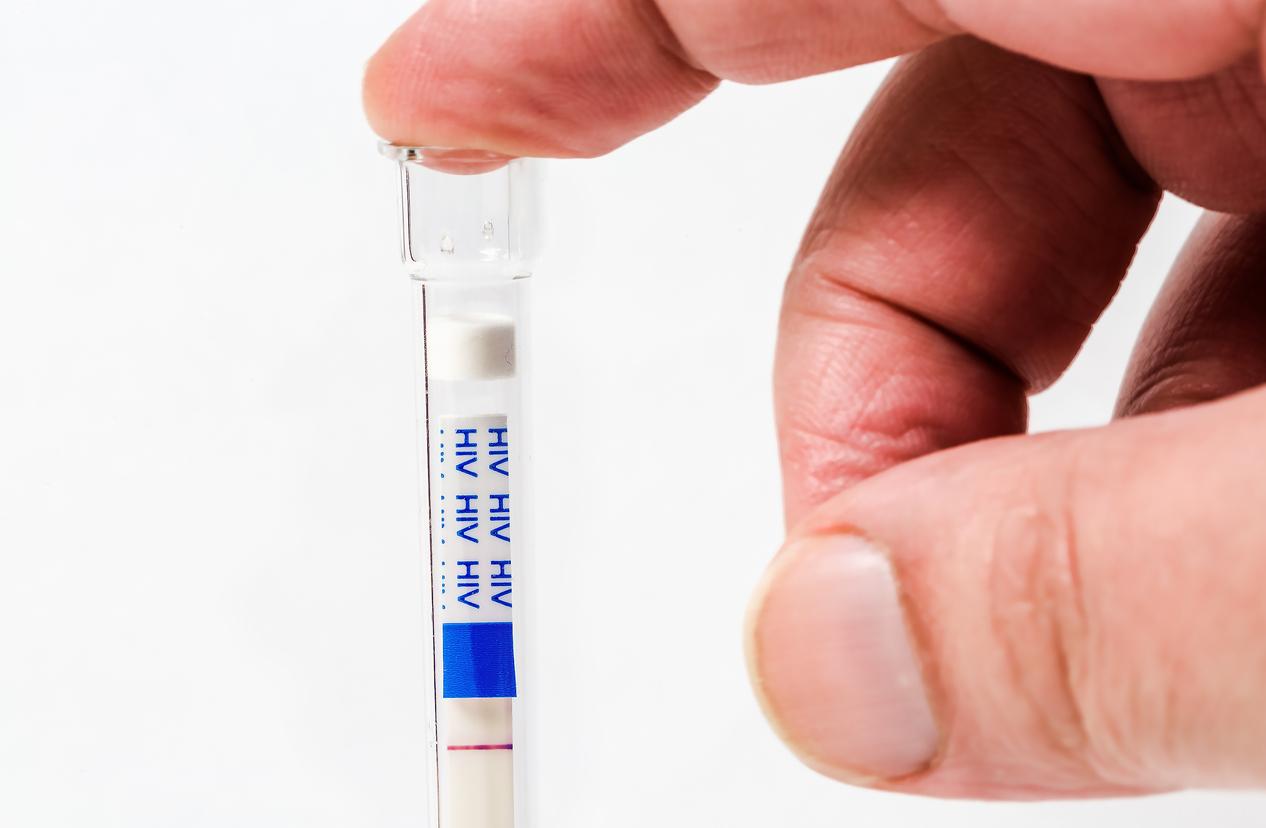
Faced with the acceleration of contaminations in recent months and the active circulation of HIV on French territory, the ARS calls for strengthening prevention measures, “with particular attention to people with multiple partners.” Among the actions, we find the use of condoms and regular screening, which is done in the medical biology laboratory without a prescription, without an appointment and without advance payment. As a reminder, only a blood screening test allows you to know if you are a carrier of the human immunodeficiency virus, because the infection often remains silent, more precisely asymptomatic. It is recommended to be screened systematically after taking a risk (6 weeks after exposure) and at certain stages of life (planned pregnancy, etc.).

HIV: what to do in case of exposure?
In the event of potential exposure to HIV after unprotected sex or condom breakage, emergency treatment, called TPE or post-exposure preventive treatment, may be prescribed. The latter “helps control the multiplication of the virus and prevent transmission.” To benefit from it, you should go to the nearest hospital emergency room as quickly as possible. To be effective, TPE must begin as soon as possible and no later than 48 hours after exposure.