Researchers have developed a high-performance computer device that can detect viruses potentially dangerous to humans.
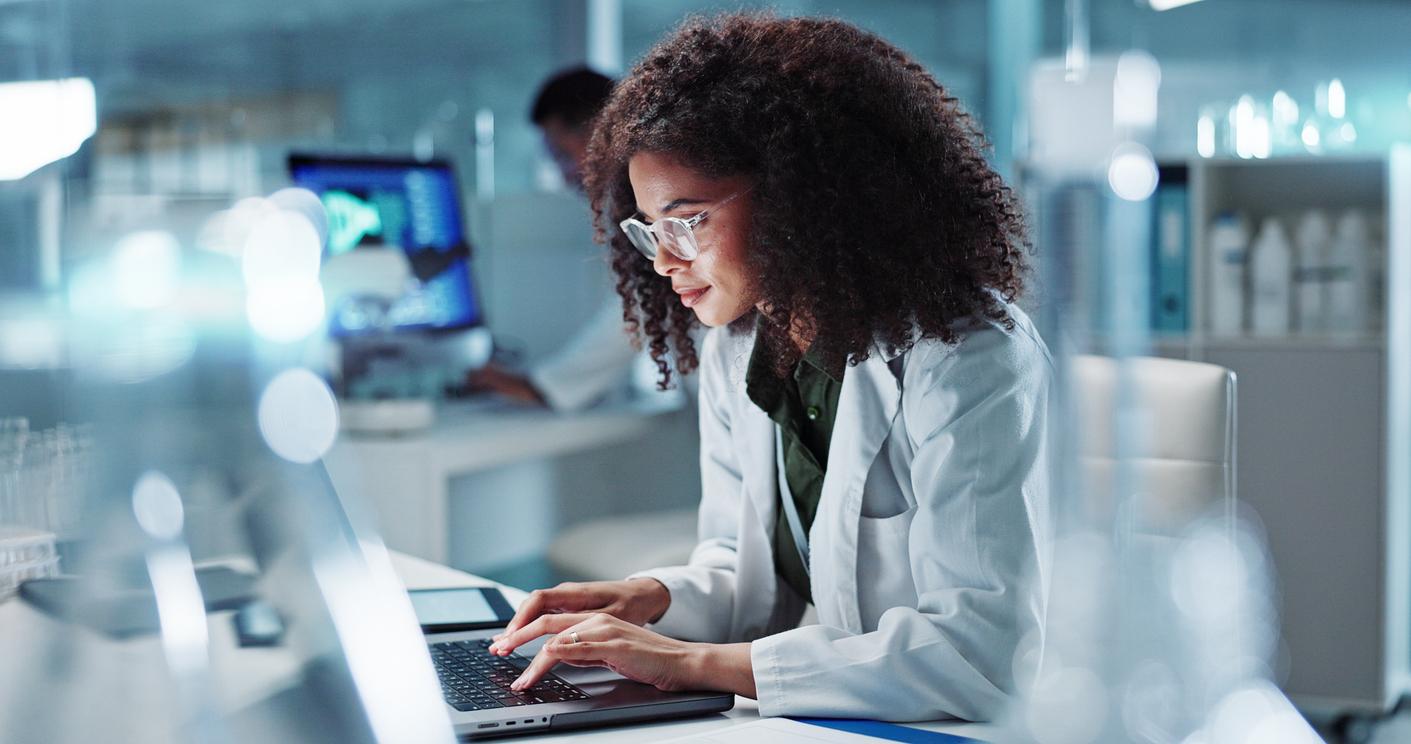

- A computer device has been developed to identify unknown viruses, which could help prevent their spread.
- The first tests of this method were carried out on vertebrates.
- Nearly 40 unknown nidoviruses, which are part of the coronavirus family, have been discovered in this family of animals.
SARS-CoV-2 is a member of the coronavirus family, viruses that can sometimes infect humans. The Covid-19 virus has undergone numerous modifications to its genome, which has caused the appearance of variants, classified as worrying and to be monitored. To monitor the sudden emergence of threatening pathogens, virologists from the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) have developed a computer-assisted analysis method.
Identification of 40 unknown nidoviruses
As part of this research published in Pathogen Plots, scientists studied nearly 300,000 data sets using high-performance computers. They observed animals infected with viruses, in order to obtain and study viral genetic material on a large scale. They mainly focused on nidoviruses, which are part of the coronavirus family. “Using a new computer-assisted analysis method, we discovered 40 previously unknown nidoviruses in various vertebrates, from fish to rodents, including 13 coronaviruses”described Stefan Seitz, group leader at the DKFZ.

A computer process capable of determining virus variants
During this work, the researchers found that recombination of viral genes can occur during virus replication in animal hosts infected with different pathogens. Nidoviruses identified in fish are believed to frequently exchange genetic material between different virus species. “And when distant relatives ‘interbreed’, this can lead to the emergence of viruses with completely new properties (…) a genetic exchange, such as we have seen in fish viruses, will probably also occur in mammalian viruses Bats, which, like shrews, are often infected with a large number of different viruses, are considered a real melting pot. The coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 probably developed in bats. and passed from there to Man”explained Stefan Seitz.
With the development of this new computer process, scientists are therefore able to identify virus variants potentially dangerous to humans. This advance could help prevent the spread of new pathogens.