A study suggests that the medicinal herb Terminalia chebula has potential as a natural remedy for the treatment and prevention of mild cognitive impairment.
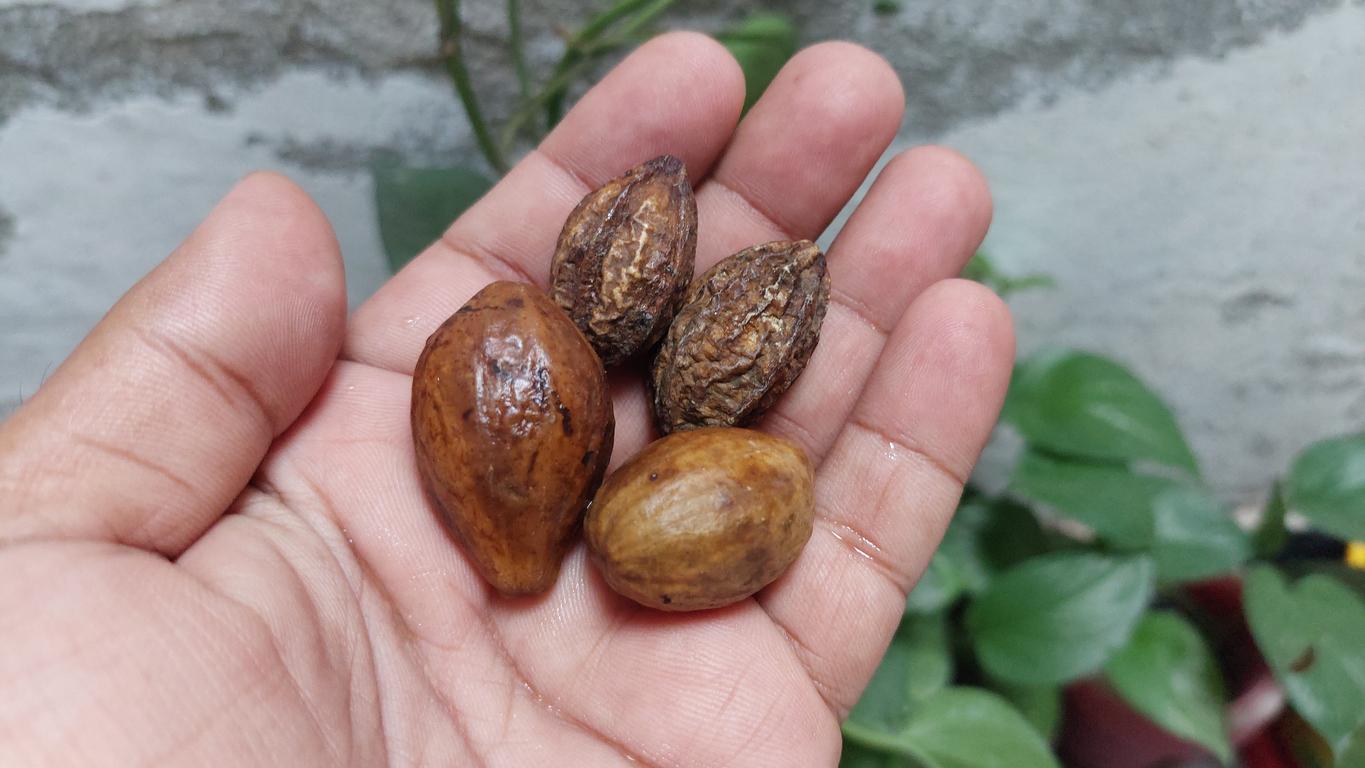

- In Tibetan medicine, the medicinal herb Terminalia chebula (T. chebula) is known for its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiviral and hypoglycemic properties.
- According to one study, the plant has “neuroprotective effects”, which allows it to protect neurons from oxidative stress and neurotoxicity, reduce neuronal inflammation and promote synaptic plasticity.
- It also seems “beneficial for sleep, a critical problem in mild cognitive impairment”, but this remains to be confirmed, according to the authors.
Viruses, bacteria, oxidation, inflammation, blood sugar… The medicinal herb Terminalia chebula is used in Tibetan medicine. It comes from the dried fruit of a deciduous tree in the Combretaceae family, native to parts of China, India, Malaysia and Myanmar. Due to its vast properties, the medicinal value of this plant is gradually being recognized. This is why it is prescribed for many physical conditions. More and more research has looked into its potential in improving mild cognitive impairment. However, the question of whether Terminalia chebula could constitute a safe and effective treatment against this alteration of brain functions, which can progress to Alzheimer’s disease if left untreated, has not been sufficiently studied.
171 components of the medicinal herb Terminalia chebula were analyzed
Thus, scientists from the University of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Chengdu (China) carried out a study to analyze the role of this Tibetan medicinal herb in alleviating mild cognitive impairment. To carry out the work, they evaluated the chemical profile of 171 components of Terminalia chebula, including flavonoids, phenolic acids, tannins, triterpenoids and even volatile compounds, and examined their possible use. Researchers believe the plant’s anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiviral, and hypoglycemic effects primarily serve to reduce symptoms.

The Tibetan plant protects “neurons from oxidative stress and neurotoxicity”
“The neuroprotective effects of Terminalia chebula come from its potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. It protects neurons from oxidative stress and neurotoxicity, reduces neuronal inflammation, and promotes synaptic plasticity while improving cerebral blood flow. Additionally , the plant appears beneficial for sleep, a critical problem in mild cognitive impairment”, explained the authors. However, further research is needed to fully understand its mechanisms for improving sleep quality, explore the specific chemical components of the plant, and to define its quality standards.