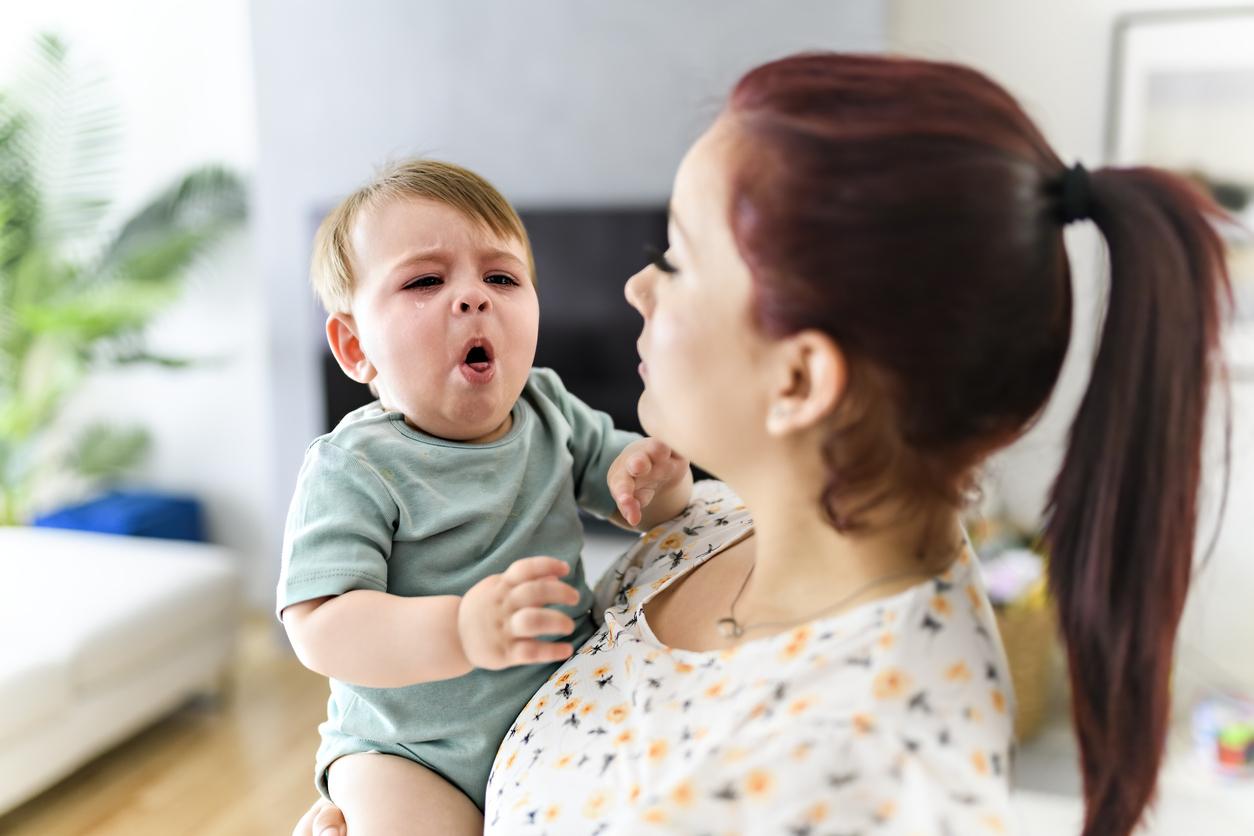
Spring causes some to sneeze and itches for others. In addition to seasonal allergies, there is the appearance of chickenpox, a very contagious disease. During the week of April 20 to 26, the Sentinels network counted 44 cases per 100,000 inhabitants which led to consultations with the general practitioner.
Chickenpox is particularly threatening in twelve outbreaks of contagion: Pays de la Loire, Champagne-Ardenne, Corsica, Haute-Normandie, Ile-de-France, Franche-Comté, Brittany, Lower Normandy and Midi-Pyrénées, and to a lesser extent , Provence-Alpes-Côte-d’Azur, Rhône-Alpes and Lorraine.
The greatest number of cases is recorded in Pays-de-la-Loire and Champagne-Ardenne, with 104 cases and 99 cases per 100,000 inhabitants, respectively.
Chickenpox is a very contagious disease that often affects children but can also affect adults. Linked to the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), from the herpesvirus group, this pathology returns epidemicly at the end of winter and at the beginning of spring. It is manifested by various symptoms such as a moderate fever (38 ° C) accompanied by headache, redness on the skin with rash of vesicles and mucous membranes as well as a feeling of itching (pruritus).
Vaccination recommended for adults
A person infected with chickenpox is contagious 24 to 48 hours before the rash appears and for about a week, that is, until the blisters or bubbles dry up and form a scab. Chickenpox is cured after 10 to 12 days.
In adults, chickenpox can be dangerous. People who are not immune (who did not have it during their childhood), are invited to to get vaccinated. The disease can indeed cause complications, such as secondary infections, skin lesions or lung infections.
>> To read also: Chickenpox: the importance of vaccination in adults
Chickenpox: stop preconceived ideas