In an interview with the magazine US Vogue, singer Billie Eilish confided in the disease from which she suffers: joint hypermobility. This pathology was diagnosed to him around the age of 13, after a fracture at the level of the hip.
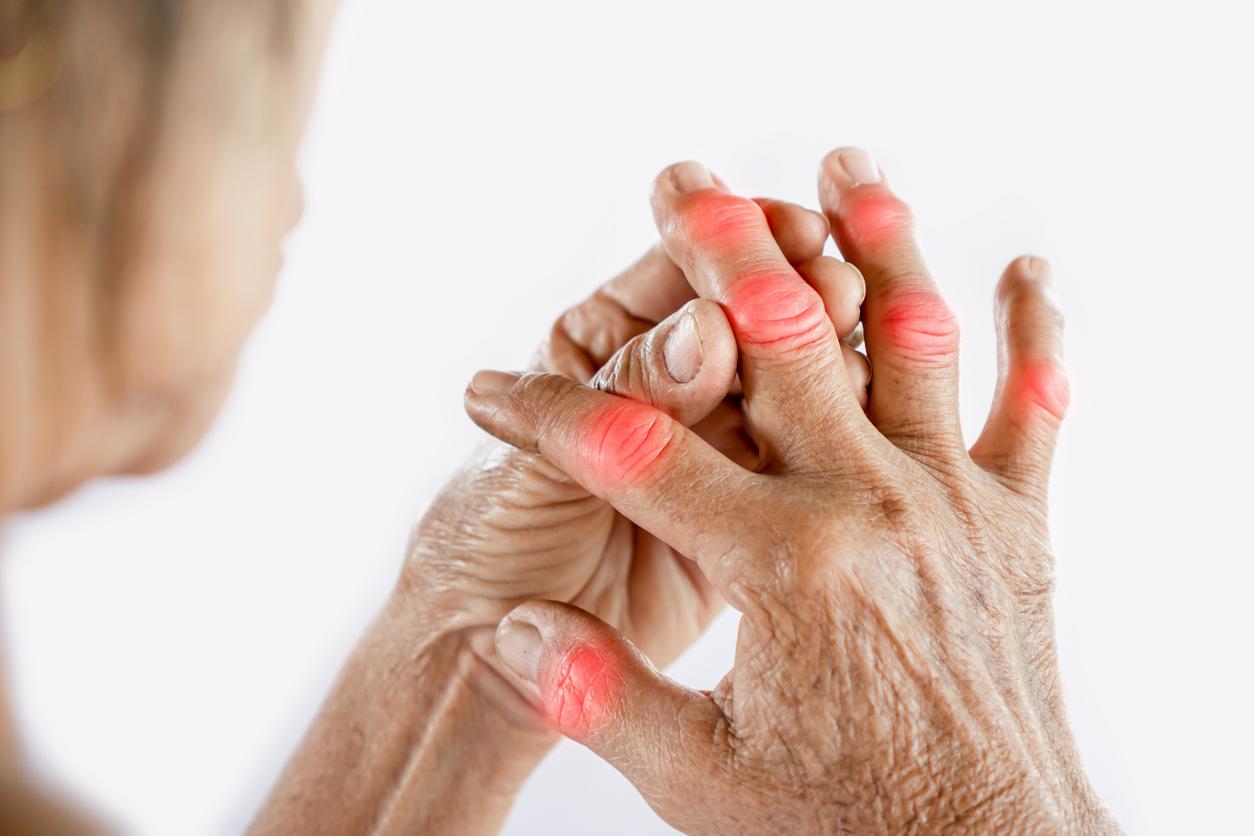
What is joint hypermobility? Joint hypermobility refers to the ability of joints to move beyond normal limits. In concrete terms, people with this pathology are able to perform movements that are normally impossible: bending their fingers backwards, placing their hands flat on the ground without bending their knees, contorting themselves…
A disease responsible for musculoskeletal disorders and chronic pain
Joint hypermobility can be local (with only one or two joints affected), peripheral (when the fingers and toes are affected) or generalized. Hypermobile joints are prone to dislocations and microtraumas; hypermobile people can also suffer from chronic pain and musculoskeletal disorders.
Joint hypermobility is currently detected using two tools: the Beighton score (which consists of asking the patient to perform movements requiring extreme flexibility: placing their thumbs on their forearms, for example) and the 5-part questionnaire (which asks the patient about how he perceives his flexibility and range of motion). Note: in recent years, we have also been talking about “hypermobility spectrum disorders (HSD)” in order to better categorize the different “degrees” of joint hypermobility.
Joint hypermobility is often associated with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. These genetic and hereditary pathologies (which affect all of the connective tissue) affect approximately 1 in 5000 people worldwide.
Source : SED’in France




-1730888646.jpg)